NoSQL database is a non-tabular database that stores and manages the data differently than the relational database. NoSQL has been adopted by big companies like Amazon, Facebook, Netflix, and Google because of their large volumes of unstructured data which cannot be handle by a relational databases. Some of the popular NoSQL databases are, CouchDB, Couchbase, RavenDB, MongoDB etc.
In this post, we will show you how to install MongoDB NoSQL server on Ubuntu using the apt package manager.
Pre-requisites:
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system
- Sudo user
Note: The procedure mentioned here has been tested on Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa).
Installing MongoDB NoSQL via the Apt Package Manager
To install MongoDB NoSQL on your system, you will need to add the MongoDB package repository. After that, you will be able to install the most recent and stable release of MongoDB NoSQL on your system. Let’s get started with the installation:
Step 1: Import the Public Key for MongoDB
First, we will need to import the public key for the official MongoDB repository. To do so, execute the following command in Terminal:
$ wget -qO mongodb.asc https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.4.asc
Then using the below command, add the downloaded key to the apt list of trusted keys:
$ sudo apt-key add mongodb.asc
If you see the OK in the output of the above command, this shows that the key has been added successfully.
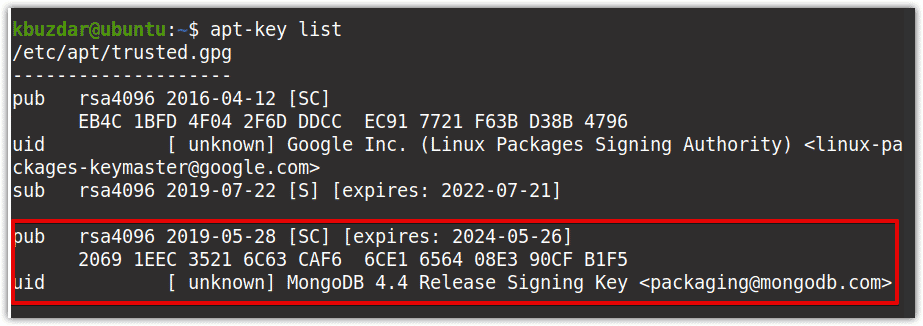
Once you have added the key, verify it by executing the following command in Terminal:
$ apt-key list
In the output, you will see the MongoDB key listed there:
While adding the key, you may receive an error indicating that gnupg is missing. If this is the case, install gnupg using the below command in Terminal:
$sudo apt-get install gnupg
Once installed, again try to add the key.
Step 2: Create a List File in sources.list.d Directory
Now we will create a list file /mongodb-org-4.4.list for MongoDB in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d directory. Execute the following command in Terminal to do so:
$ echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu focal/mongodb-org/4.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.4.list

Step 3: Update Local Repository Index
Now update the local repository index using the following command in Terminal:
$ sudo apt-get update
Step 4: Install the MongoDB Package
Now that our local repository is updated with the MongoDB repository, we can install the latest version of MongoDB. Here is the command to install the MongoDB in your system:
$ sudo apt-get install mongodb-org
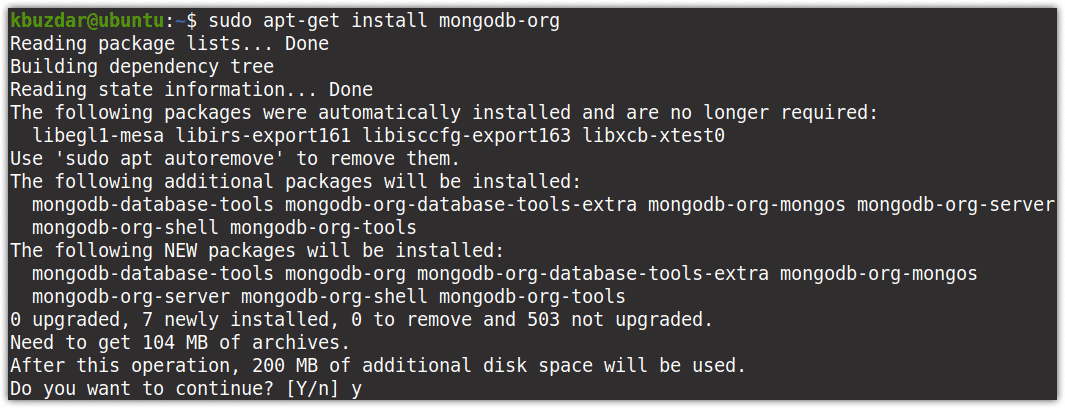
Now you may be asked to choose y/n (yes/no) option to continue the process. Press y to continue, after which installation of MongoDB will be started on your system.
Once installed, you can verify the installation and view the installed version of MongoDB as follows:
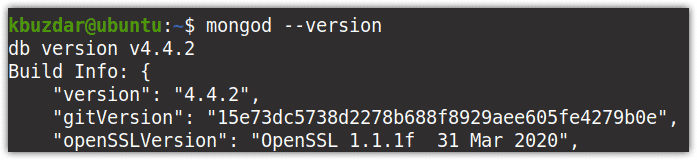
$ mongod --version
The following output shows that the MongoDB version installed on your system in 4.4.2.
Step 5: Setup Firewall
If a firewall is enabled on your system, MongoDB can still be accessed locally from the same system. However, if you need to access MongoDB from another system on the network or from the internet, you will need to add a rule in the firewall.
To allow incoming connection to MongoDB from a specific IP address, add the following rule:
$ sudo ufw allow from ip_address/ to any port 27017
To allow all incoming connection to MongoDB, add the following rule:
$ sudo ufw allow 27017
Step 6: Start Service
Now we can start the MongoDB service. Use the below command to do so:
$ sudo systemctl start mongod.service
After running the above command, if you experience this error:
Failed to start mongod.service: Unit mongod.service not found.
Then execute the below command to reload the systemd and try to start the service again.
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
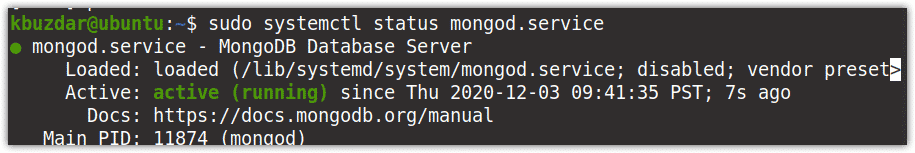
Then execute the below command to verify whether the service is running:
$ sudo systemctl status mongod.serivce
The below output shows the MongoDB service is active and running.
Now execute the below command to enable the MongoDB service to start automatically at boot:
$ sudo systemctl enable mongod.service
In case you need to stop the MongoDB service, execute the below command in Terminal:
$ sudo systemctl stop mongod.service
To restart the MongoDB service, execute the below command in Terminal:
$ sudo systemctl restart mongod.service
Uninstall MongoDB
In case you no longer need the MongoDB NoSQL, follow the below steps to completely remove it from your system.
1. Stop MongoDB service using the below command:
$ sudo service mongod stop
2. Now, remove MongoDB along with all the configuration files:.
$ sudo apt-get purge mongodb-org*
3. To delete the MongoDB logs, use the below command:
$ sudo rm -r /var/log/mongodb
To delete the MongoDB libraries, use the below command
$ sudo rm -r /var/lib/mongodb
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed how to add MongoDB’s official repository and install the latest stable release of MongoDB NoSQL in the Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system. We have also discussed how to completely uninstall from the system in case you no longer need it.
If you would like to know how to install MongoDB on Linux Mint 20, click here.