Introduction:
Volatility is a very useful memory forensics framework that is mainly used for cyber-crime investigation, digital evidence collection, and malware analysis. This tool can easily be used with any of the following three operating systems i.e. Linux, macOS, and Windows. However, in this article, we will be sharing with you the procedure following which you will be able to install this tool on a Linux Mint 20 system.
Installation of Volatility on Linux Mint 20:
The installation procedure of Volatility on a Linux Mint 20 system is very simple and will be depicted by the following steps:
Step # 1: Install Python on your System:
First, you need to install the relevant version of Python on your system which is compatible with Volatility with the help of the command shown below:
$ sudo apt install python2.7
![]()
Step # 2: Install the Other Required Packages on your System:
After installing Python on your system, you also need to install some other additional packages on your system by running the following command:
$ sudo apt install python3-pip python-setuptools build-essential python-dev-is-python2
![]()
Step # 3: Install Distorm 3 on your System:
Once you have installed the packages mentioned in step # 2, you need to install the relevant version of Distorm on your system by executing the command shown below:
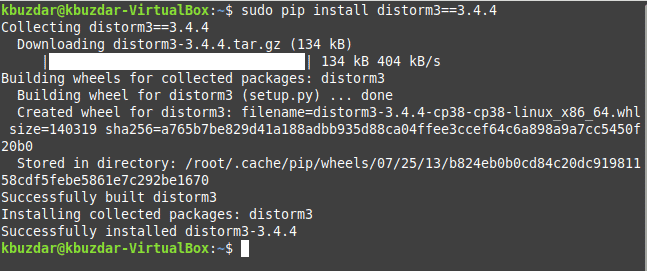
$ sudo pip install distorm3==3.4.4
![]()
The successful installation of Distorm will display the following output on your screen:
Step # 4: Install Git on your System:
Now, you need to install Git on your system by running the command shown below:
$ sudo apt install git
![]()
Step # 5: Clone the Volatility Repository onto your System:
Once Git is installed on your system, you need to clone the Volatility repository onto your system by executing the following command:
$ git clone https://github.com/volatilityfoundation/volatility.git
![]()
Step # 6: Make the Newly Cloned File Executable:
After cloning this repository to your system, you need to make this newly cloned file executable with the help of the command stated below:
$ chmod +x volatility/vol.py
![]()
Step # 7: Move the Executable File to a Relevant Directory:
Now, you need to move this executable file to the “opt” directory of your system by running the following command:
$ sudo mv volatility /opt
![]()
Step # 8: Make a Symbolic Link of the Executable File:
Once you have moved your target file to the desired directory, the last thing that you need to do is to create a symbolic link for it to ensure its availability globally. This can easily be done by running the command shown below:
$ sudo ln –s /opt/volatility/vol.py /usr/bin/vol.py
![]()
Step # 9: Test the Volatility Tool on your System:
Now, to test whether this tool is working correctly or not, you will have to run the following command:
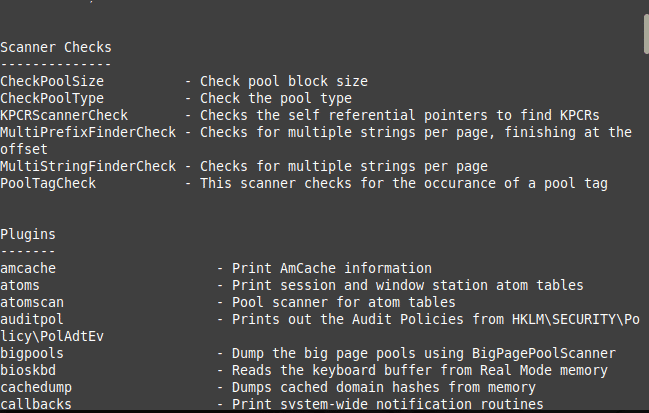
$ vol.py --info
![]()
This command will produce a very extensive output on your terminal. You can scroll up or down to see all the details that have been provided by this tool. A glimpse of this output is shown in the image below which also verifies that this tool has been successfully installed and is also working correctly on your system.
Conclusion:
By following the procedure explained in this guide step by step, you will instantly be able to install Volatility on your system, and hence, you will be able to keep a record of all the activities taking place on your system. Additionally, you will also be able to trace back all the important events and even possibly avoid any unwanted circumstances.




