For the virtualization of the x86 computing architecture, there is an open-source software known as VirtualBox. It creates a virtual machine on which the clients or users can virtually run several operating systems. A virtual machine’s configuration options include how many CPU cores, RAM, and disc space should be allocated to the VM. A few methods for installing VirtualBox in Ubuntu 22.04 will be covered in this tutorial.
How can we Install VirtualBox in Ubuntu 22.04?
For installing and using a different OS within a virtual machine, virtualization software such as VirtualBox can be used. For instance, we can install Linux inside of Windows using VirtualBox. In a similar vein, VirtualBox enables us to install the Windows operating system on top of Linux. Have a look at several methods for installing VirtualBox on Ubuntu.
Method # 1: Installing using the Ubuntu repository
Searching for and installing VirtualBox via the Software Center is the simplest way to do it on Ubuntu. The advantage of utilizing this approach to install VirtualBox is that it makes the process incredibly simple and quick. However, this approach has a drawback. The software that we get using this method will be quite outdated.
You can find the “Ubuntu Software” app on the left taskbar on the desktop.
If you can’t locate it there, try looking for it from the application menu.
When you write “software” in the search bar, the app will appear, and you can open it by clicking on it.

After opening the app, you have to write the name of the software, i.e., “VirtualBox” in the search bar so the software will appear to install.
Clicking the software will take you to the installation page from where you can install the software just by clicking the install button.
You can also perform the installation procedure using the command line. After opening the terminal, you will write the following script to do so.
First, update the system’s package repository by running the following command before installing VirtualBox using the APT package repository.
![]()
After writing the script, we will execute it by pressing the enter key. Use the command shown below to install VirtualBox after upgrading the system’s APT cache repository.
![]()
You will be asked for permission to use the disc space after running this to install VirtualBox.
![]()
To proceed, type “Y/y” and then, from your keyboard, press the enter key. This will install the VirtualBox software on your system. However, you’ll realize that the VirtualBox offered by Ubuntu’s repository is outdated if you check the version before or after installing it. For instance, the Software Center version of VirtualBox is 5.2, although the latest version that VirtualBox offers is 6.1. This implies that you won’t receive the more recent features added to the most recent version of VirtualBox.
After VirtualBox has been installed, the extension package can also be installed if you require features like USB device compatibility, webcam connectivity, remote control of a virtual machine, and more. To install the required extension package, run the following command.
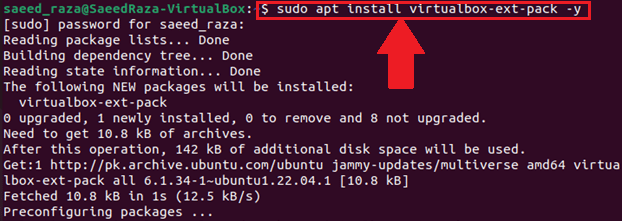
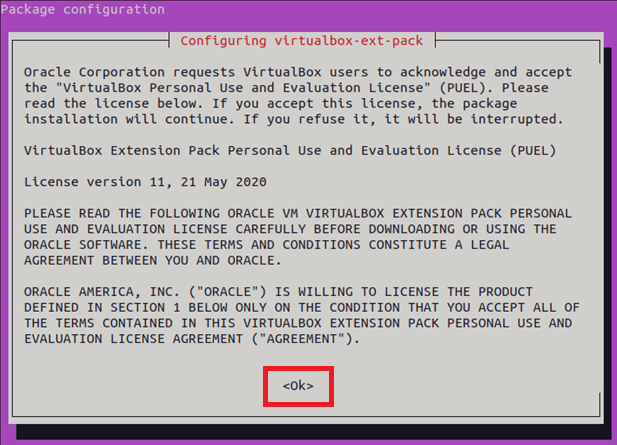
A license, which contains the terms and conditions of the software/product, will pop up on the screen. Read the license and click “Ok” on the package configuration window.
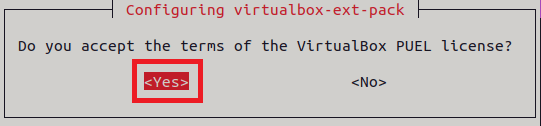
Then it will ask you “do you accept the terms of license”, press enter by selecting “yes” to proceed with the installation.
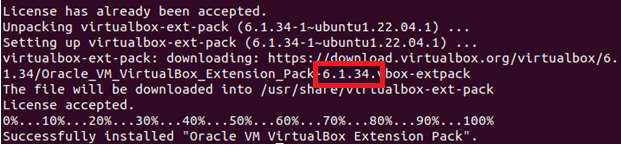
Your Ubuntu 22.04 LTS system should now have the most recent stable version of VirtualBox, i.e., 6.1.34. After installing the extension pack, launch VirtualBox by typing “VirtualBox” into the “Applications” menu and selecting the VirtualBox icon by clicking.
Now VirtualBox’s latest version has been installed on your system and can be used by clicking the icon.
Method # 2: Installing From the Oracle’s Website via the GUI Method
The simplest method is to install by using the deb file if you want to install the most recent VirtualBox version on Ubuntu. You can use any web browser to navigate the VirtualBox website and select the link for the most recent Ubuntu release.
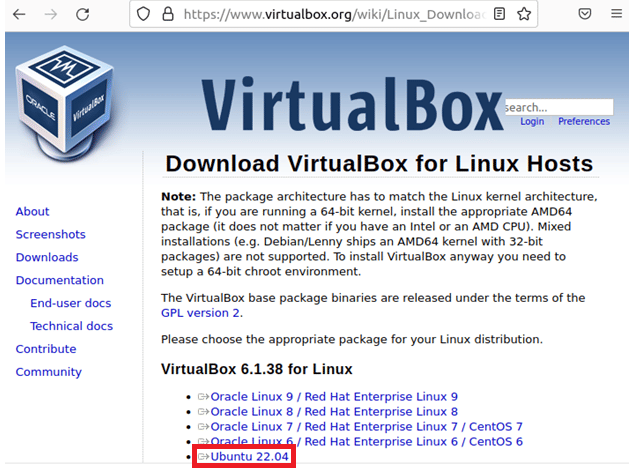
You can select the current version for your Linux OS to start the downloading process.
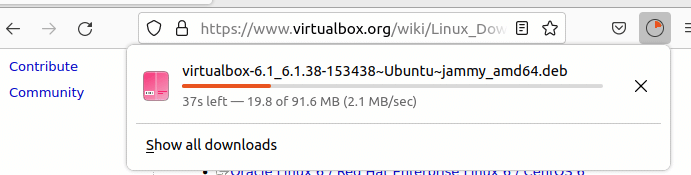
It will save the .deb file on your system. The file will by default be saved inside the download folder.
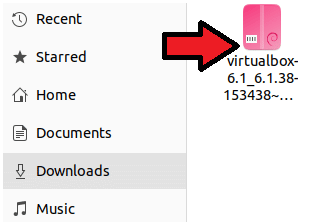
To launch the file, double-click it. Then click the install button in the installer window of the software to start installing VirtualBox. For the installation to proceed, you will need to enter your password.
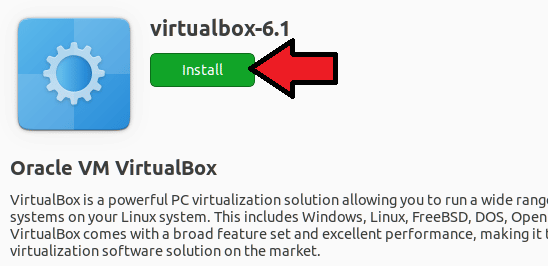
Your Ubuntu machine will have VirtualBox installed once the installation is done. It can be opened by searching for it in the application menu.

Method # 3: Installing Using the Oracle’s Repository
As opposed to the methods above, this approach has a few advantages, You’ll get the most recent VirtualBox version, which will be updated with new releases (automatically).
First, you have to import Oracle VirtualBox’s repository to your repository’s list to install VirtualBox by using the command line. To make the system trust this repository, you will then add its GPG key. Instead of Ubuntu’s repository, VirtualBox will now be installed from Oracle’s repository. If a new version is published, both the system updates and the VirtualBox installed on our system will be updated.
We will download and import the GPG repository keys by using the command below.
![]()
Use the following command to now import the Oracle repository into the list of repositories.
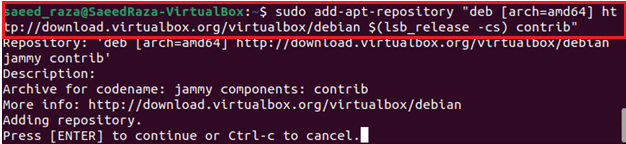
After executing the command, press the enter button to add the repository.
Now that the required repository has been imported, we can now install the required VirtualBox version. It might be wise to write “sudo apt install virtualbox-“. Then, hit the tab button to view the different VirtualBox versions that are available for installation, and then fully type the name of the version you want to install.
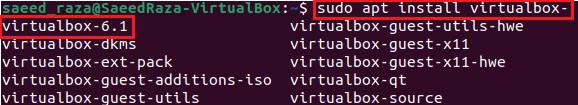
As you can see, the latest available version is 6.1, so we can write the same command along with the version and then press enter to start the installation.
![]()
Conclusion:
This article explains what VirtualBox is and how to install it on Ubuntu 22.04. We discussed three methods for installing VirtualBox on Ubuntu. One of these approaches makes use of the simple-to-install APT package repository (Ubuntu’s repository). The second approach makes use of a GUI-based DEB Binary package. The third method makes use of the Oracle repository; when a new version of VirtualBox is published, the version that was will be updated automatically.



