In this article, we will cover starting, stopping, and restarting services in Ubuntu 20.04. You should know how this works as it gives you more control. But, first things first, what are services? Services are background processes that run when the OS boots and end when it shuts down.
Managing services in Ubuntu using systemd
Systemd is System Management Daemon and it refers to all the libraries, packages, and utilities around daemon.
Viewing all services
Before you get started on staring, stopping, or restarting your services, you need to know the ones that are available on your system. You can see a list of all the services available on your system by using:
systemctl list-unit-files --type service –all
![]()
You will be able to view the services as in the image below:
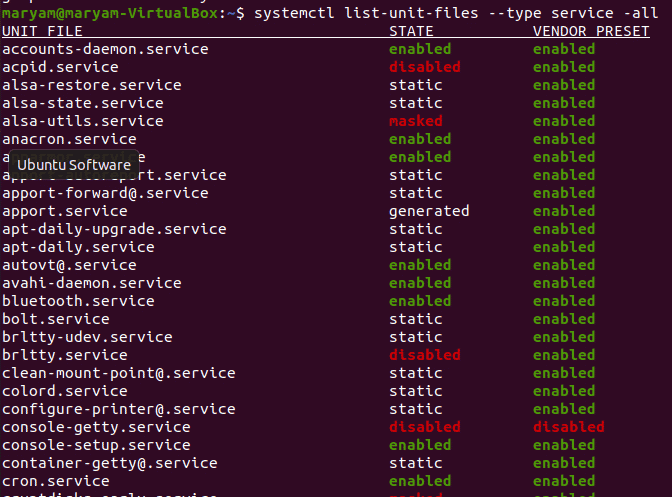
The state of your services can be enabled, disabled, static, masked, or generated.
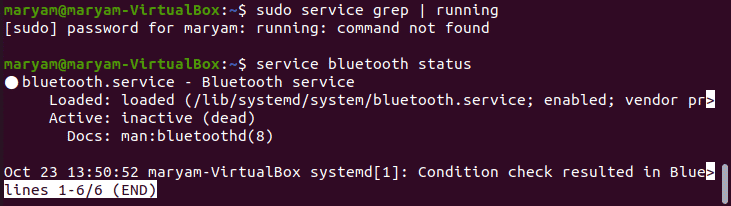
View running services
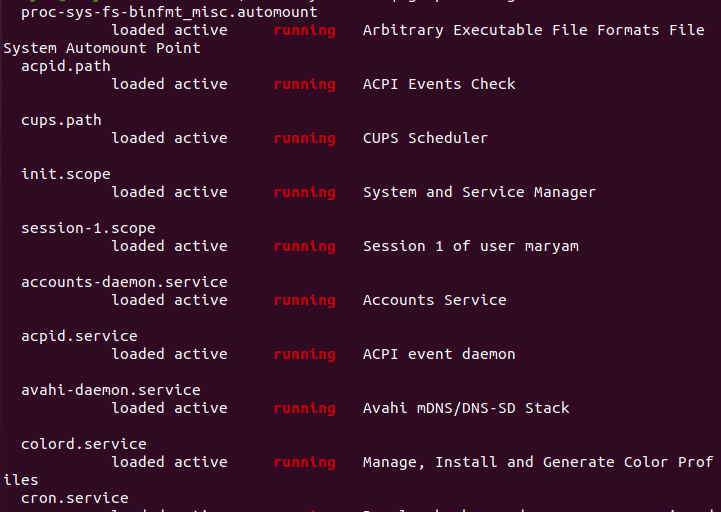
To view running services, use:
sudo systemctl | grep running
![]()
The result of this command is a list of running services, as shown below.
Start a service
Use the command below to start a service:
systemctl start {service-name}
![]()
Stop a service
Use the command below to stop a service:
systemctl stop {service-name}
![]()
Restart a service
Use the command below to restart a service:
systemctl restart {service-name}
![]()
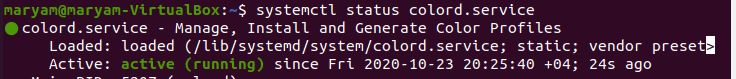
Status of a service
Use the command below to view the status of a service:
systemctl status {service-name}
Managing services in Ubuntu using service
Service is a high-level command that redirects on different binaries. It is less advanced compared to systemd and is a part of init.
Viewing all services
Compared to system, the service commands are a lot simpler. To view all services use,
service --status-all
![]()
You will be able to view the services as in the image below:
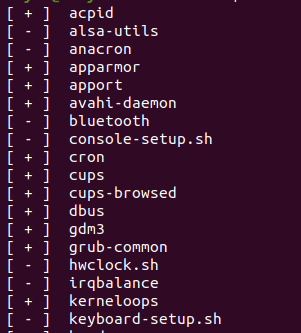
The way they are displayed is different. [ + ] means the services is enabled and [ – ] means disabled.
Start a service
Use the command below to start a service:
service {service-name} start
![]()
Stop a service
Use the command below to stop a service:
service {service-name} stop
![]()
Restart a service
Use the command below to restart a service:
service {service-name} restart
![]()
Status of a service
Use the command below to view the status of a service:
service {service-name} status
Managing services in Ubuntu using init
The init scripts for services are loaded in the directory /etc/init.d/. Init stands for initialization, it is a daemon process that starts when the computer starts and ends when it shuts down. If init does not start, no process starts and the system reaches the Kernel Panic stage. It has been replaced by systemd which reduces computational overhead.
Start a service
Use the command below to start a service:
/etc/init.d/{service name} stop
![]()
Stop a service
Use the command below to stop a service:
/etc/init.d/{service name} stop
![]()
Restart a service
Use the command below to restart a service:
/etc/init.d/{service name} restart
![]()
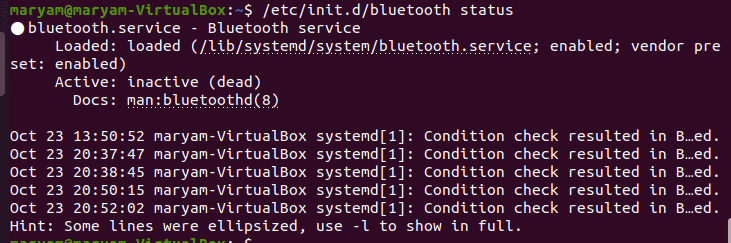
Status of a service
Use this command to view the status of a service:
/etc/init.d/{service name} status
And that is how you stop, start, or restart a service in Ubuntu 20.04.