Monit is a lightweight and effective tool that is used for monitoring system services. Using the Monit web interface, you can easily monitor processes and system resources such as Memory, CPU usage, load average, server uptime, network connections, and different server applications. It is originally used as a single server. However, the commercial version of the Monit server can monitor multiple servers at the same time through just one web interface.
We will talk about the installation of the Monit monitoring server on the Ubuntu 20.04 system through the command line method in this article.
Prerequisites
Users must have sudo privileges or log in as root users on your system for the installation of Monit.
Installation and configuration of Monit on Ubuntu 20.04
The following steps need to perform for the installation and configuration of the Monit monitoring server on your Ubuntu 20.04 system:
Step 1: Install of Monit Monitoring server on Ubuntu 20.04
Open the ‘Terminal’ application on your system by pressing ‘Ctrl+Alt+t’. The Monit application can be directly installed from Ubuntu’s official repository. However, use the following command for the installation of the Monit server:
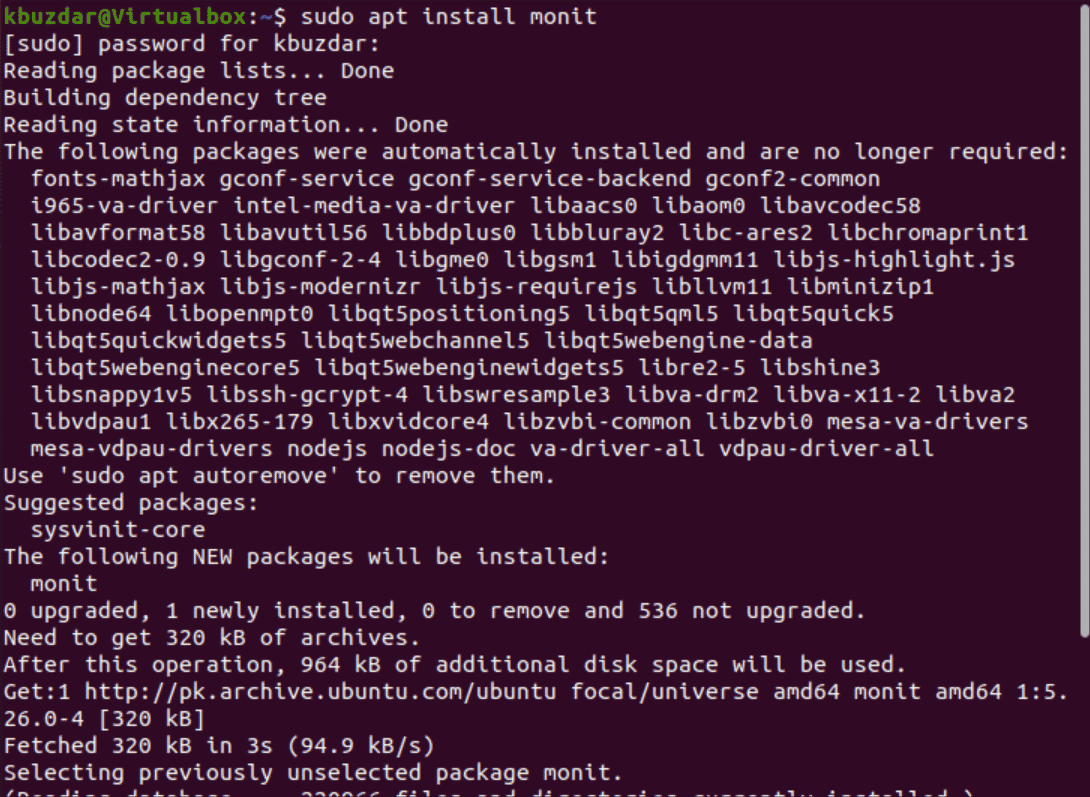
$ sudo apt install monit
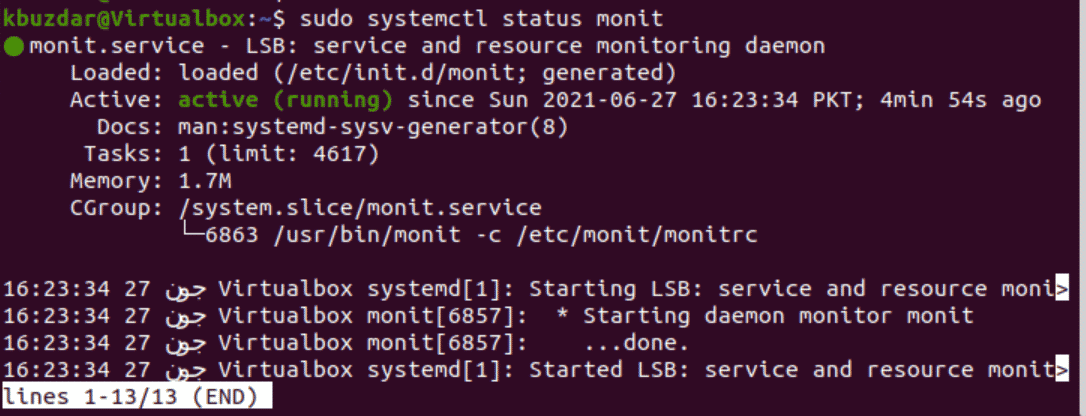
After completing the installation of the Monit server, use the below-given command to check the monit services are running or not :
$ sudo systemctl status monit
Step 2: Monit Server Configurations
The default configuration file of Monit is available at the ‘/etc/monit/monitrc’ location. Monit offers a web interface to monitor the services through the web browser. The monit web interface is not enabled by default. But, it can be enabled by changing few lines in the configuration file by using the below-mentioned command:
$ sudo nano /etc/monit/monitrc
Search the below-mentioned lines in the configuration file and uncomment these lines:
set httpd port 2812 and
allow admin:monit
Here, the admin password is ‘monit’. Save the edited configurations and press ‘Ctrl+x’ to exit from the configuration.
Step 3: Check Syntax errors
In this step, you will check that the configuration file is without any syntax errors by running the following command:
$ sudo monit -t
The following output should print on the terminal window:

Step 4: Enable Monit services
If Monit service is not enabled then, use the following command to enable it automatically on system boot:
$ sudo /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable monit

Now, restart or reload the services of Monit by using the below-given command:
$ sudo systemctl restart monit

$ sudo monit reload

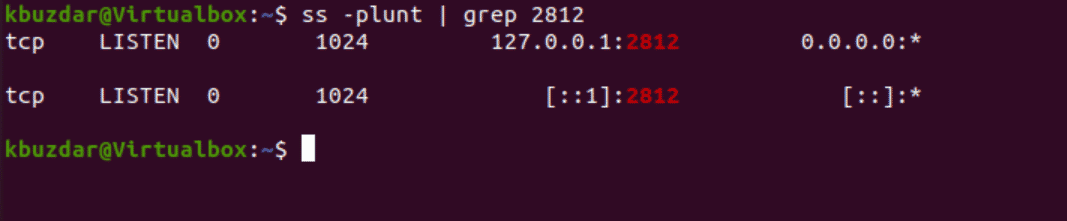
To verify that port 2812 is listening or not, use the below-given command:
$ ss -plunt | grep 2812
Step 5: Check Monit Status
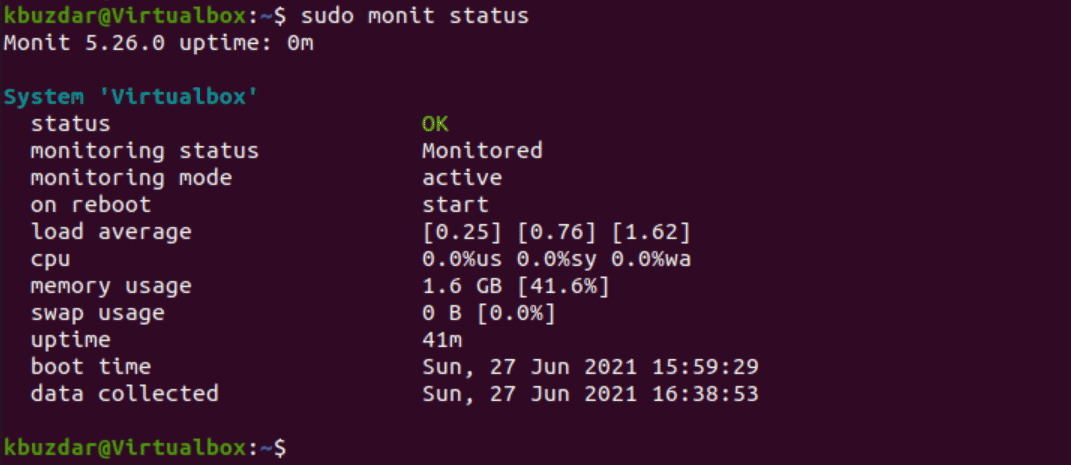
To verify that everything is working good, use the following command:
$ sudo monit status
Step 6: Allow Firewall access to the port
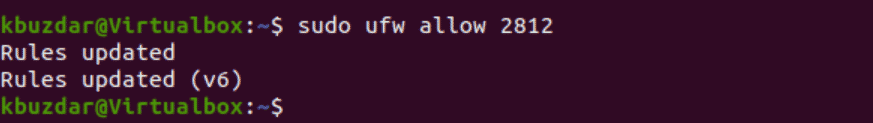
If you want to access the Monit web interface from the outside to your localhost then, use the following command to allow access to public users:
$ sudo ufw allow 2812
Step 7: Access the Monit web interface
Access the web interface of the Monit server through the web browser. Enter the IP address of the server or machine where the Monit is installed as follows:
http://your-server-ip-address:2812
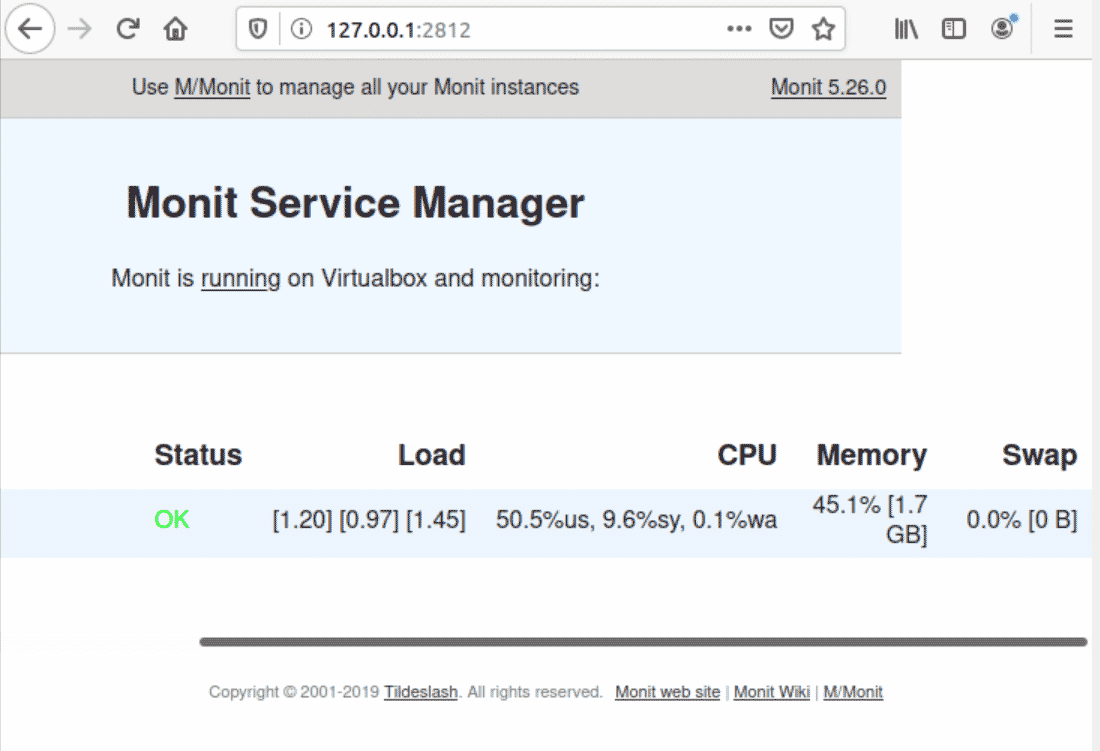
The dialogue box will pop up on your browser. Enter the username and password. After that, the following web interface displays on your system’s browser:
Conclusion
We have installed the Monit monitoring server on the Ubuntu 20.04 system in this article. You can easily monitor your system using this lightweight tool.