There comes a time for Linux users when they need to run some of their favorite Windows applications on their system. However, all applications are not compatible to run in the Linux environment. For this reason, Linux created the Wine compatibility layer which allows you to run actual Windows versions of applications on the Linux system. This post demonstrates how to install Wine on Debian OS.
Note: We have tested the commands and procedure explained in this post on a Debian 10 (Buster) system.
Installing Wine on Debian
We will install Wine through the WineHQ repository as it provides the latest version of Wine. Here are the installation steps that you need to follow in order to install Wine on your Debian system.
Step 1: Enable 32 bit Support
Enable support for 32-bit packages in your system. Run the following command to do so:
$ sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
Step 2: Install Dependency
To install Wine on Debian 10, you will need to first install both the i386 and amd64 “libfaudio” dependency package. The “libfaudio0” is not included in the WineHQ repository. Therefore, you will need to manually install it as follows:
Download the i386 and amd64 “libfaudio0” packages using the following commands in Terminal:
$ wget https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/Emulators:/Wine:/Debian/Debian_10/amd64/libfaudio0_20.01-0~buster_amd64.deb
$ wget https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/Emulators:/Wine:/Debian/Debian_10/i386/libfaudio0_20.01-0~buster_i386.deb
Then to install both the packages; run the following command in Terminal:
$ sudo apt install ./libfaudio0_20.01-0~buster_amd64.deb
$ sudo apt install ./libfaudio0_20.01-0~buster_i386.deb
Step 3: Download and Install the Repository Key
Now you will have to add the WineHQ repository signing key. Run the following command in Terminal to download the signing key for WineHQ repository:
$ wget -nc https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key
Then install the key using the following command:
$ sudo apt-key add winehq.key
Step 4: Add WineHQ Repository
Now add WineHQ repository to your apt sources. There are two methods you can add the WineHQ repository to your system which are as follows.
The first method is to add the WineHQ repository in the sources.list file. Edit the /etc/apt/sources.list file
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
Then add the following lines in it:
deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/debian/ buster main
The alternative method is to add the repository using the apt-add-repository command as follows:
$ sudo apt-add-repository 'deb http://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/debian/ buster main'
You can use any of these methods.
Step 5: Update apt
Now update apt sources list to include the newly added WineHQ repository:
$ sudo apt update
Step 6: Installing Wine
Now that the repository and the its key has been added, you can install Wine on your system. Following is the command to install Wine on your system:
$ sudo apt-get install --install-recommends winehq-stable

It may take some time as it is also going to install a few additional packages.
Step 7: Verify Installation
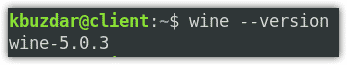
You can verify if the Wine is installed successfully by running the following command in Terminal:
$ wine --version
This command also shows you the installed version of Wine which you can see is 5.0.3.
Uninstalling Wine
There may come a time when you no longer need a specific piece of software on your system. If this is the case, you can completely uninstall it from your system.
In order to completely remove Wine along with all its configuration files from your system, run the following command:
$ sudo apt purge winehq-stable
Now if you also want to remove the packages that were automatically installed with the Wine, run the following command:
$ sudo apt autoremove
In this post, we have demonstrated the step by step process to install Wine on Debian via WineHQ repository. In the end, we have also mentioned how to uninstall Wine, in case you no longer need it on your system. For official documentation, you can visit Wine for Debian.
If you are working on Linux Mint OS, visit our post on How to Install Wine on Linux Mint 20.