Suricata is an open-source network threat detection tool with features such as intrusion detection, intrusion prevention, as well as network security monitoring. It excels at deep packet inspection and pattern matching, making it an invaluable tool for detecting threats and attacks.
Suricata can generate logs, drop traffic, and trigger alerts in case suspicious packets are in your network. This guide will take you through the installation of Suricata IDS on ubuntu 20.04
Step 1: Update your system
First, ensure your system packages are updated. Run the command:
$ sudo apt update
Once the package index is updated, proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Add Suricata Repository
The latest stable version of Suricata is available on the PPA repository maintained by OISF. Therefore, we are going to add the Suricata repository on your Ubuntu system as shown;
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:oisf/suricata-stable
Thereafter, update your system’s package index.
$ sudo apt update
With the PPA in place, head over to the next step and install the Suricat IDS.
Step 3: Install Suricata
To install Suricata run the command:
$ sudo apt install suricata
With the installation of Suricata, let’s go a step further and enable it to start on boot time.
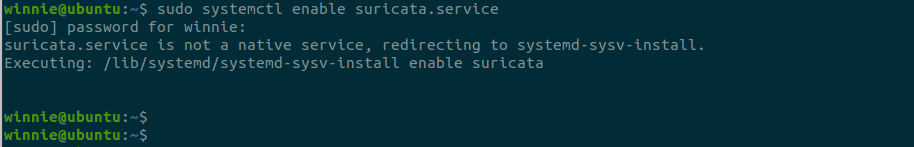
$ sudo systemctl enable suricata.service
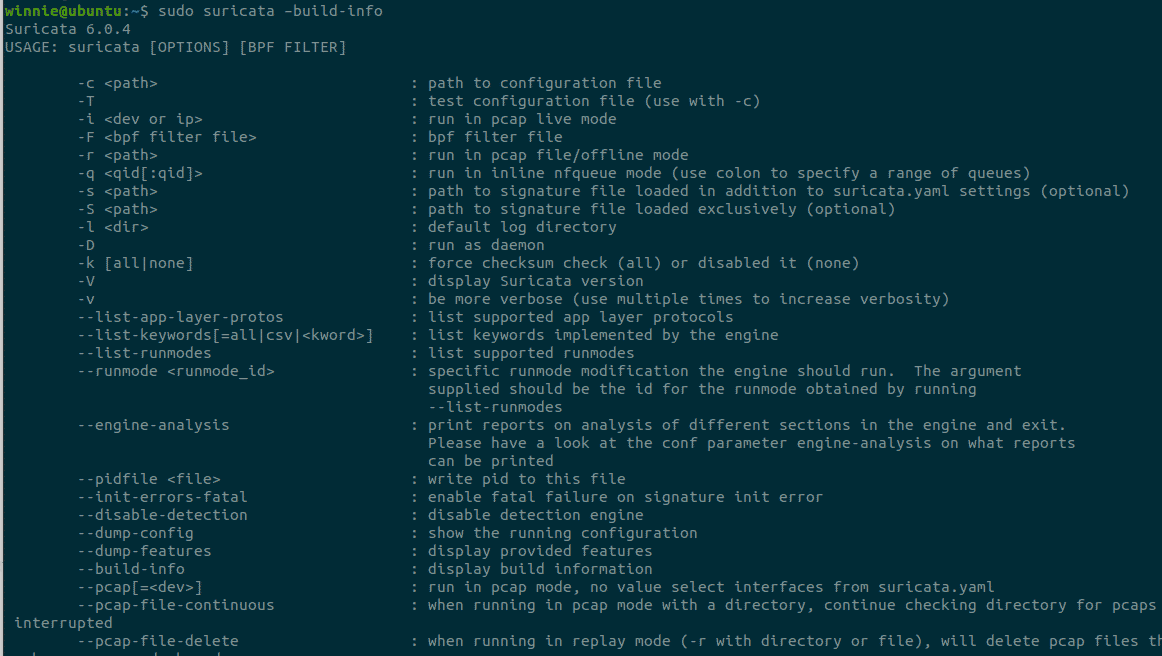
Next, ensure that the installation was successful by running the following command:
$ sudo suricata –build-info
Confirm that Suricata’s systemd service is running as follows:
$ sudo systemctl status suricata
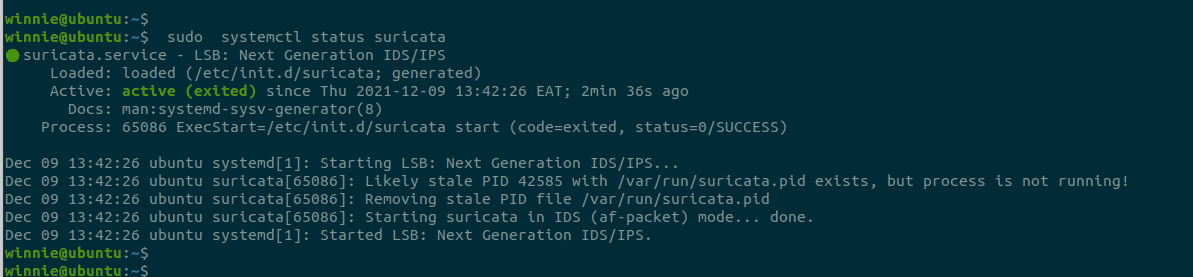
The output confirms that Suricata is up and running on Ubuntu 20.04
Step 4: Basic setup
Suricata’s configuration file is located in the /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml path. For basic setup, we need to configure Suricata for your internal and external network. Open the configuration file as shown:
$ sudo vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml
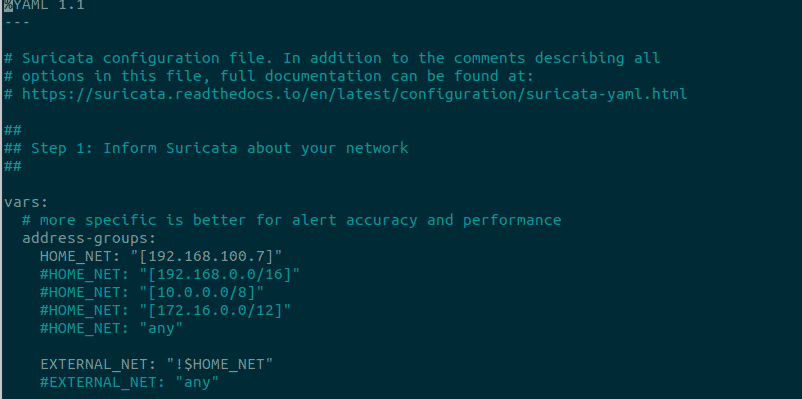
Then, specify the ip address for the HOME_NET variable. In this case, my IP address is 192.168.100.7. The HOME_ NET variable is the IP address of your local network or interface you want to monitor. Next, define the value for EXTERNA_ NET as being any network that is not your local ip address.
Next, go to the af-packet section in the configuration file and change the interface name to reflect the network interface chosen above.
Step 5: Suricata Rules
Suricata allows you to create network rules or signatures according to your requirements. The most common rules include Emerging Threats and Emerging Threats Pro.
The rules file is located in the /etc/suricata/rules/ directory. To view the contents run:
$ ls /etc/suricata/rules/

To install the Emerging Threats Open ruleset, run:
$ sudo suricata-update
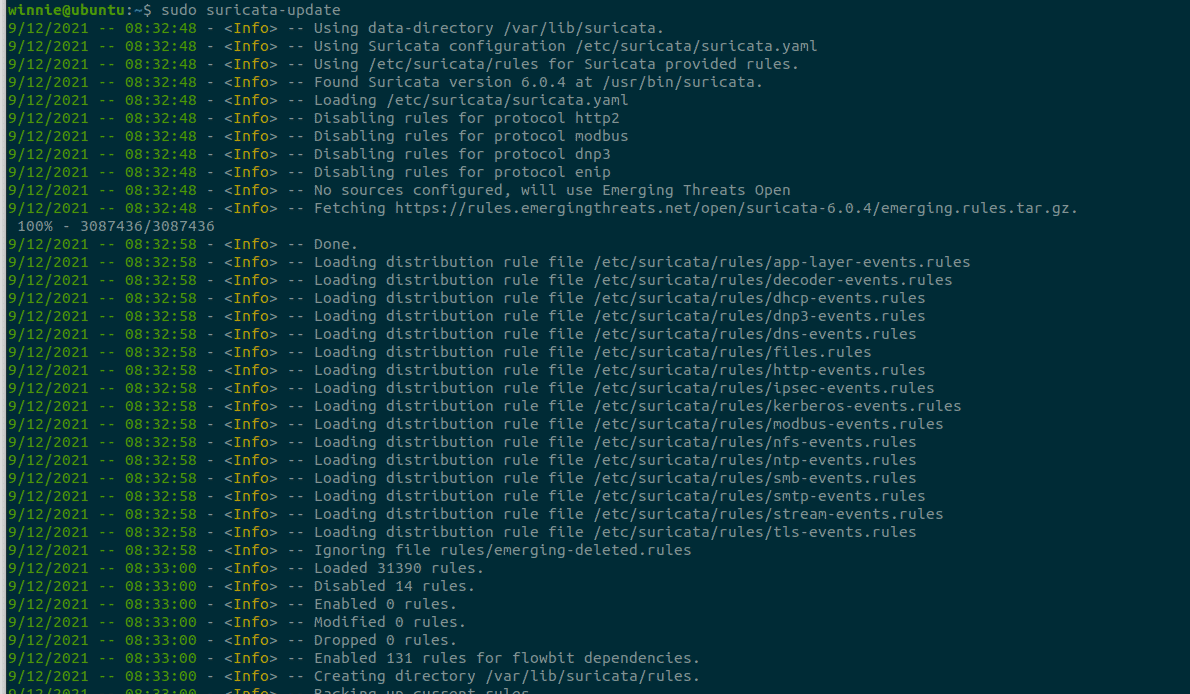
This will install the rules to the /var/lib/suricata/rules/ directory.
Step 6: Running Suricata
After installing all the rules, you can restart the Suricata IDS service as shown:
$ sudo systemctl restart suricata
You can also check the Suricata logs as shown:
$ sudo tail /var/log/suricata/suricata.log
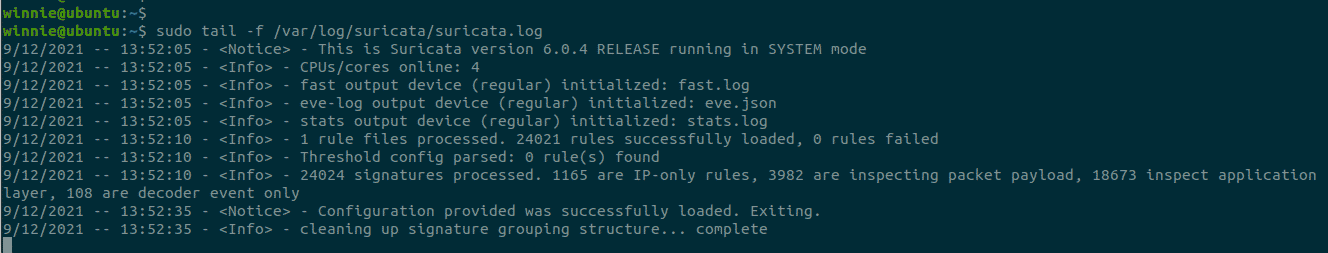
That’s it with installing Suricata IDS on Ubuntu 20.04. For more information head over to the documentation page.