A matrix is an array having exactly two-dimensions and this concept is very important in mathematics. All elements in a matrix are organized into rows and columns. For example, the matrix given below has 2 rows and 3 columns and is pronounced as “two by three” matrix.
As there is no built-in data type for matrices in python so we can create matrix by following methods:
- By using nested lists
- By using numpy array function
- By using numpy matrix function
- By using numpy reshape function
- By taking input from user
1. By using Nested Lists
We can use a nested list to create a matrix.
A = [[5, 1, 8], [7, 5, 3], [4, 6, 3]] for i in A: print(i)
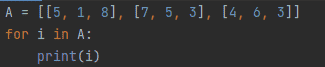
Figure 1: Using nested list
Output:
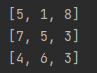
Figure 2: Output
In figure 1, we have three sub-lists inside the main list. We iterate through every row individually using for loop as displayed in figure 2. We did not print the list directly because that will print the list in a single line.
2. By using numpy Array Function
We can create a matrix using the numpy.array() function in Python.
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [3, 4, 5]])
print(A)
print('No. of Dimensions:', A.ndim)
print('Dimensions:', A.shape)
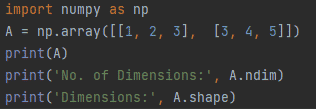
Figure 3: Using numpy.array() function
Output:
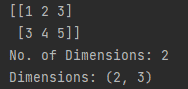
Figure 4: Output
In figure 3, we import numpy module as np and pass np.array function as a nested list which creates a matrix, whereas its dimension can be seen in figure 4 containing 2 rows and 3 columns.
3. By using numpy Matrix Function
Matrix function of numpy module returns a matrix from an array-like object, or from a string of data. In python matrix objects inherit all the attributes and methods of ndarray objects.
Example 1
import numpy as np A= np.matrix([[1, 2, 6], [3, 4, 8],[4,8,9]]) print(A) print(type(A))
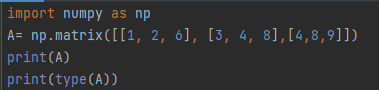
Figure 5: Using numpy.matrix() function for array input
Output:
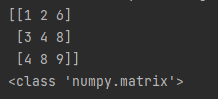
Figure 6: Output
In figure 5, we import numpy module as np and pass np.matrix function a nested list. A 3×3 matrix is created which belongs to numpy.matrix class.
Example 2
import numpy as np
A = np.matrix('4 7 8; 7 9 1')
print(A)
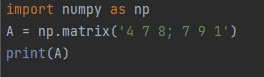
Figure 7: Using numpy.matrix() function for string input
Output:
![]()
Figure 8: Output
In the example 2, we have passed numpy.matrix function as a string matrix and we have separated the columns with commas or spaces whereas semicolons separating the rows. The output matrix is having 2 rows and 3 columns as shown in figure 8.
4. By using numpy Reshape Function
The numpy.reshape() can also be used to create matrix and this function alters the shape of the array so we can use it to change the shape of a 1-D array to a 2-D array without changing elements. We must need to check the number of elements in an array before changing its shape.
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[4,1,8,7,5,7,9,6,8]]).reshape(3,3)
print("Matrix= \n", A)
print("Dimensions = ", A.shape)
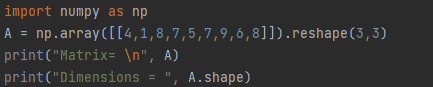
Figure 9: Using numpy.reshape() function
Output:

Figure 10: Output
In the above example, we have a 1-dimensional array consisting of nine elements, whereas The reshape() function altered this to a 2-dimensional array thus the elements are arranged with the dimension of 3×3 having 3 rows and 3 columns.
5. By taking Input from the User
In Python, we can create a matrix taking input from user as well.
row = int(input("enter the number of rows:"))
col = int(input("enter the number of columns:"))
# Initialize matrix
m = []
print("enter the entries row wise:")
# For user input
for i in range(row): # A for loop for row entries
a = []
for j in range(col): # A for loop for column entries
a.append(int(input()))
m.append(a)
# For printing the matrix
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
print(m[i][j], end=" ")
print()
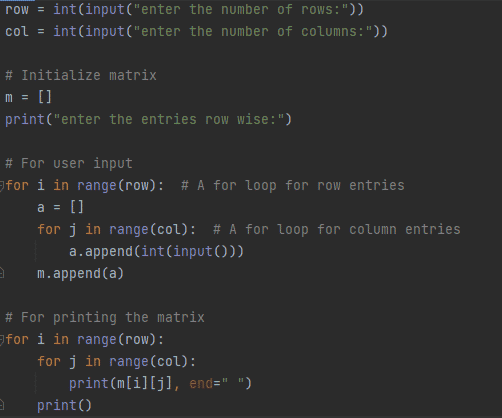
Figure 11: Using input method
Output:
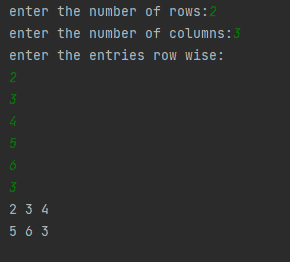
Figure 12: Output
In the above example, we take a number of rows and columns as input from the user. We declared an empty list ‘m’. Using nested for loop elements are added for row and column to ‘m’ list whereas the elements of the matrix are printed shown in figure 12.