Copy-paste procedures are used in user-interface design and human-computer interaction to provide an inter process communication method for moving data across a system’s user interface. The “copy” command is used to duplicate data and place it in a temporary location. i.e., clipboard. The clipboard data is then put in the desired spot. Any program that supports the capability and allows data transfer can access the duplicated data.
Rather than inputting long sentences word by word, you can save time by using copy-pasting strategies. You may have copied and pasted text several times in your Ubuntu Graphical User Applications using the conventional keyboard instructions “CTRL+C” and “CTRL+V”. Many standard keyboard shortcuts, however, do not work with Ubuntu Terminal, which may surprise you.
Methods for Copy and Paste in Ubuntu
In this article, the two different approaches through which you can copy and paste in Ubuntu will be discussed. These approaches involve:
- Using the right-click context menu
- Using keyboard shortcuts
Method-1: Copy-Paste using “right-click context menu”
Copy-paste can be done using the mouse right-click, just like in other Ubuntu applications. For this purpose, choose the text you wish to copy. Then right-click on it and select “Copy” from the drop-down menu. This copied command can be pasted into a terminal window, a script, or any other document.
Let’s go through some basic examples for a better understanding of this concept:
Example-1: Copy and Paste between two terminal windows
By using the right-click method, you can copy any text from one terminal window and paste it on another terminal window.
For this purpose, pick the command and choose the “Copy” option from the drop-down menu:
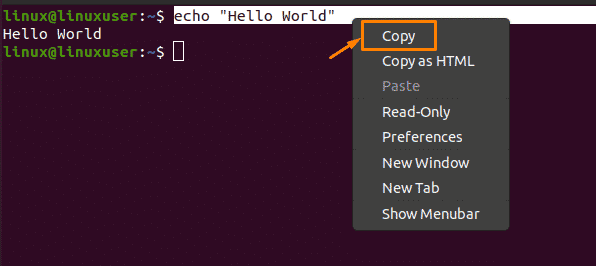
After copying the selected command, you can paste it into the other terminal by choosing the “Paste” option from the drop-down menu:
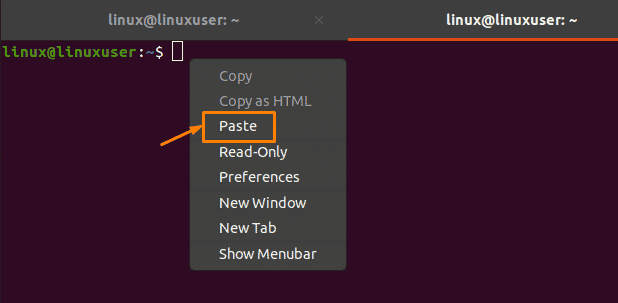
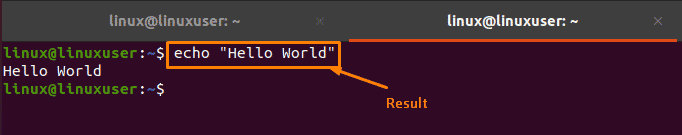
After clicking on the “Paste” option, you will get the exact copied text as output:
Example-2: Copy and paste between the terminal and text document
By using the right-click method, you can copy any text from one terminal window and paste it into any text document. For this purpose, pick the command and choose the “Copy” option from the drop-down menu:
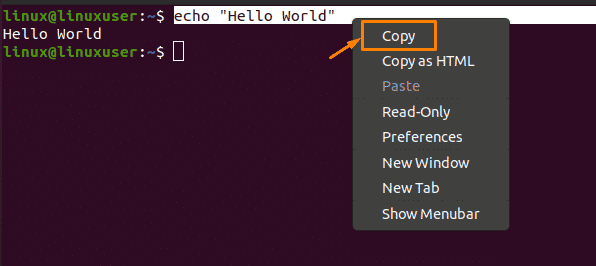
Then, you have to create a text document by using the “Touch” command and place the file in your desired location. In my case, I have created a text document named “myfile” by using the command “touch myfile” and placing it in the “home” location. After copying the selected command, you can paste it into the text document by choosing the “Paste” option from the drop-down menu:
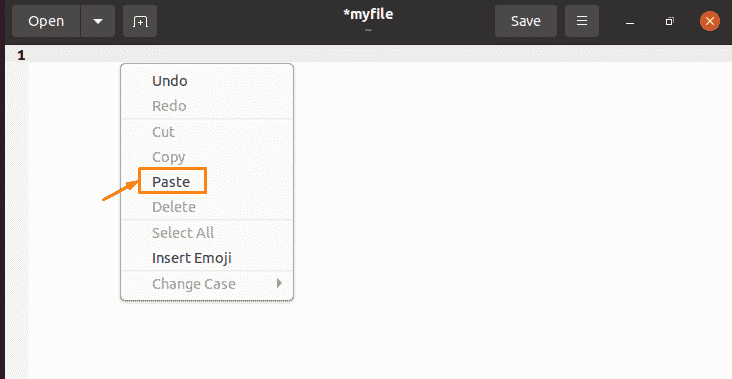
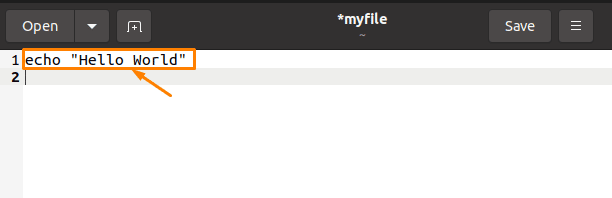
After clicking on the “Paste” option, you will get the exact copied text as output:
Method-2: Copy-Paste using keyboard shortcuts
Most computer users are familiar with the shortcuts “CTRL+C” and “CTRL+V” for copying and pasting text. On the Ubuntu Desktop, these shortcuts also work, but not in the case of the terminal. To copy or paste commands in the Ubuntu terminal, you have to include the “Shift” key in the “CTRL+C” and “CTRL+V” shortcuts.
The rules are straightforward:
- You can press “CTRL+Shift+C” to copy text or commands from the Ubuntu terminal.
- You can press “CTRL+Shift+V” to paste text or a command into the Ubuntu terminal.
- You can press “CTRL+C” to copy text or a command from outside the Ubuntu terminal.
- You can press “CTRL+V” to paste text or command into any document or script.
Let’s go through some basic examples for a better understanding of this concept:
Example-1: Copy and Paste between two terminal windows
By using keyboard shortcuts, you can copy any text from one terminal window and paste it into another terminal window.
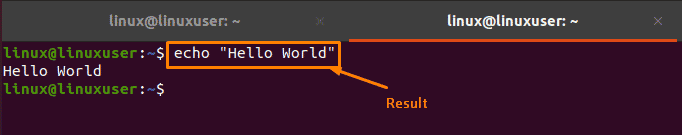
For this purpose, pick the command and press “CTRL+SHIFT+C” to copy the command:
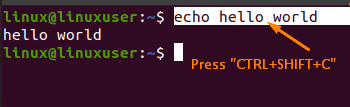
After copying the selected command, you can paste it into the other terminal by pressing “CTRL+SHIFT+V”:

After pressing “CTRL+SHIFT+V,” you will get the exact copied text as output:
Example-2: Copy and Paste between the terminal and text document
By using the right-click method, you can copy any text from one terminal window and paste it into any text document.
For this purpose, pick the command and press “CTRL+SHIFT+C” to copy the command:
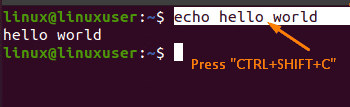
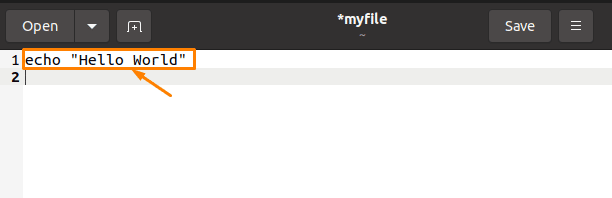
Then, you have to create a text document by using the “Touch” command and place the file in your desired location. In my case, I have created a text document named “myfile” by using the command “touch myfile” and placing it in the “home” location. After copying the selected command, you can paste it into the other terminal by pressing “CTRL + V”:

After pressing “CTRL+V,” you will get the exact copied text as output:
Conclusion
Copy-paste in Ubuntu provides the facility to copy and paste text or commands without having to retype them. This method also saves you time, which you can put to better use. The two distinct approaches to “how to copy-paste in Ubuntu” are discussed in this article. i.e., right-click approach and keyboard shortcuts approach. Using the keyboard shortcuts approach for copy-paste is easier than using the mouse right-click approach.