Graylog is the open-source centralized log management solution that enables real-time analysis, search, and monitoring of large amounts of machine data. It was developed in Hamburg, Germany with the purpose to deliver a more robust and easier-to-use analysis platform, faster analysis speeds, easy administration and infrastructure management.
In this article, we will learn the way to install and configure Graylog in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
Prerequisites
Before continue to install the Graylog you must set up the following things,
- Oracle Java SE 8 (OpenJDK 8) as the Elasticsearch is a java based project.
- Elasticsearch 6.8, and version 7 up to 7.10 as version later is not supported by Graylog.
- MongoDB (4.0, 4.2 or 4.4).
Installing Graylog
Let’s begin with installing as java 8 is required to run Elasticsearch. We will need some additional packages also let’s install them along with it.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jre-headless pwgen apt-transport-https uuid-runtime
After installing the java you can verify the installation by using the following command.
$ java -version
Now, Let’s install Elasticsearch. First, we need to add a package repository to our system package repository list using the following command.
$ wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
$ echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/oss-7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list
Then, install the Elasticsearch using the apt command.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install elasticsearch-oss
Once Elasticsearch installation is complete, update the following line in the configuration file.
$ sudo vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: graylog
action.auto_create_index: false
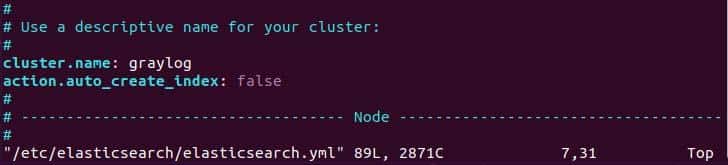
Now, enable and restart the service to apply the modification.
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
$ sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
Next, Let’s install a database for Graylog, Graylog uses MongoDB as the database to store data. First, we need to register a public GPG key for the repository using the following command.
$ sudo apt install gnupg
$ wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.4.asc | sudo apt-key add -
Now download and add package repository to the system package repository list. To do so run,
$ echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu focal/mongodb-org/4.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.4.list
Finally, install MongoDB using the apt command.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install -y mongodb-org
And, to install a specific version of the MongoDB run along with prefer version,
$ sudo apt install -y mongodb-org-mongos=4.4.6 mongodb-org=4.4.6 mongodb-org-tools=4.4.6 mongodb-org-shell=4.4.6 mongodb-org-server=4.4.6
Now, enable and restart the MongoDB using the systemctl command,
$ sudo systemctl enable mongod
$ sudo systemctl restart mongod
Note: During run time if you get ‘mongod.service: Main process exited, code=exited, status=14/n/a’ execute the following command.
$ sudo chown -R mongodb:mongodb /var/lib/mongodb
$ sudo chown mongodb:mongodb /tmp/mongodb-27017.sock
$ sudo systemctl restart mongod
Lastly, installing the Graylog server after all prerequisite packages are installed. To install Graylog first download the deb package then parse it using the dpkg command and finally, install it.
$ wget https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-4.1-repository_latest.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i graylog-4.1-repository_latest.deb
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt -y install graylog-server
Now, enabling the Graylog using systemctl command,
$ sudo systemctl enable graylog-server.service
Configuring Graylog
We have installed every package that is required to run Graylog but it is not ready to run. Before we start using Graylog we need to configure the password_secret and root_password_sh2. The default path for the config file is /etc/graylog/server/server.conf and we will use the sed command to infuse the password generated by pwgen.
For password_secret we will use the pwgen command to generate a random 128 character password. To install it run,
$ sudo apt install pwgen
Now, we will generate a password using the following command and inject it using the sed command. To do so run,
$ sudo -E sed -i -e "s/password_secret =.*/password_secret = $(pwgen -s 128 1)/" /etc/graylog/server/server.conf
Next, let’s generate the SHA 256 hash password for the root_password using the following command. Don’t forget to replace the your_password with the actual password.
$ sudo sed -i -e "s/root_password_sha2 =.*/root_password_sha2 = $(echo -n 'your_password' | shasum -a 256 | cut -d' ' -f1)/" /etc/graylog/server/server.conf
Lastly, configuring a domain for the Graylog using your preferred editor.
$ sudo vim /etc/graylog/server/server.conf
Then, find and set the value of the variable in the configuration in the following way.
http_bind_address = your_server_ip:9000 http_external_uri= http://your_server_ip or domain:9000/
Then, write and quit the file.
Once everything is set, restart the graylog-server using the systemctl command to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart graylog-server.service
Testing the Graylog server
Now, everything is ready to use. When you visit your configured http_external_url you can see the web interface like below.
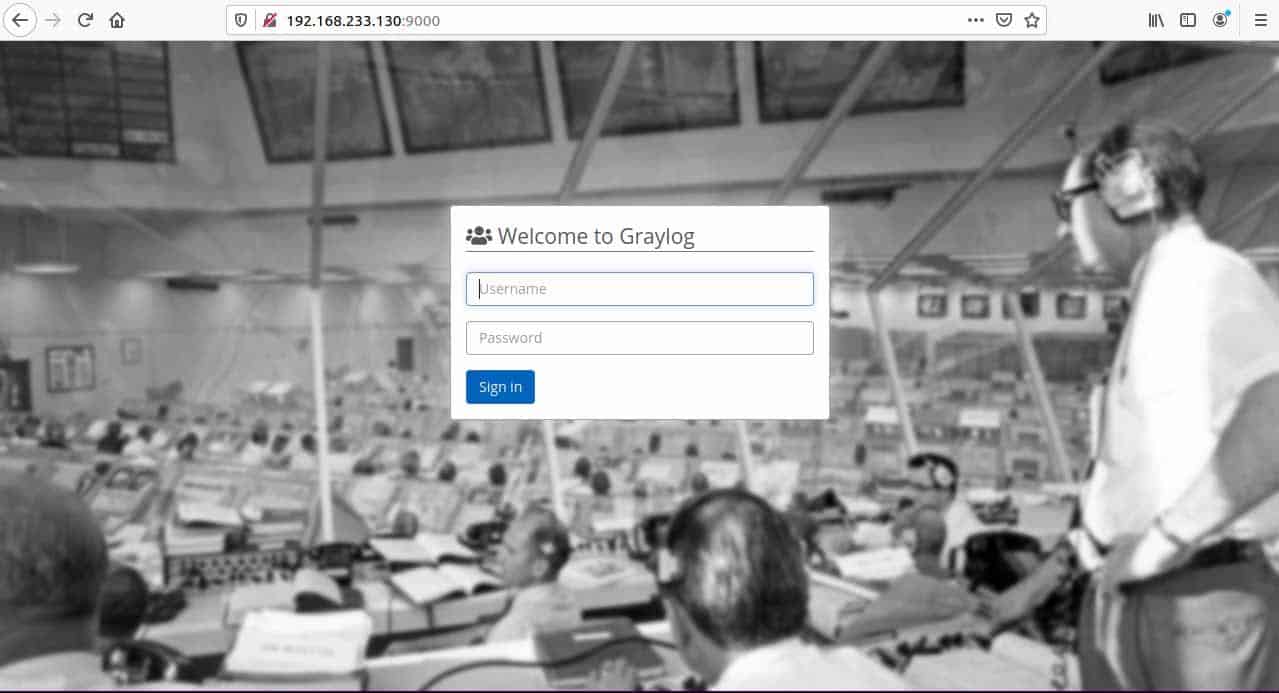
Then, authenticate using the admin username and for password use the plain text password that you used during hashing.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading till the end even if you are a newcomer or professional. I hope you have a clear mindset to configure and install Graylog in ubuntu. Now you can work with the log using the Graylog server.