One of the several duties of a Linux administrator is to manage and keep track of the installed packages on a system. In the Ubuntu system, you can install a package through different methods which involve installation through apt, dpkg, and snap. Ubuntu also comes with a lot of packages pre-installed on it. Therefore, in this article, we will see how to list all the installed packages on Ubuntu including the packages which come preinstalled and those which were manually installed.
In this article, we will be covering how to:
- List installed packages using apt command
- List installed packages using dpkg command
- List installed snap packages
- Count installed packages
The commands mentioned here have been tested on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa).
List Installed Packages using apt Command
Apt is a command-line package management tool for Debian based Linux distributions that is used to install, update, and remove the packages from a system. With apt, you can list the installed packages on a system.
To list the installed packages in Ubuntu using the apt command, issue the following command in Terminal:
$ sudo apt list --installed
Now enter the password for sudo, after which it displays a long list of the installed packages in alphabetical order. The list will include the packages that were installed through dpkg and apt commands. This list also includes the dependencies. The packages displayed in the list also includes the version information of the installed packages. 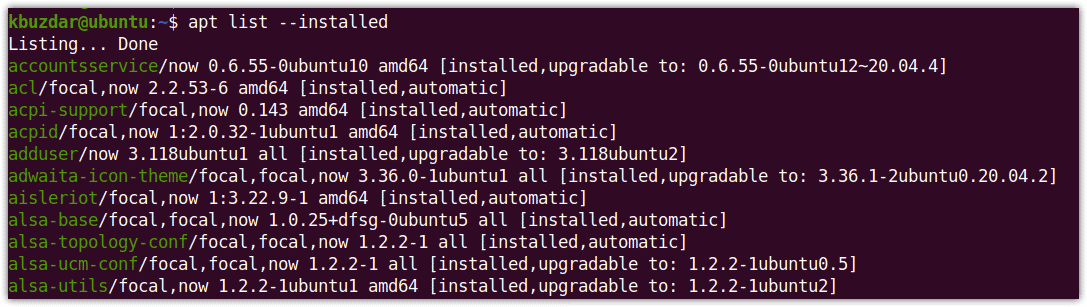
As the displayed list is so long, it is a little hard to find a specific package. If you need to verify whether a specific package is installed or not, you can pipe the output of the above command to grep as follows:
$ apt list --installed | grep package_name
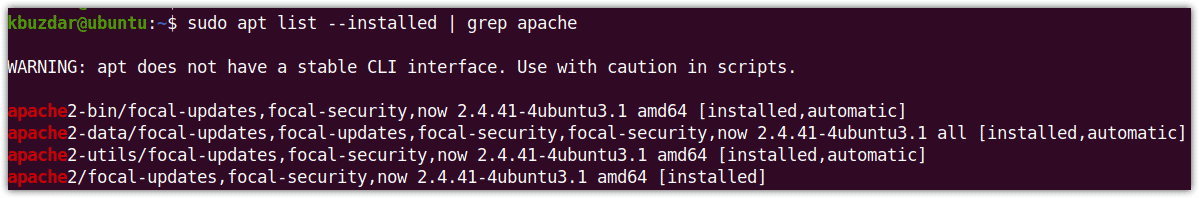
For example, to check whether the Apache server is installed or not, issue the following command in Terminal:
$ apt list --installed | grep apache
List Installed Packages using dpkg Command
Dpkg is also used for installing, building, and removing packages in Debian based OS. It can also be used to list installed packages in a system.
To list the installed packages in Ubuntu using the apt command, issue the following command in Terminal:
$ dpkg --list
Now enter the password for sudo, after which it displays a long list of all the installed packages in alphabetical order. The packages displayed in the list also includes the version information of the installed packages.
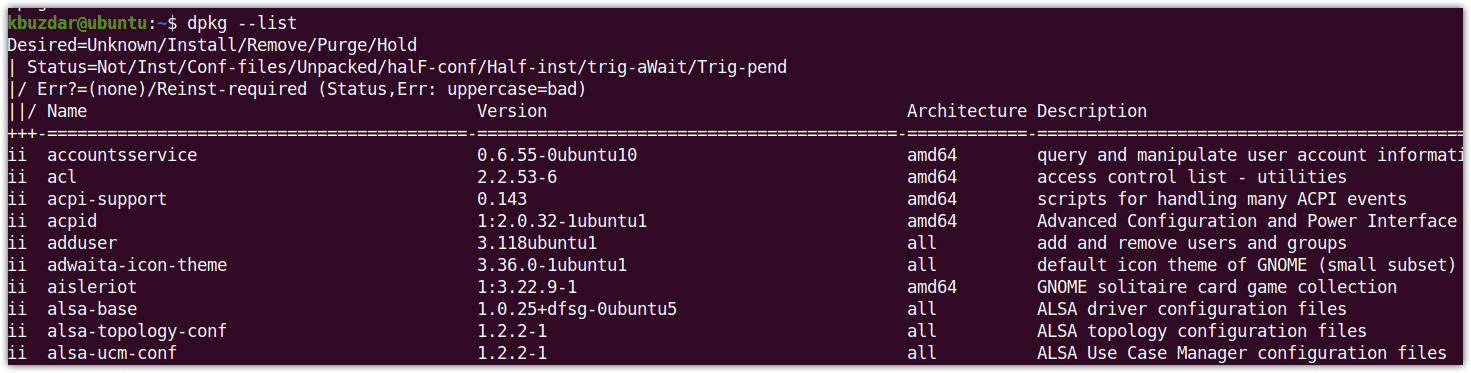
As the displayed list is so long, it is a little hard to find a specific package. If you need to verify whether a specific package is installed or not, you can pipe the output of the above command to grep as follows:
$ dpkg --list | grep package_name
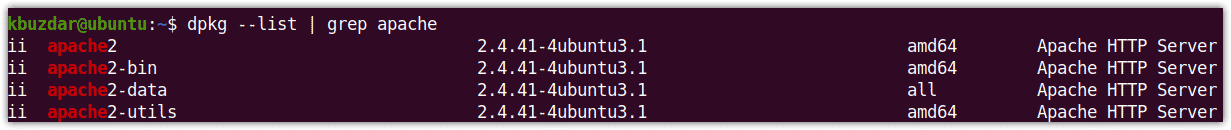
For example, to check whether the Apache server is installed or not, issue the following command in Terminal:
$ dpkg --list | grep apache
List Installed Snap Packages
The above-described methods list the packages that were installed using apt and dpkg. It does not include the packages that were installed as snaps.
To list installed snap packages in Ubuntu, issue the following command in Terminal:
$ snap list
It will list all the snap packages installed on your system.
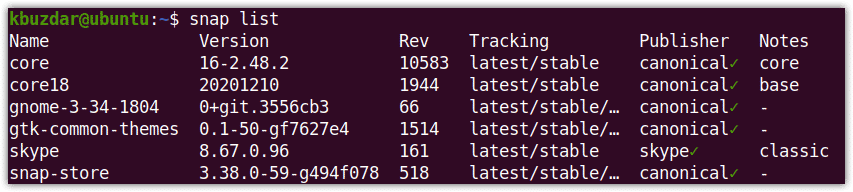
If you want to check whether a specific package is installed or not, you can pipe the output of the above command to grep as follows:
$ snap list | grep package_name
For example, to check whether the Skype package is installed or not, issue the following command in Terminal:
$ snap list | grep skype

Count Installed Packages
You can also count the number of installed packages on your Ubuntu system. Issue the following command to do so:
$ dpkg --list | grep -v "^Listing" | wc --lines
This is how you can list installed packages on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system. Moreover, you can also filter a specific package from the list and count the number of installed packages on your system.