MongoDB (known as Mongo) is a document-oriented database management system. It is categorized as a NoSQL database as it is a non-relational database and does not work with the conventional table-based relational database structure. It efficiently works will large-scale data. Some of the well-known companies which use MongoDB are Facebook, Cisco, Forbes, Adobe, Nokia, etc.
This article describes how to install MongoDB on the Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system. You can follow the same procedure on previous Ubuntu releases: Ubuntu 18.04 LTS and 16.04 LTS.
We can install MongoDB on Ubuntu through following two ways:
- Using package manager
- Using archive
Note: You will require sudo access to install the MongoDB on the Ubuntu OS.
Installing MongoDB Using Package Manager
The MongoDB package available in Ubuntu is not managed by MongoDB Inc. Here, we will show you the installation of the official MongoDB package version 4.4. which is managed by MongoDB Inc. Follow the below instructions to install MongoDB using the Ubuntu package manager.
Step 1: Import MongoDB Public Key
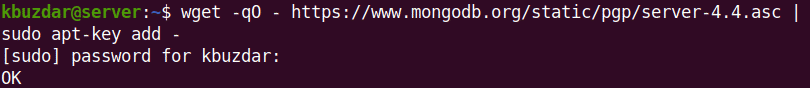
First, you will need to add the MongoDB repository key to your apt keyring. By doing this, your system will trust the added repository. Run this command to add the MongoDB key.
$ wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.4.asc | sudo apt-key add -
If it is added successfully, you will see OK in the output.
Step 2: Add MongoDB Repository
Add MongoDB repository to your system’s list of sources. To do so, edit the sources.list file using the command below:
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
Append the below line in the file:
deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu focal/mongodb-org/4.4 multiverse
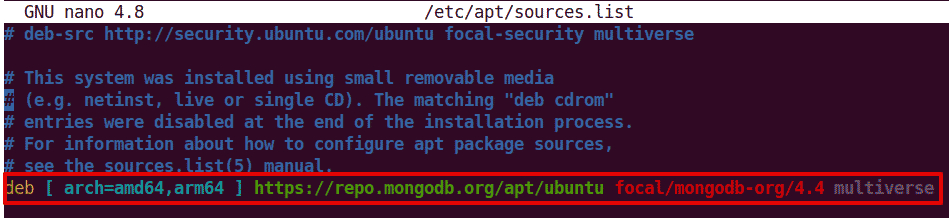
Now save the file and close it.
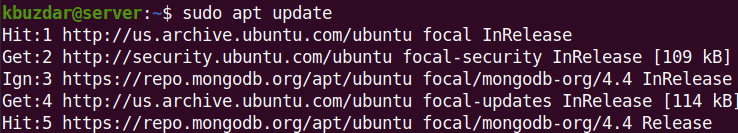
Step 3: Update Repository Index
Now use the below command to update your system’s repository index:
$ sudo apt update
Step 4: Install MongoDB
Now the MongoDB repository has been added to our system’s list of sources, we can install it as follows:
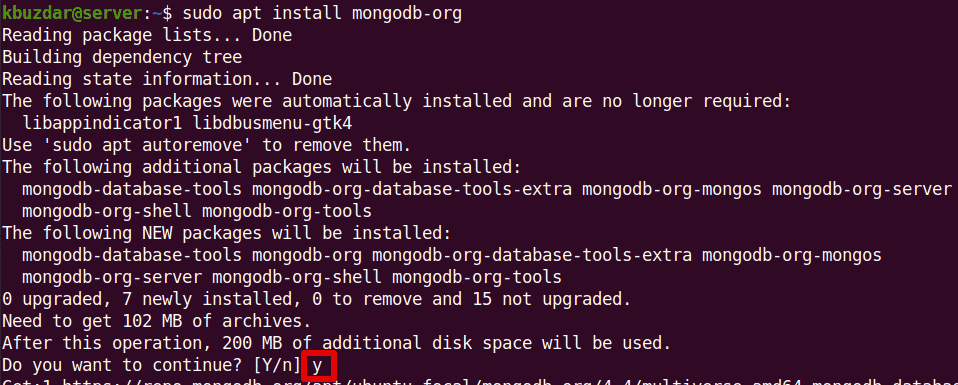
$ sudo apt install mongodb-org
When prompted with the y/n option, press y to continue.
Step 5: Run MongoDB
To run MongoDB, start the mongod service (daemon for MongoDB) using the command below:
$ sudo systemctl start mongod
If the service does not start or you encounter an error like “service not found”, issue the command below:
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
After starting the mongod service, check its status to verify if it is running fine. Use the command below to do so:
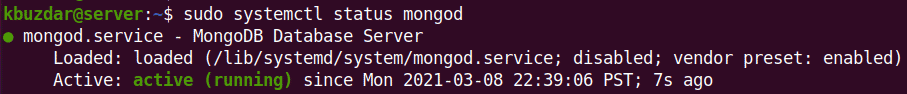
$ sudo systemctl status mongod
If it is running fine, you will see the below output.
To start the MongoDB automatically at each boot, the command is:
$ sudo systemctl enable mongod
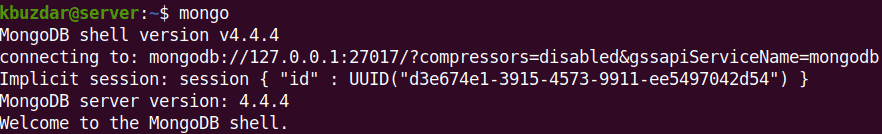
Now to start the mongo shell from the same system running the mongod process, the command is as follows:
$ mongo
Installing MongoDB Using Archive
Although, the recommended way of installing MongoDB on Ubuntu is by using apt package manager as it installs the required dependencies during the installation. However, you can use archive (.tgz tarball) for manually installing it in Ubuntu. Follow the below instructions to install MongoDB using the using official MongoDB archive.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Use the command below to install the dependencies needed for the installation of MongoDB:
$ sudo apt install libcurl4 openssl liblzma5
When prompted with the y/n option, press y to continue.
Step 2: Download MongoDB archive
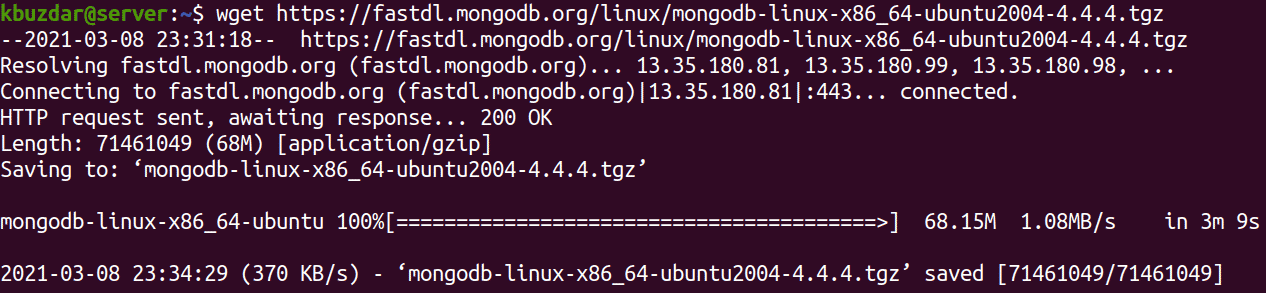
Now you will need to download the MongoDB archive (.tgz tarball). Use the below command to download the current latest version of MongoDB to your system:
$ wget https://fastdl.mongodb.org/linux/mongodb-linux-x86_64-ubuntu2004-4.4.4.tgz
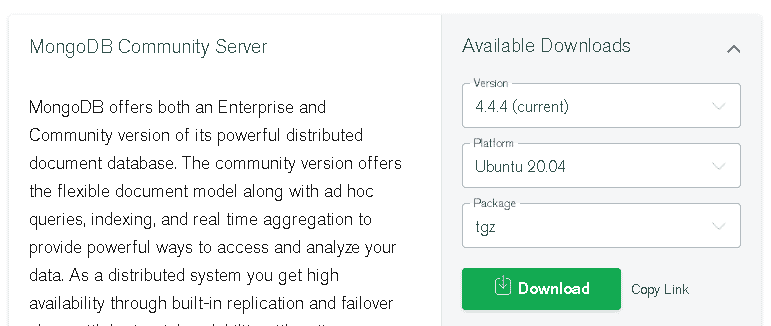
Alternatively, you can also download MongoDB by accessing their official Downloads page. Access the page and choose the MongoDB version you want to download, your OS platform, and the package (tgz). Then click Download to download the package.
Step 3: Extract MongoDB Archive
Extract the MongoDB archive using the command below:
$ tar -xvzf mongodb-linux-x86_64-ubuntu2004-4.4.4.tgz
This extracts the files from the archive as clear in the below screenshot: 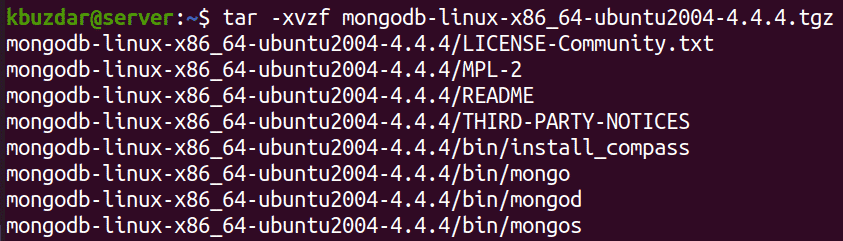
Step 4: Copy Binaries to a Directory in PATH environment Variable
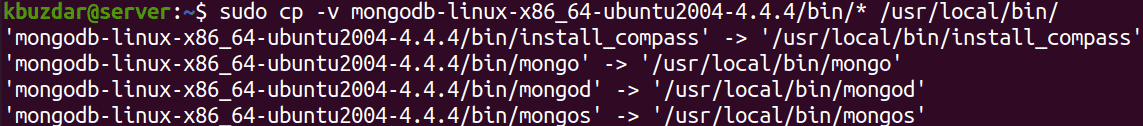
Now copy the binaries located in the linux-x86_64-ubuntu2004-4.4.4/bin to one of the directory in the $PATH like /usr/local/bin.
$ sudo cp -v mongodb-linux-x86_64-ubuntu2004-4.4.4/bin /usr/local/bin/
Step 5: Run MongoDB
To run MongoDB, follow the below steps:
1. Create directories for storing data and logs. Issue the below commands to do so:
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/mongo $ sudo mkdir -p /var/log/mongodb
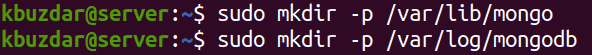
2. Use the below command to assign your user account read/write permissions to the MongoDB data directory:
$ sudo chown `whoami` /var/lib/mongo
Then assign permission to log directory:
$ sudo chown `whoami` /var/log/mongodb

3. Run the mongod process (daemon for MongoDB) using the command below:
$ mongod --dbpath /var/lib/mongo --logpath /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log --fork

4. Now to start the mongo shell from the same system running the mongod process, the command is as follows:
$ mongo
Uninstall MongoDB
If you no longer need MongoDB, you can completely uninstall it from your Ubuntu system. To do so, first stop the mongod process:
$ sudo service mongod stop
To remove MongoDB that you have installed using package manager, the command is as follows:
$ sudo apt purge mongodb-org
If you want to remove the logs and data directories too, use the commands below:
$ sudo rm -r /var/lib/mongodb $ sudo rm -r /var/log/mongodb
If you have installed MongoDB through the archive, you can uninstall it by removing the MongoDB binaries from /usr/local/bin.
This is how you can install MongoDB on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS using either the apt package manager or by downloading and installing through the archive. For more information, visit MongoDB’s official documentation.