Keeping track of your passwords can be quite a tedious task. This is especially true when having numerous accounts each with a unique username and password. A common habit that most users have is to jot down usernames and passwords on a notebook or a sticker. While this might come in handy in case you forget the login credentials, it’s considered a risky practice should another party get a hold of the details.
A better approach to managing passwords is to use a password manager. Bitwarden is an opensource and secure password manager that allows you to not only store usernames and passwords but also other personal information such as credit card details, PIN numbers etc. Bitwarden can be installed on a desktop PC and also on mobile applications.
Bitwarden provides both free and premium plans. All Bitwarden plans provide the following core features.
- Password generator for generating strong and secure passwords for each of your account logins. This helps mitigate bruteforce attacks.
- Two-factor authentication for providing extra security when verifying logins. You can get a One Time Password (OTP) code via email, use an authenticator app such as Google Authenticator, or log in using a YubiKey for the premium version.
- Unlimited devices and syncing.
- Unlimited vault items.
- Password security audits for evaluating the strength of your passwords.
- Zero knowledge encryption.
- A digital wallet that allows users to store records such as Bank account details, credit card/debit card details, and safe combinations.
- Mobile Apps and browser extensions that help users to autofill passwords during login.
In this guide, we will walk you through the installation of Bitwarden on Ubuntu 20.04.
Step 1: Update the system
Let’s start off by updating the package index as follows.
$ sudo apt update
With the package lists up to date, head over to the next step.
Step 2: Install dependencies
Some dependencies are required for the installation of Bitwarden. So, before we proceed any further install them as shown.
$ sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg-agent software-properties-common
With all the essential packages installed, head over to the next step
Step 3: Install Docker and Docker Compose
We are going to deploy Bitwarden from Docker containers with the help of Docker Compose which is a tool that is used for executing multi-container Docker applications.
But first, let’s Add the Docker GPG key. To do this, first switch to root user and execute:
# curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | apt-key add -
Once done, proceed and append the Docker’s repository to your system.
# add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
Then update Ubuntu’s package lists once more.
$ sudo apt update
With the successful update of the package lists, install Docker, Docker compose and other crucial Docker tools as follows.
$ sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose
The command installs all the defined Docker tools, some extra package, libraries and dependencies.
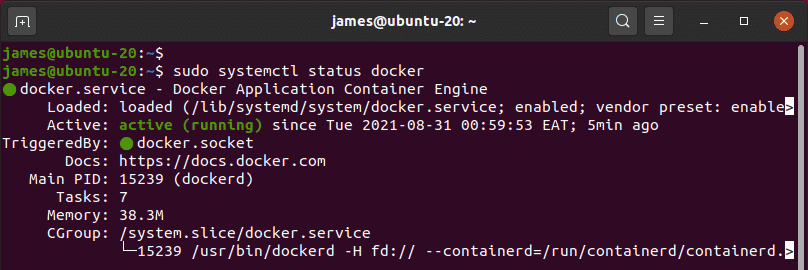
By default, the Docker daemon starts once the installation is complete. You can confirm this as follows.
$ sudo systemctl status docker
You can go a step further and enable Docker to start on boot time:
$ sudo systemctl enable docker
You can confirm the version of Docker installed as shown
$ docker --version
Similarly, you can check Docker Compose version as shown
$ docker-compose --version
Step 4: Obtain Bitwarden’s Installation key and ID
The installation of Bitwarden requires you to provide an installation key and ID. To obtain these crucial details, head over to the Bitwarden page and provide your email address.
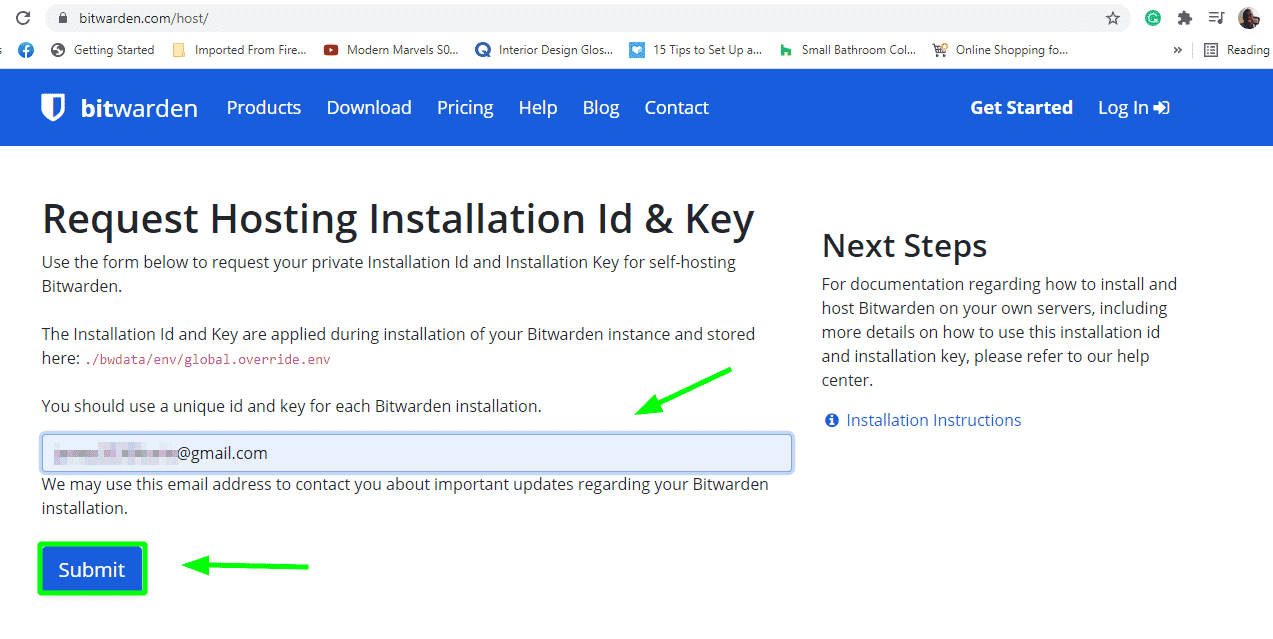
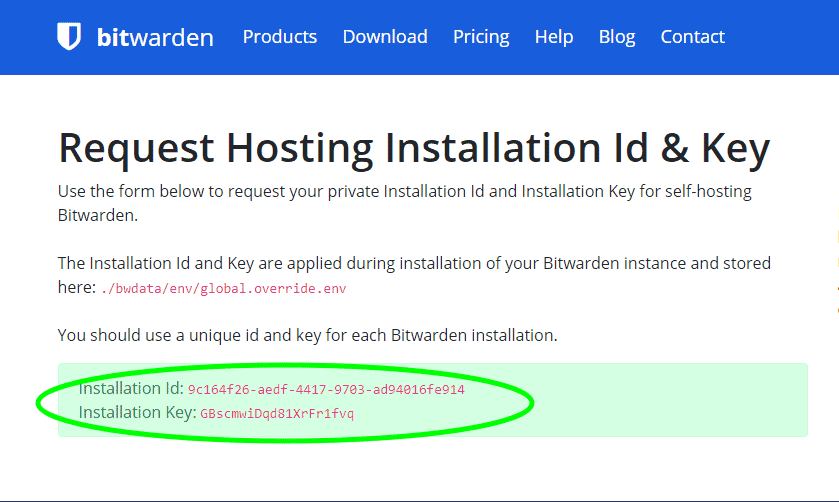
Once you click the ‘Submit’ button, you will get the following page that contains a unique installation Id and key for each installation. Copy the details to a notepad as you will be required to provide them in the next few steps.
Step 5: Install Bitwarden
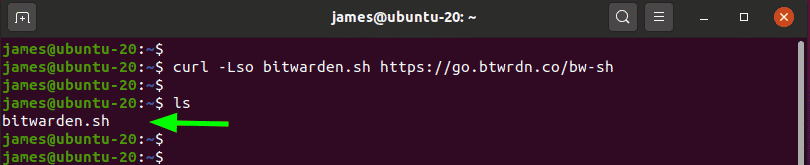
With the installation id and key at hand, download Bitwarden’s installation script using the command shown:
$ curl -Lso bitwarden.sh https://go.btwrdn.co/bw-sh
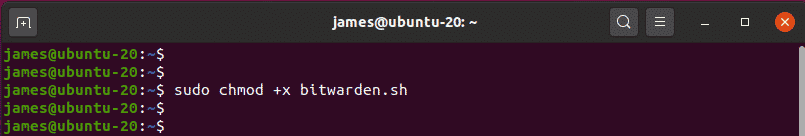
Assign the script execute permissions.
$ sudo chmod +x bitwarden.sh
Then install Bitwarden password manager.
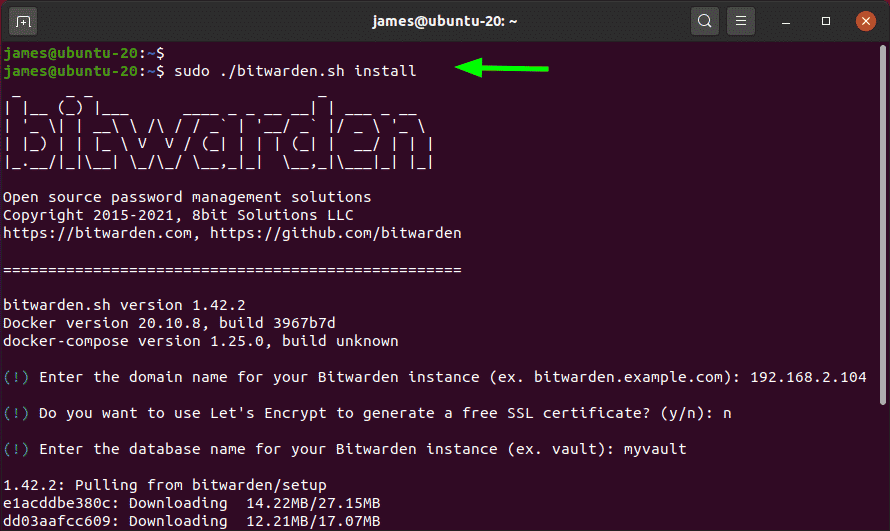
$ sudo ./bitwarden.sh install
You will be taken through a series of prompts. You will be asked to provide a domain name for your system. Provide a fully qualified domain name if you have it for example, example.com. If you do not java a domain name for your server instance, you can simply provide an IP address.
Next, you will be asked if you want to opt for Let’s Encrypt for the generation of a free SSL certificate. If you provided a domain name, then press ‘y’ otherwise, press ‘n’ since Let’s Encrypt requires an FQDN that is pointed or associated with the server. Then provide an arbitrary name for the database.
The script will start pulling Bitwarden setup containers.
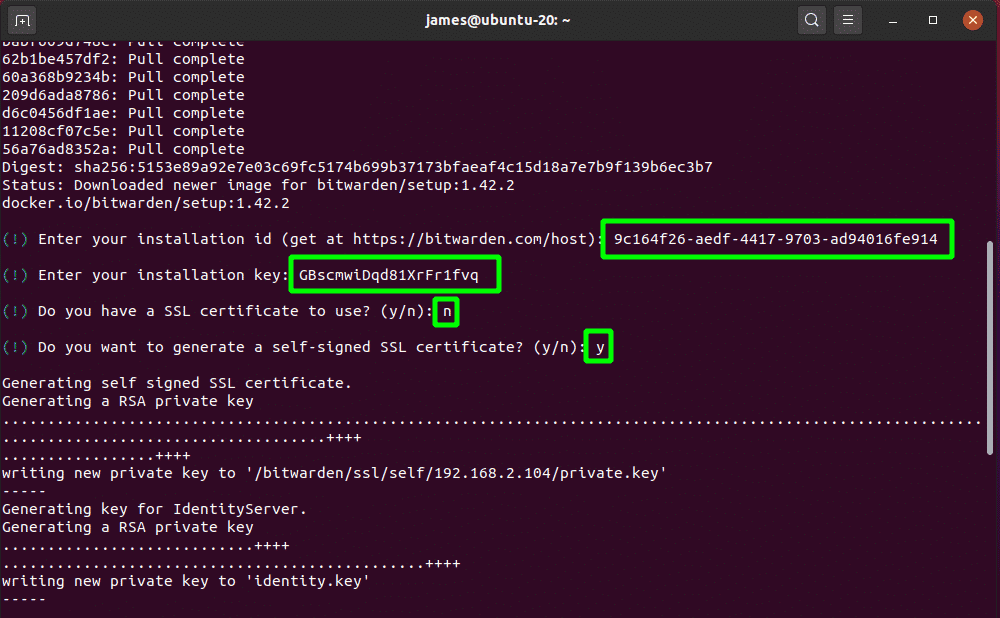
Once all the containers have been pulled, you will be prompted for the Bitwarden Installation Id and key. Remember the details you generated from the Bitwarden site in the previous step? Copy and paste them accordingly.
Since we do not yet have an SSL certificate, we will select ‘n’ and proceed to generate a self-signed certificate by pressing ‘y’.
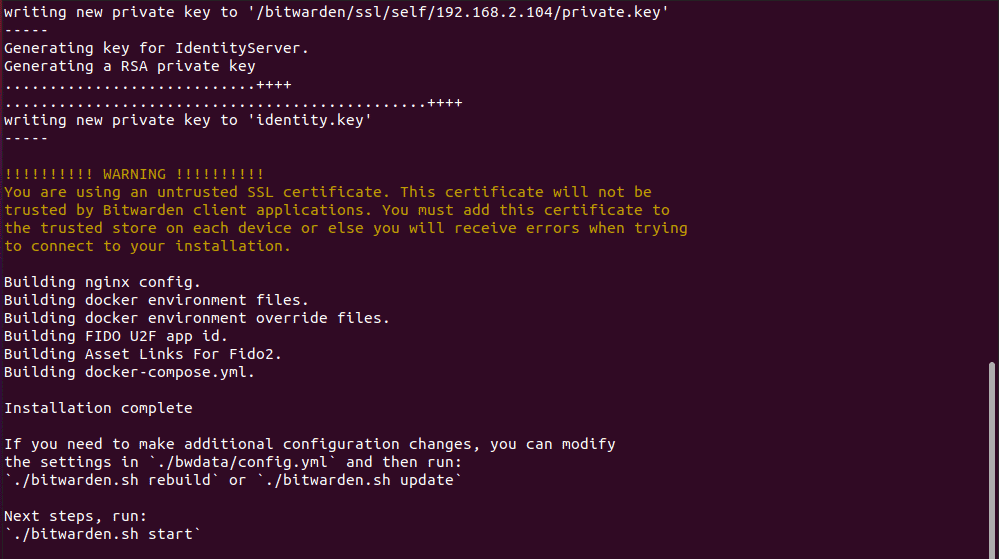
The installation will then continue and complete successfully with additional steps printed at the very end.
Step 6: Running Bitwarden
To start Bitwarden Docker containers, execute the command:
$ sudo ./bitwarden.sh start
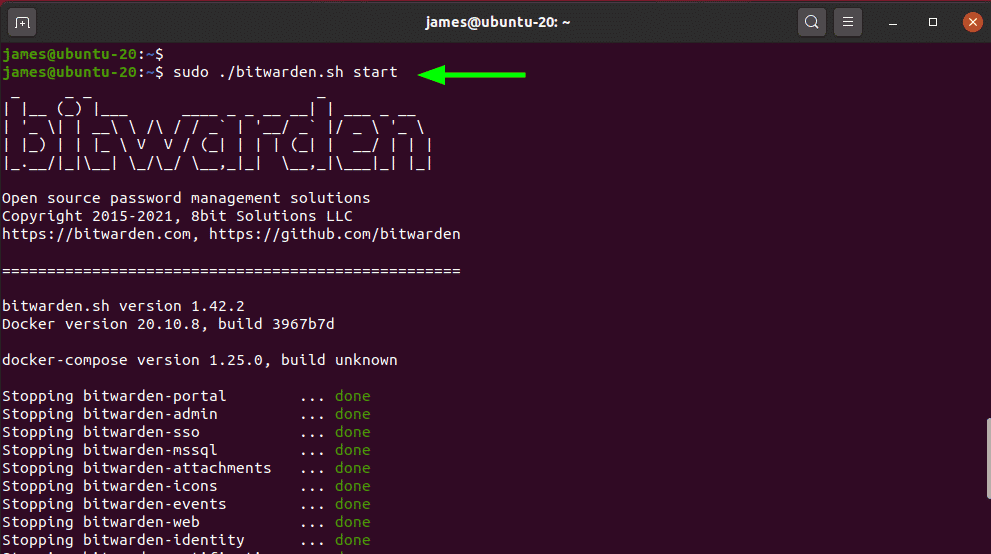
To access the Bitwarden web interface, head over to the URL shown:
https://server-ip/
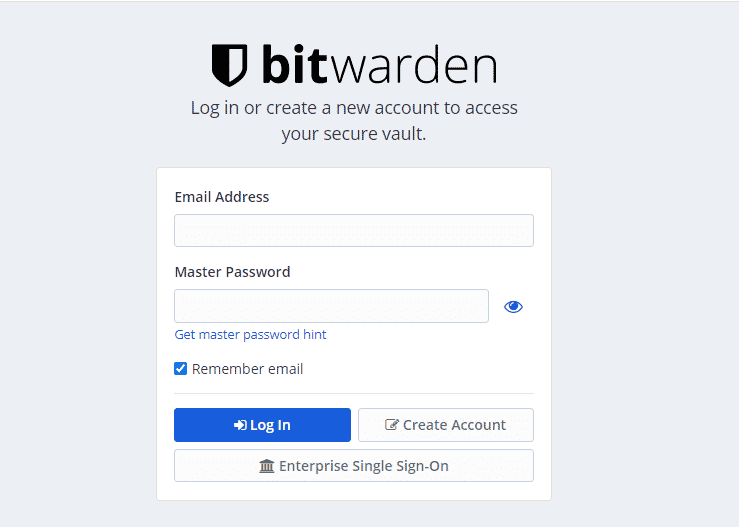
Be sure to create a new account first to begin accessing your vault.
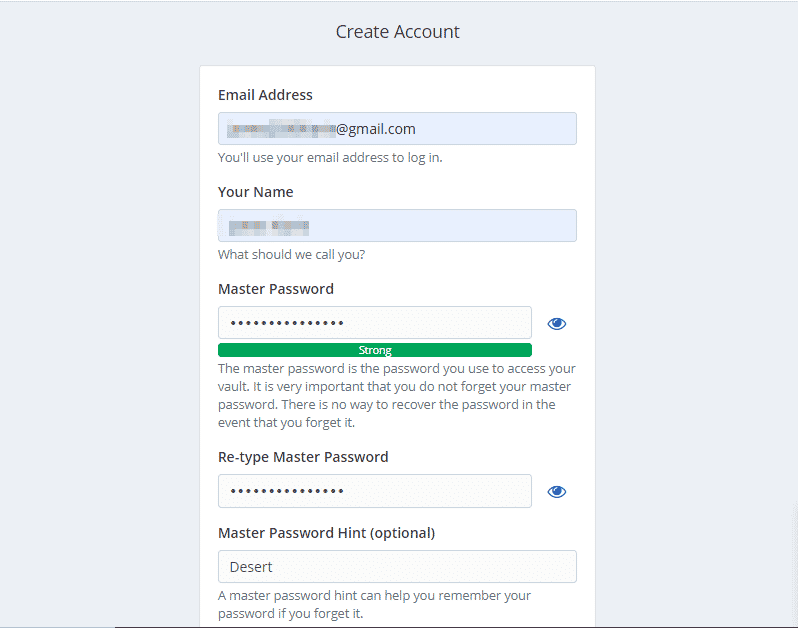
Then finally, log in with your details to access your vault.
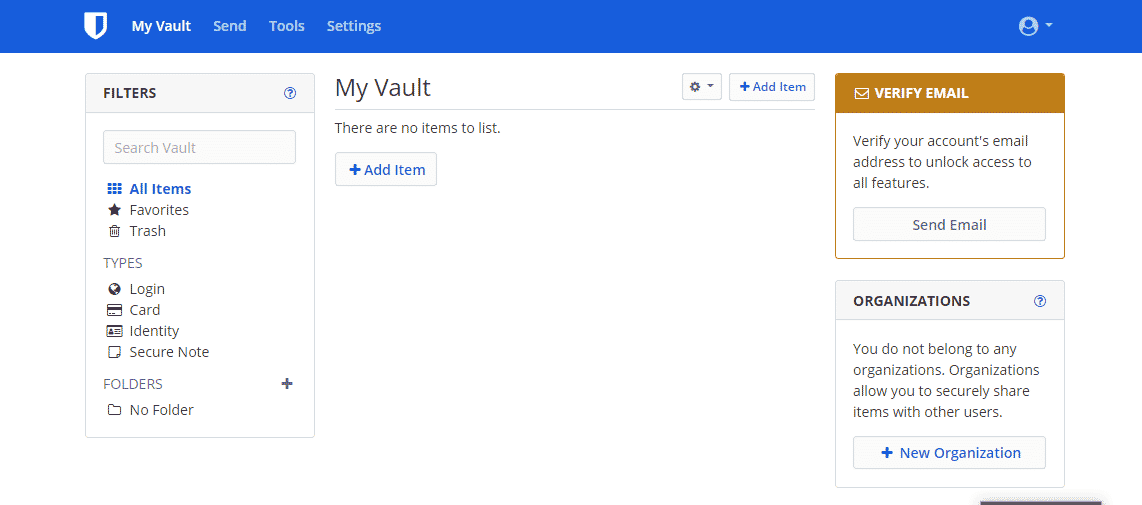
Congratulations! You can now start saving your passwords and other confidential information in your Bitwarden vault.




