As we all know Linux and distributions can be installed and used smoothly on as low as 20GB of disk space. But with time disk space is something that is never abundant. Unlike Windows, Linux and its distros don’t come with tools like defragmenter hence after sometime Ubuntu gets slower due to unnecessary files and applications taking up space on the disk.
So, to keep the Ubuntu system steady and fast you need to get rid of unneeded trash at regular intervals. Here I’m going to show you the ways in which you can free up the disk space in Ubuntu and be never short on disk space.
I will be covering both GUI as well as command-line methods to free up disk space.
Remove APT Cache
Every time we install any application or package using Terminal, APT creates and keeps a cache of the previously downloaded and installed app or package on the disk. The cache of these apps and packages stays on disk even after they are uninstalled from the system.
APT also known as Advance Package Tool is used by Ubuntu to install, uninstall, and manage applications on the system. Generally, a cache of DEB packages is stored in the location /var/cache/apt/archives.
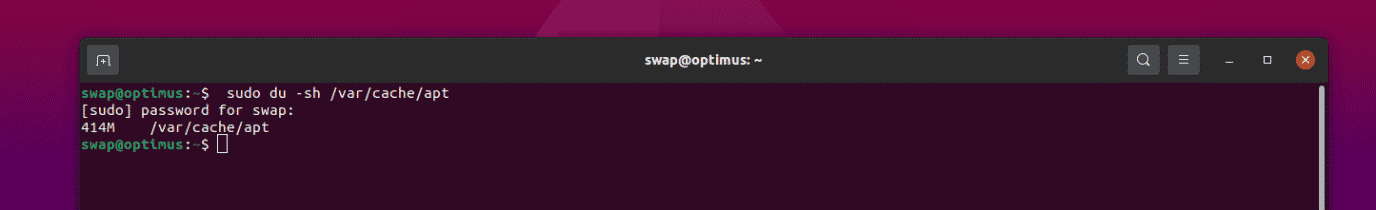
To know the exact size of the cache, run the following command in Terminal.
$ sudo du -sh /var/cache/apt
You will get the following output.
Now you have two options to remove the APT cache, either to remove only outdated packages or remove all of them.
Remove only outdated packages:
$ sudo apt-get autoclean
Remove all packages
$ sudo apt-get clean
Stacer
Stacer is an open-source system optimizer that helps you keep track of your system’s performance. It is a modern tool with a modern user interface which makes it attractive and easy to use.
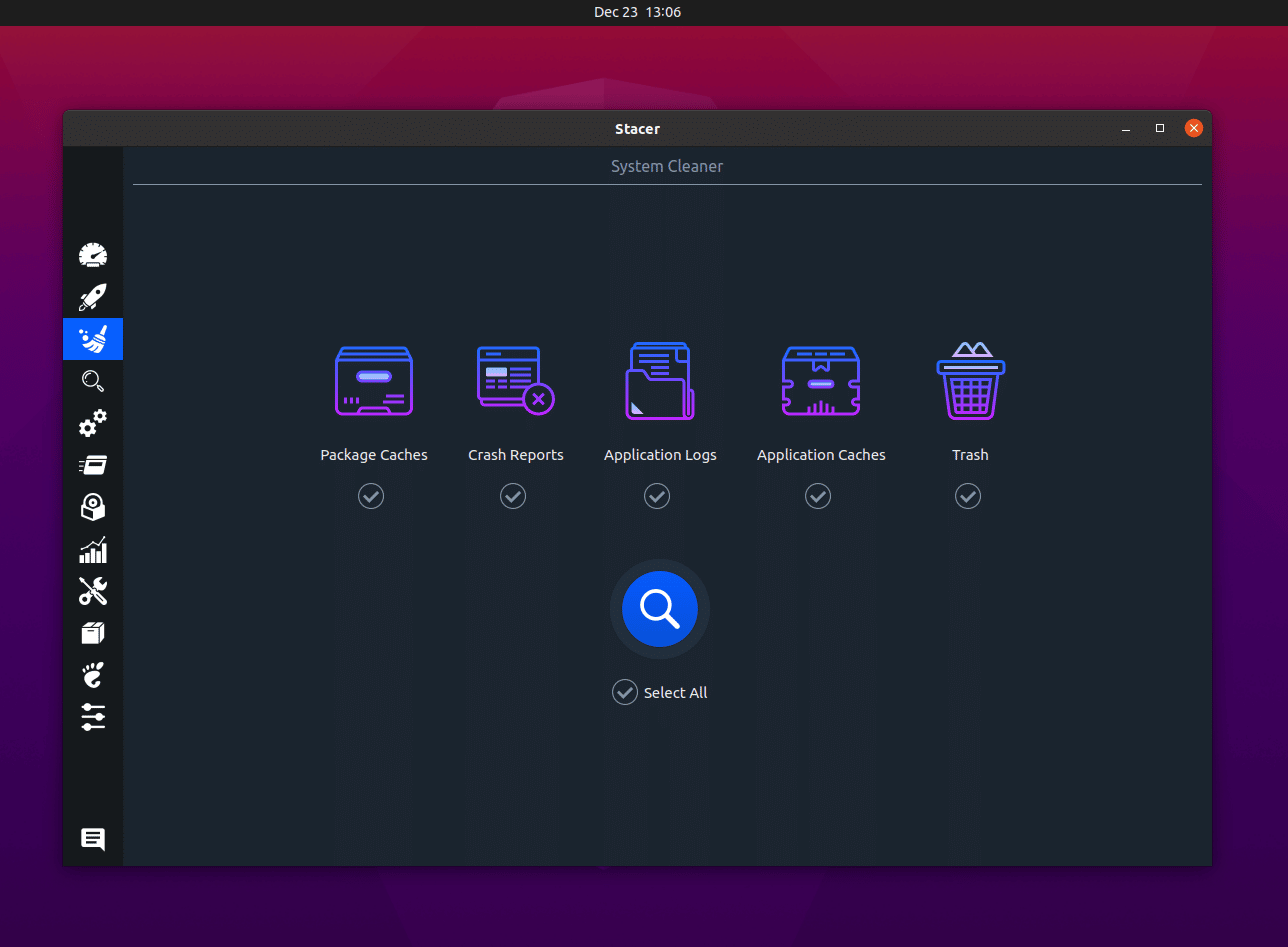
It is a feature-rich tool and you can also clean up disk space using its dedicated feature.
Remove Old Kernels
You can remove old kernels from your system which are no longer required. But you have to do this step with caution because it may damage the system.
Old kernels can leave huge junk of files on the disk and slow down the Ubuntu system. Use the following command to remove the old Kernels from the system.
Before removing the older kernel, you must check the installed Linux kernel versions on your system. To do this run the following command in Terminal.
$ sudo dpkg --list ‘linux-image*’
Now you can remove the older version using the following command.
$ sudo apt-get remove linux-image-version
Or simply you can run the following command to remove old kernels.
$ sudo apt-get autoremove --pruge
Uninstall Unnecessary Applications
Everyone has some applications on their system they hardly use and these applications only there to eat some space on disk which can be used for better purposes.
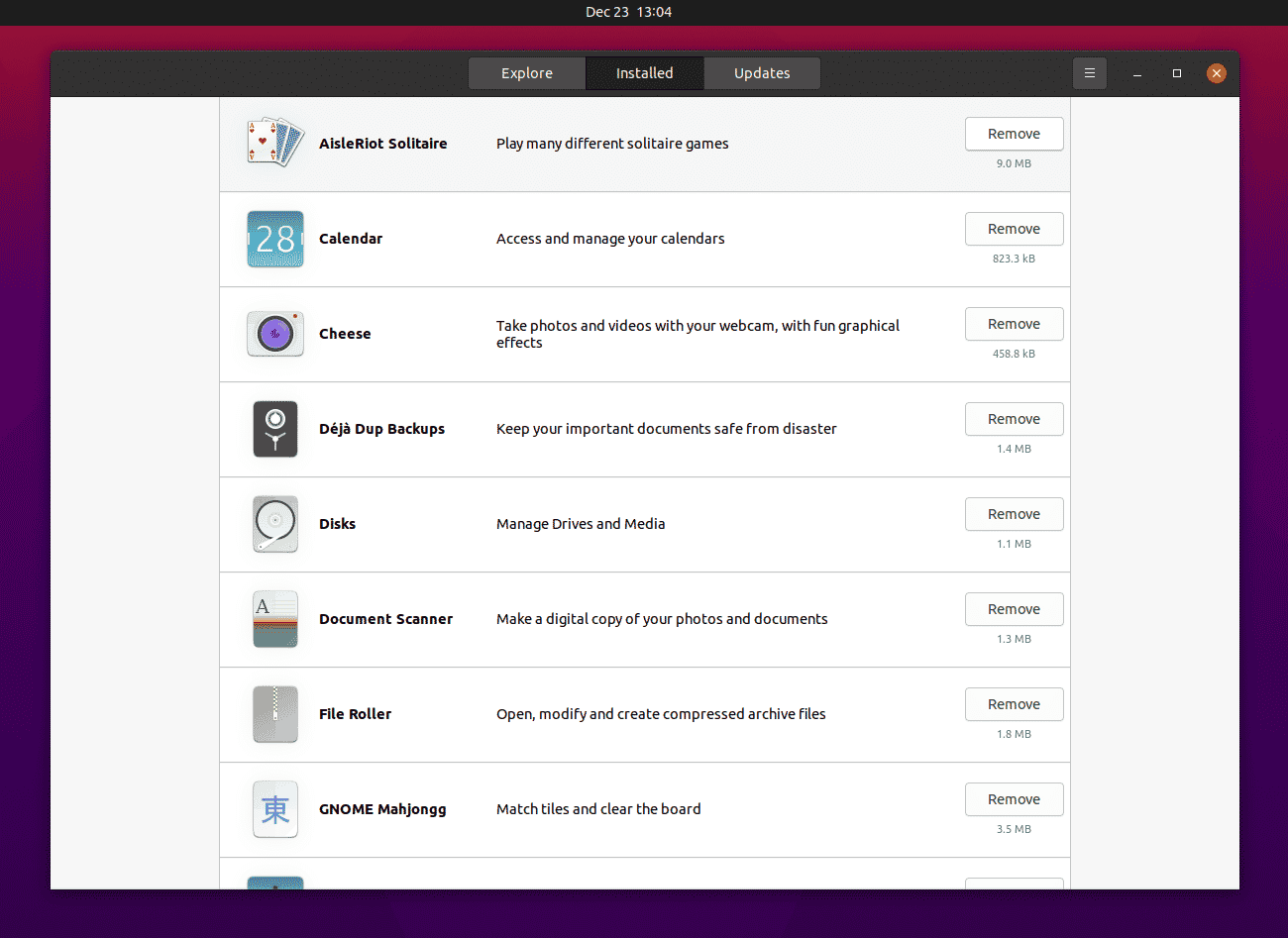
So, head over to Ubuntu Software Centre and then click on Installed. Here you will see the list of apps and games installed on your system. You can uninstall the apps or games you don’t use or need and free up some space on your disk.
Keep System Up to Date
From the smartphone OS to the desktop OS I use, I like to keep them up to date. As soon as updates get released, I update my system. It helps me keep my system smooth and fresh. Not many recommend this but it is worth it. Some updates also bring fixes that stop apps and packages from occupying too much of disk space. So, it is always a good idea to keep your system up to date.
So, these are the best ways to free up some disk space on your Ubuntu system or other Linux distro. There many other ways to do so but these 5 are very reliable. Feel free to share your views with us in the comments below.
Have a Great Day!
A Software Engineer who loves football and passionate about traveling. I often spend my free time playing with gadgets and exploring new possibilities in the tech world. I am a Linux enthusiast and have about 6 years of experience in web development. I have a good command of Python, Java, SQL, and system security.