Docker-decompose tool is commonly used to configure multiple container-based Docker applications. Let’s we can say that Docker-compose is a command-line tool that helps to deploy multiple containers and Docker applications by using a just single command. Using the Docker-compose you can include the Docker containers into a docker-compose.yml file and mention all container services or configurations that are necessary for an application. This tool can be used in the development, testing, and production environment, apart from all of these facts it also helps in Continuous Integration workflow.
In this article, we are installing the Docker-compose on CentOS 8 system. We will describe how you can use and configure it on your system through the command-line.
Installation of Docker-decompose on CentOS 8
Follow the below-mentioned steps to install the Docker-compose on your CentOS 8 system. The docker-compose can be installed on CentOS 8 by using the following two different ways:
Method 01: Install Docker-compose using Python-pip tool
Docker-compose can be installed on CentOS 8 system by using the python-pip tool. Use the following commands, if you want to install Docker-decompose through this method:
$ sudo yum install epel-release
$ sudo yum install python-pip
# pip install docker-compose
# docker-compose --version
Method 02: Install Docker-compose from the GitHub repository
To install Docker-decompose by using the curl command, you need to execute the following command to install curl on CentOS 8 if it is not already installed:
$ sudo dnf install curl -y
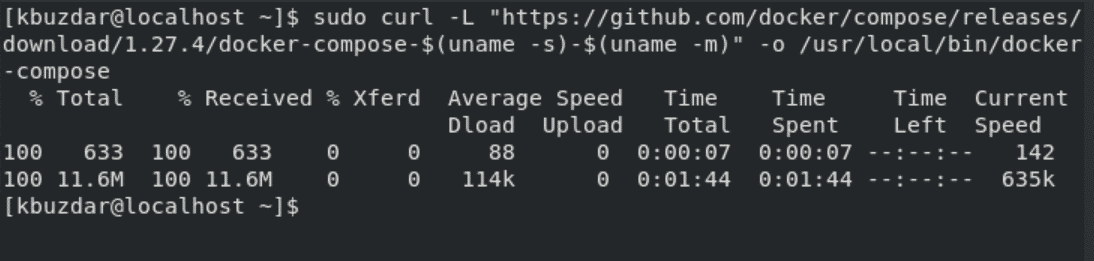
Now, download the Docker-compose binary from GitHub by using the curl command as follows:
$ sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.27.4/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Use the below-mentioned command to set permissions on a binary executable file:
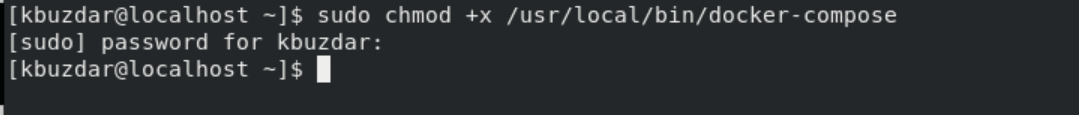
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
To show the Docker-compose version which is installed on your CentOS 8 system, type the following command:
$ docker-compose –version

Now, the Docker-compose has been successfully installed on CentOS 8. In the rest article, we are explaining some set of commands that will help you in using the docker-compose tool.
How to use Docker-compose on CentOS 8?
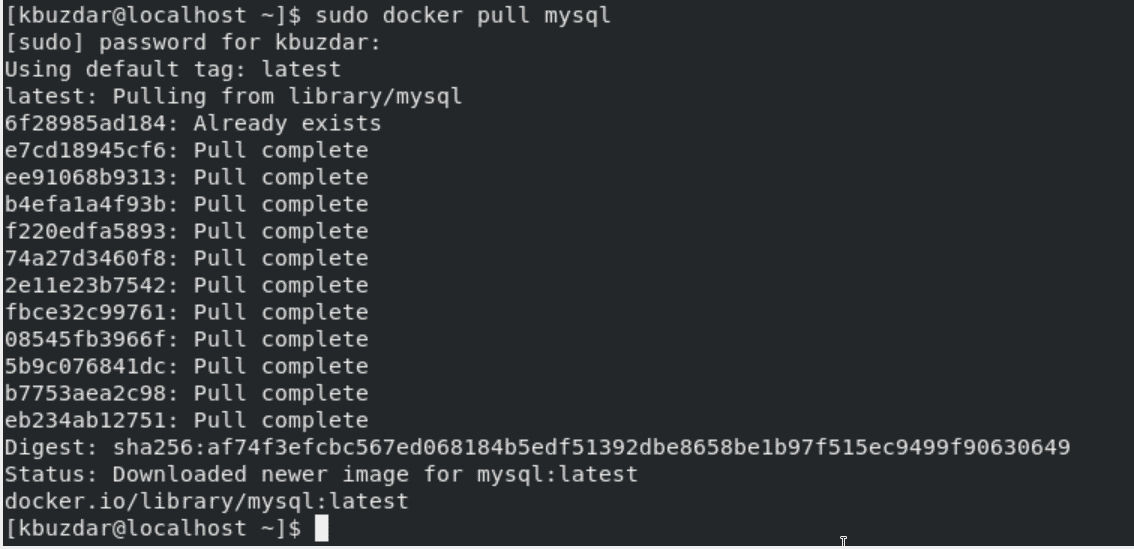
All configurations about the containers-based services and container images are defined in the ‘docker-compose.yml’ file. Here, we are pulling container images of WordPress and MySQL by using the following commands:
$ sudo docker pull wordpress
$ sudo docker pull mysql
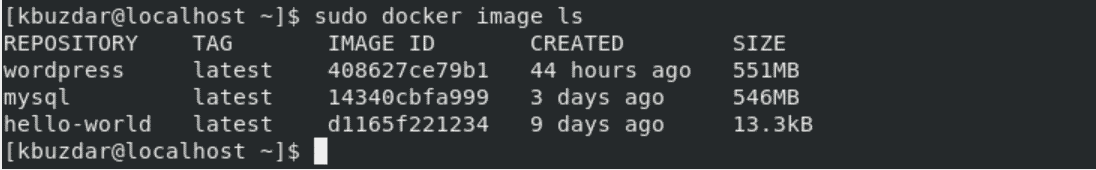
$ sudo docker image ls
Now, create a new directory with the name ‘wordpress-site’ and navigate into it as follows:
$ mkdir wordpress-site
$ cd wordpress-site/
Here, create a docker-compose file ‘docker-compose.yml’ and paste the following code in this file:
version: '3.0' services: webserver: image: wordpress container_name: wp_web ports: - 8080:80 links: - dbserver:mysql environment: WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: 6zcznAEjLWp79P dbserver: image: mysql:latest container_name: wp_db environment: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: 6zcznAEjLWp79P
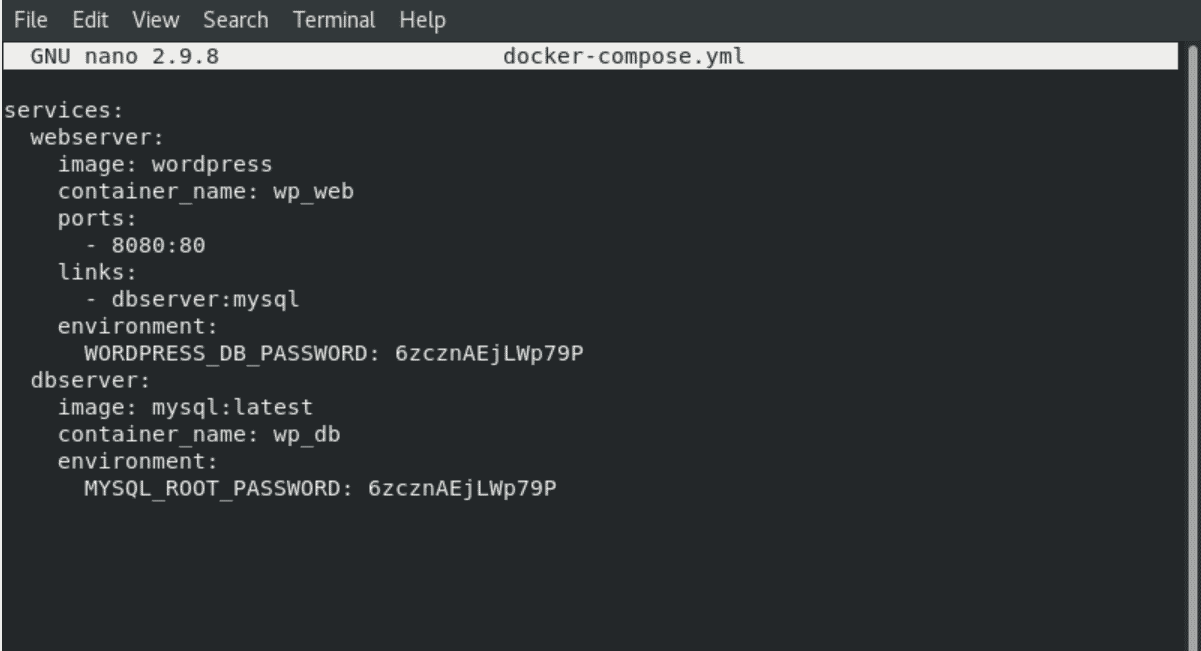
In the above file, two different container services are defined such as ‘webserver’ and ‘dbserver’. We have also defined container images and then mentioned the WordPress and dbserver passwords.
Now, deploy these containers by running the below-mentioned command as the root user:
# docker-compose up
Now, browser the WordPress site URL.
http://{docker_host_ip}:8080
To start and stop the containers, use the following commands respectively:
# docker-compose start
# docker-compose stop
To explore more about the Docker-compose usage, use the following command:
$ docker-compose --help
Conclusion
We have elaborated in this article on how to install and use the Docker-compose on CentOS 8 system. By using the Docker-compose, you can deploy multiple Docker applications with container services through a single command. Visit more details related to Docker-compose through the above help guide.