Lynis is an open-source security auditing tool used for in-depth system-wide security scans. It provides useful information about vulnerabilities in your system and suggestions on how to improve security. Lynis allows you to easily scan your system features such as application patch management, ports, file system, kernel, databases, and much more. System admins and security professionals can scan systems extensively in a very short time.
Lynis can be used in both enterprise environments and on small and medium enterprises.
In this article, I will explain how to install and use Lynis on Ubuntu 20.04
Step 1: Check version available in repo
First, let’s check the Lynis version available in the Ubuntu 20.04 repo. Run:
$ apt-cache policy lynis
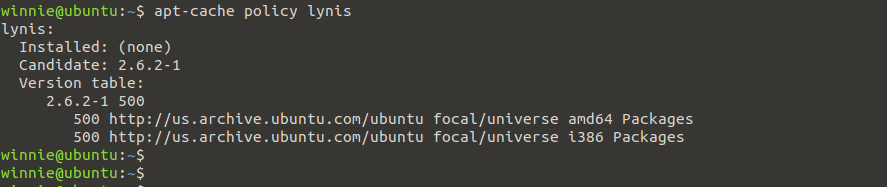
As you can see, the Lynis v2.6.2 is available in the ubuntu universe repos. By the time of writing this tutorial, Lynis 3.0.6 is the current stable release version.
You can download the latest release from the Lynis community software repository.
Step 2: Install PGP key & Repo.
First, download and add the PGP signing key from a central keyserver. Execute the commands:
$ wget -O - https://packages.cisofy.com/keys/cisofy-software-public.key | sudo apt-key add -
Next, add the Lynis repository to the system package repository list as shown:
$ echo "deb https://packages.cisofy.com/community/lynis/deb/ stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cisofy-lynis.list
To use Lynis with only English, disable translations from being downloaded as shown:
$ echo 'Acquire::Languages "none";' | sudo tee /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/99disable-translations
Step 3: Update Packages
Next, update the system packages before proceeding with the installation. Run the commands:
$ sudo apt install apt-transport-https $ sudo apt update
Step 4: Install Lynis
Now we are ready to install Lynis on our system. Execute the command:
$ sudo apt install lynis
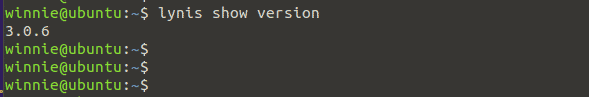
Once the installation is done, confirm the Lynis version installed on your system as shown:
$ lynis show version
Step 5: Lynis Command Line Syntax and Options
Now that the latest version of Lynis is installed, let’s learn how to use this tool to audit the system. The syntax of the Lynis command is as follows:
$ lynis [scan mode] [other options]
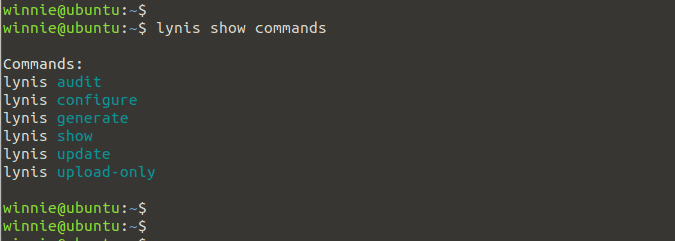
We can view the Lynis commands as shown:
$ lynis show commands
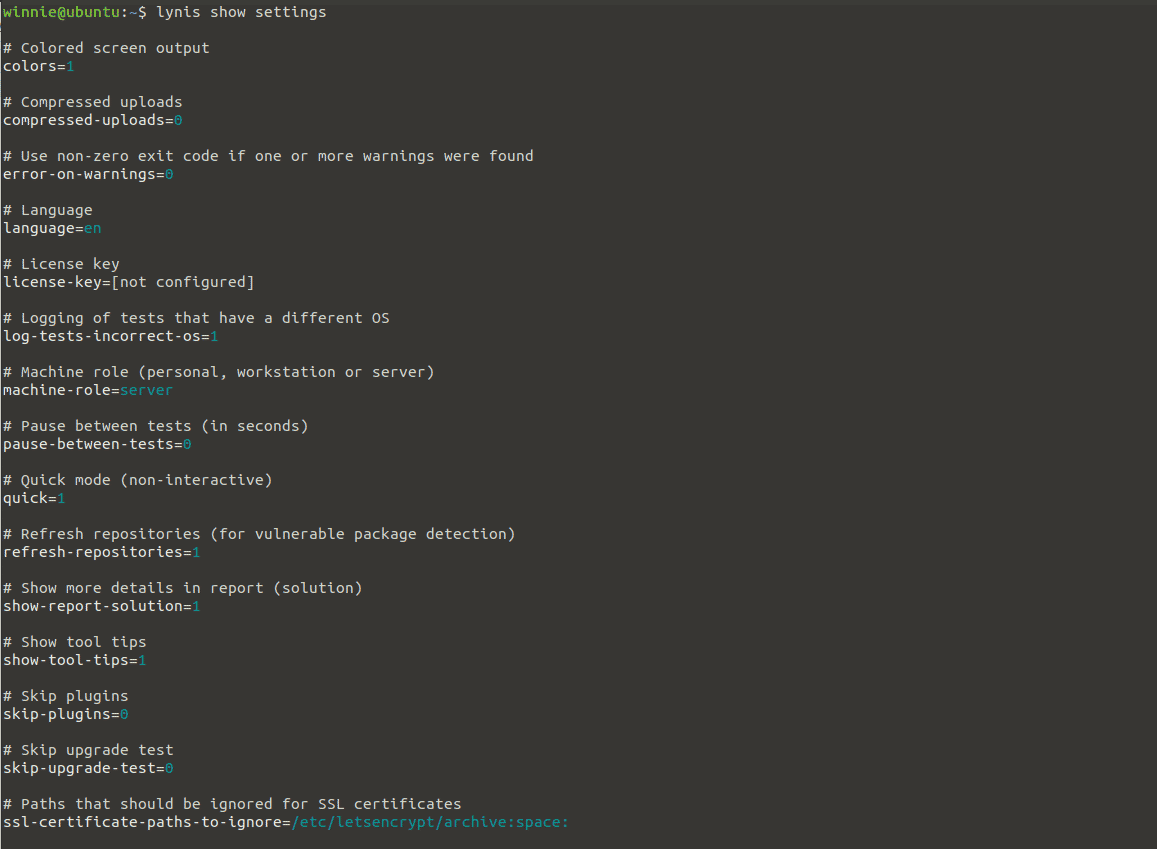
To view settings run:
$ lynis show settings
Step 6: Auditing a Linux System Using Lynis
Let’s proceed and perform a system audit on the machine. Run the following command:
$ sudo lynis audit system
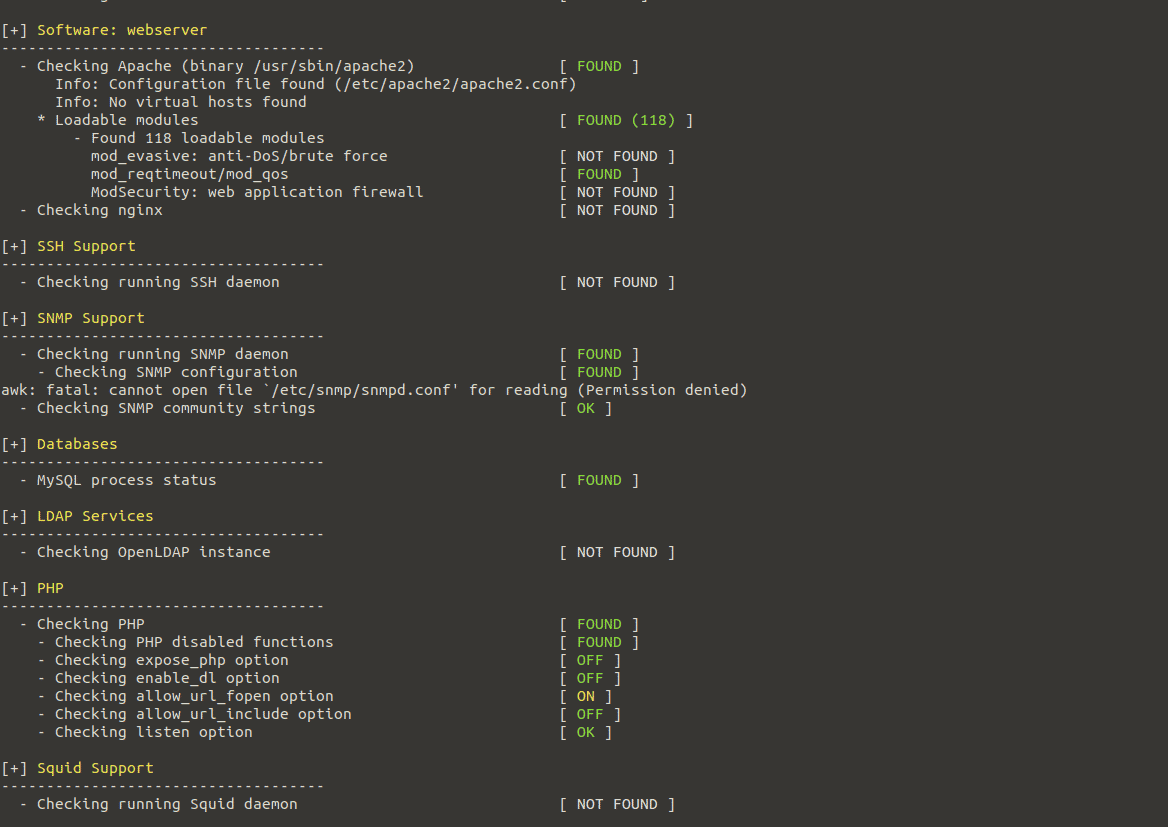
During the auditing process, Lynis executes tests and generates output separated into many areas such as security, suggestions, file system, test result, debug information, and so on. The auditing report is saved to /var/log/lynis-report.dat, and all test and debug information is written to /var/log/lynis.log. The report file contains general information on the system application, server vulnerable packages, and so forth. The prior test results will be overwritten each time you perform a new system audit.
The example below displays several auditing results labeled by keywords such as Enabled, Found, Not Found, Ok, Suggestion, etc. Any output with the Warning keyword needs to be checked and fixed.
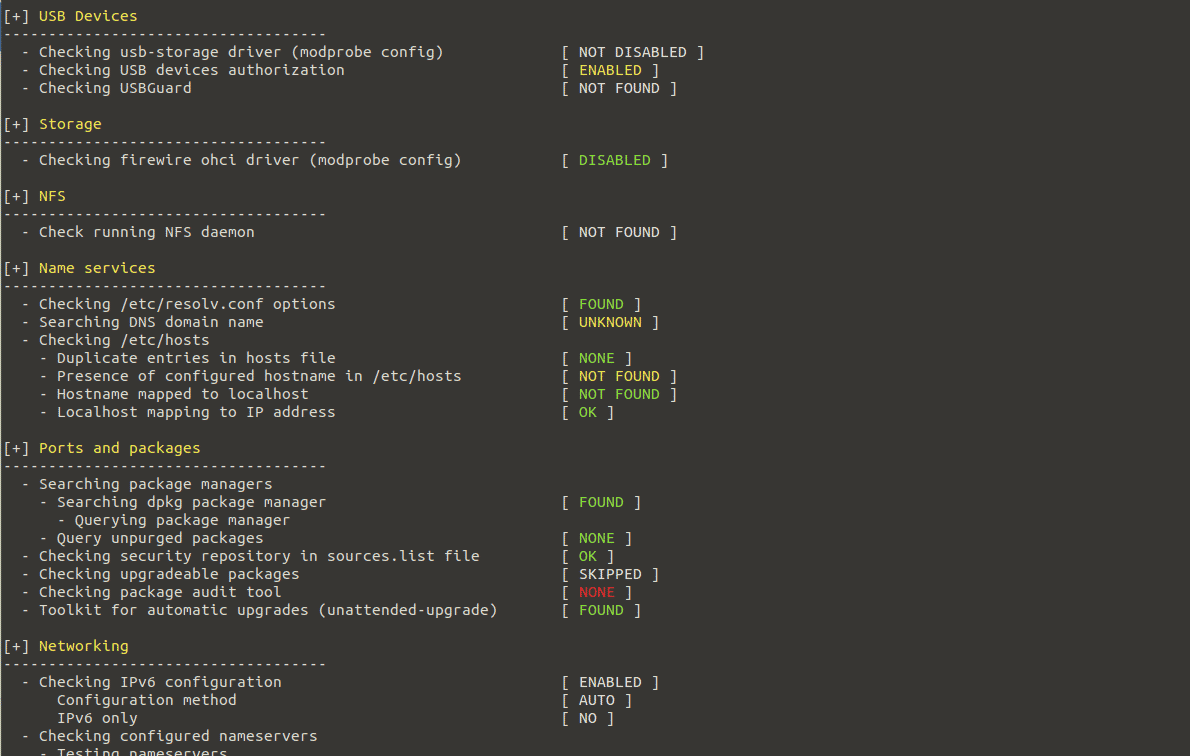
System Audit Output
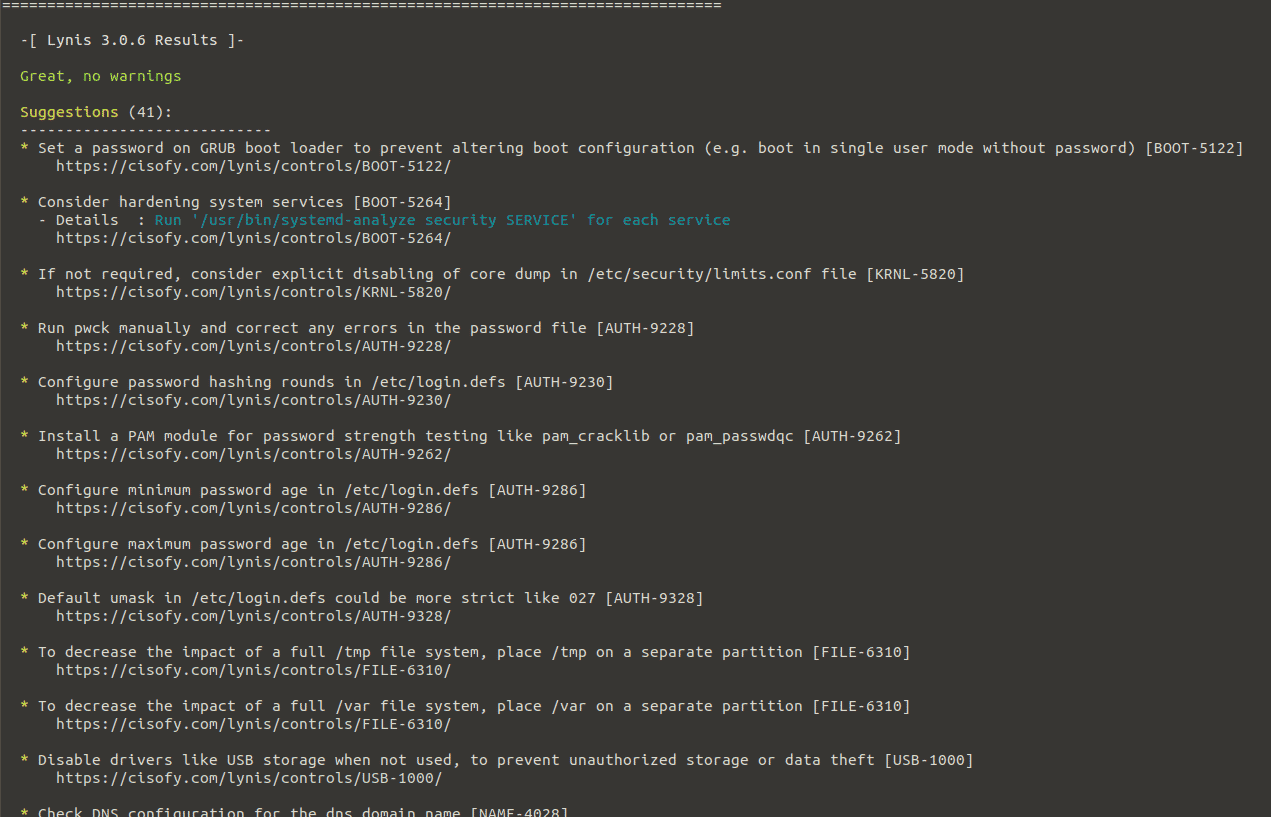
Lynis provided suggestions at the end of the auditing on how to harden your system.
Display Details of a Specific Test or Suggestion
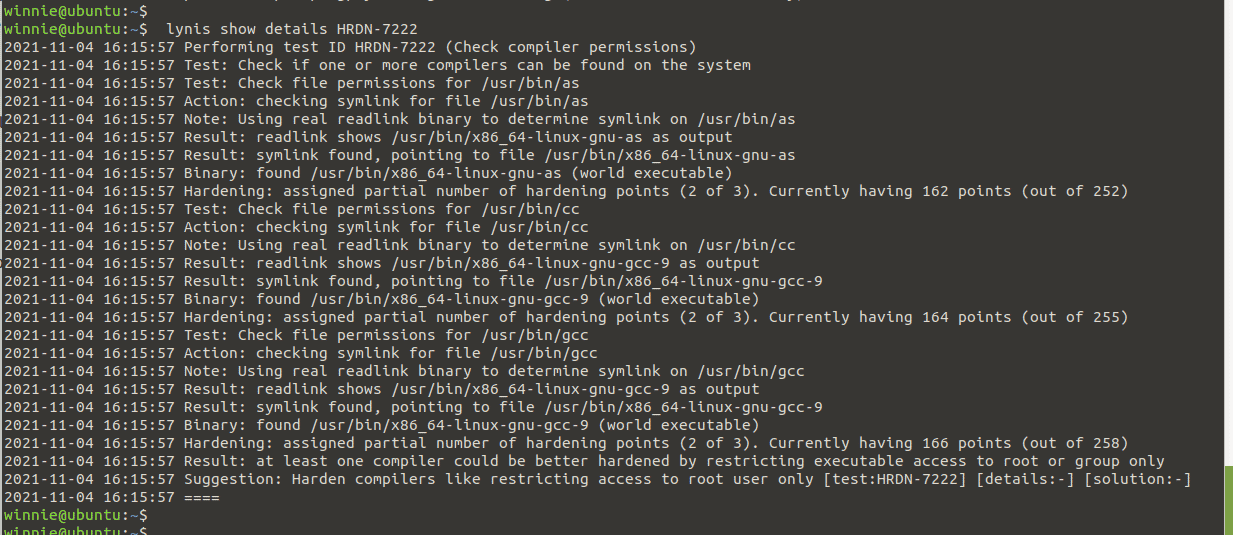
Each system check has a unique test ID. If you require additional information about a certain test, use the command below and its ID and display further information.
$ lynis show details TEST-ID
In this example, we will find out more about a test with a suggestion from Lynis.
$ lynis show details HRDN-7222
We have learned how to install and use the Lynis tool to audit our Ubuntu system. For further information on how to use it, check out the official site.