Nmap is an open-source network scanner and security auditing utility. The system and network administrators can use Nmap for several useful tasks like for port scanning, administration, network inventory, security auditing, etc. It can collect a wealth of information like OS version, MAC address, running services, and much more. Nmap can monitor a single host or a large network comprising of several hosts.
In an earlier post, we covered the installation of Nmap on Ubuntu OS. In today’s post, we will cover the installation of Nmap on a CentOS machine. We will install it using these methods:
- Installation via Yum Package Manager
- Installation via Snap Package Manager
Note: We have demonstrated the installation procedure on CentOS 8 machine.
Installing Nmap via Yum Package Manager
The first method we will explain is using the yum package manager for installing Nmap. At the time of writing, the Nmap version available in the yum default repository is 7.70. To install Nmap using the yum package manager, use these steps:
1. Open the Terminal in your CentOS machine. Press the Windows key and then search the Terminal program using the search box that appears.
2. Now execute the command below in order to install Nmap:
$ sudo yum install nmap
If prompted, hit y to continue.
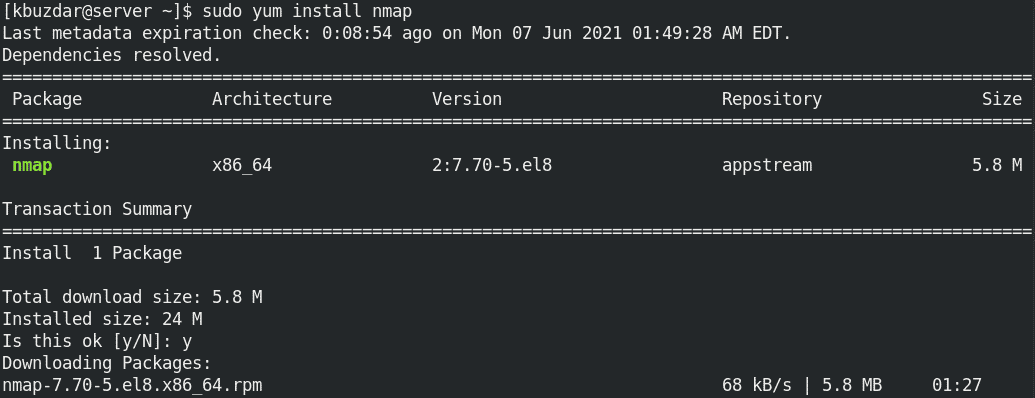
After the installation of Nmap is completed, you will see the output as shown below:

3. Now to verify the installation of Nmap and to view the version that is installed, execute the command below:
$ nmap --version
The following output indicates the Nmap version 7.70 is successfully installed on our CentOS machine.

Installing Nmap via Snap Package Manager
In the second method, we are going to cover how to use the snap package manager to install Nmap. At the time of writing, the Nmap version available via snap package manager is 7.91. To install Nmap using the snap package manager, use these steps:
1. You should first enable the EPEL repository using the command below:
$ sudo yum install epel-release
Enter sudo password and press y if prompts you with y/N.

2. You can now use the yum command to install snapd as follows:
$ sudo yum install snapd
Enter sudo password and press y if it prompts you with y/N.

3. After installing snapd, you will have to enable the snapd.socket:
$ sudo systemctl enable --now snapd.socket
4. Then you will need to create a symlink.
$ sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snap
This will enable the classic snap support.
5. You can now install Nmap:
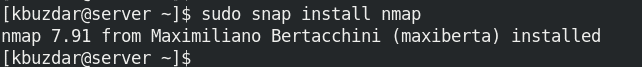
$ sudo snap install nmap
Once Nmap is installed, you should see the following similar output:
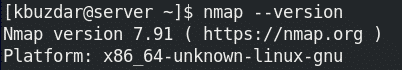
6. Now to verify the installation of Nmap and to view the version that is installed, execute the command below:
$ nmap --version
The following output indicates the Nmap version 7.91 is successfully installed on our CentOS machine.
To display the help screen along with all the options for the Nmap command-line utility, use the below command:
$ nmap --help
Uninstall Nmap
If you want to remove Nmap from your system, you can do so using the following methods:
If you have installed Nmap using the yum package manager, you can uninstall it as follows:
$ sudo yum remove nmap
If you have installed Nmap using the snap package manager, you can uninstall it as follows:
$ sudo snap remove nmap
By following either of the methods described above, you can easily and quickly install Nmap on your CentOS machine. Nmap is a handy utility for network scanning and security auditing. Nmap contains variety of options for scanning remote hosts. Visit the 15 Mostly Used Nmap Commands for Scanning Remote Hosts.