NTP (stands for network time protocol) is used to synchronize the system clock of the client system with the clock of the server. It helps the network applications to have an accurate time. In this article, we will explain how to configure the NTP server and sync a clock of NTP client machine. We will be using the Ubuntu 20.04 LTS for running the commands and explaining the procedure.
Prerequisites
- Two Ubuntu machines (For NTP host and NTP client)
- Sudo user on both Ubuntu machines
Configure NTP server
In order to install and configure the NTP server on the host machine, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Installing NTP on host server
In order to install the NTP server, first update the local repositories on the system. Open the command-line Terminal in the host system and issue the following command in it:
$ sudo apt update
Then provide sudo password.
Now install NTP on the host system. Type the following command in Terminal and press Enter:
$ sudo apt install ntp
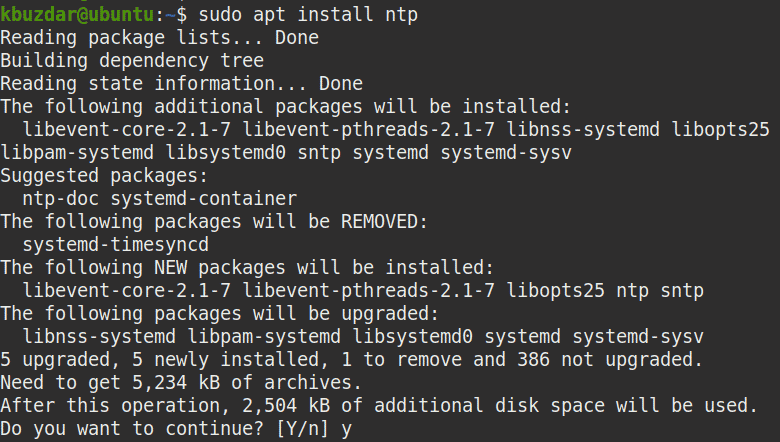
When asked for confirmation, press y, after which the system will start the installation of NTP.
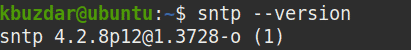
Once completed, you can verify the installation from the following command:
$ sntp --version
Step 2: Configure NTP server
By default, NTP is configured to pull the time from internet servers. However, you can manually configure it to pull time from the nearest pools based on your geographical location.
Edit NTP configuration file as follows:
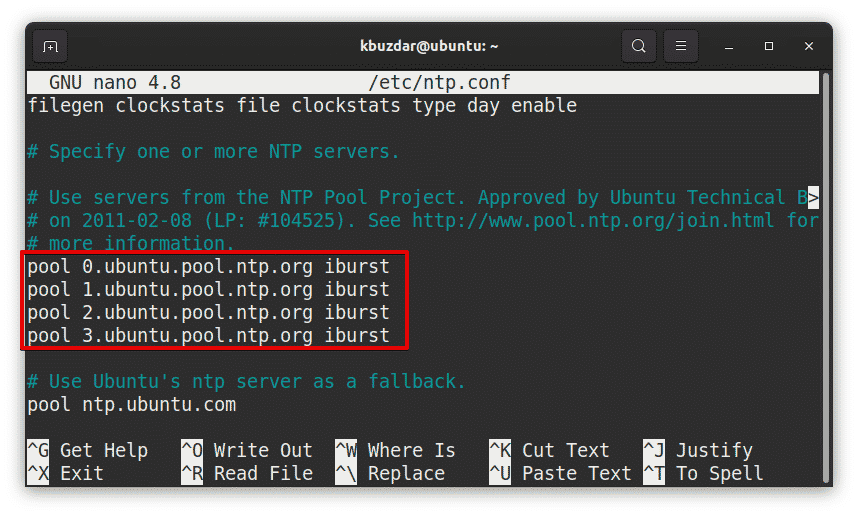
$ sudo nano /etc/ntp.conf
In the configuration file, you will see a list of pools that NTP by default uses.
To add the pools nearest to your location, visit support.ntp.org website, and select your location.
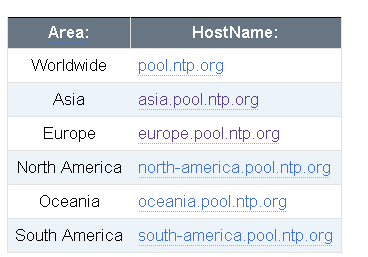
For instance, if you select Europe, you will see a list of pools as shown in the below screenshot.
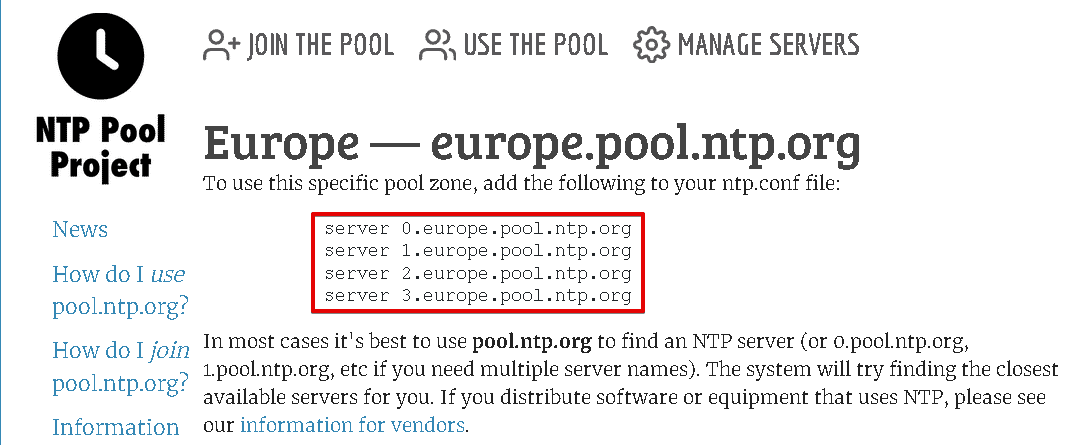
In the configuration file, remove the default list of pools and insert the list of pools that you have copied from the support.ntp.org website. In our system, we have added the pools for the Europe region.
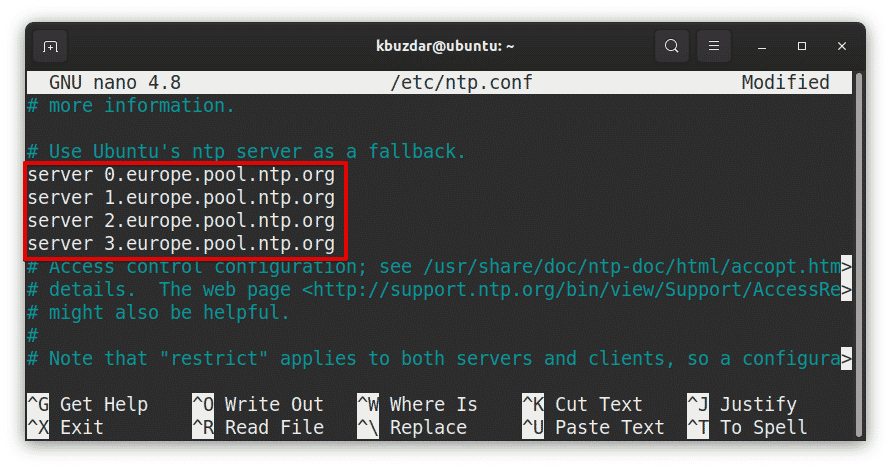
Once you are done, press Ctrl+x. Now you will be prompted if you want to save the changes, hit y.
Step 3: Restart NTP service
After making the changes to the /etc/ntp.conf file, restart the NTP service using the following command:
$ sudo service ntp restart
Step 4: Allow NTP in firewall
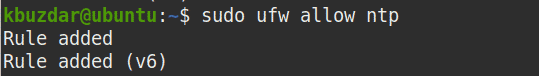
If a firewall is running on the NTP host, you will need to add a rule that allows NTP through it. Issue the following command in Terminal to add a rule to the firewall:
$ sudo ufw allow ntp
To verify if the rule has been added successfully, type the following command in Terminal and press Enter:
$ sudo ufw status
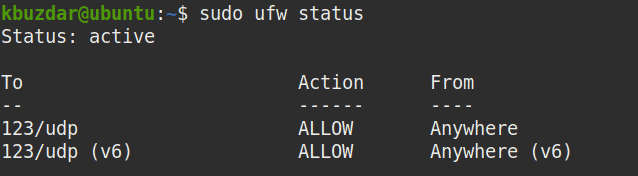
Now the NTP server has been configured on the host machine. Now let’s move towards NTP client configuration.
Sync the clock of NTP client machine with NTP server
Now we will configure the NTP client machine to sync the clock with the NTP server.
Step 1: Install ntpdate on the client machine
Ntpdate command is used for one-time sync to the NTP server. Open the Terminal in the client machine and issue the following command to install ntpdate:
$ sudo apt install ntpdate
Then enter sudo password.
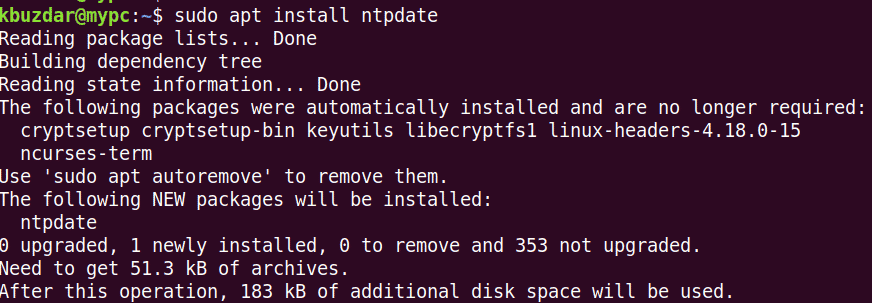
When asked for confirmation, enter y, after which the system will start the installation of ntpdate.
Step 2: Manually sync NTP client with NTP server using ntpdate
In this step, we will manually synchronize the NTP client to the NTP server to check if time is accurate and the difference is not more than 1024 seconds. To do so, issue the following command in Terminal replacing the <server-IP> with the actual IP address of NTP server:
$ sudo ntpdate <server-IP>
IN our case, the IP address of the NTP server is 192.168.72.157, so the command would be:
$ sudo ntpdate 192.168.72.157

From the above output, you can see the time difference is just 0.008231 seconds.
Step 3: Disable systemd timesyncd service
Disable the system timesyncd service as we are going to synchronize our system time with the NTP server. Run the following command to do so:
$ sudo timedatectl set-ntp off
Step 4: Install NTP on client machine
As you have seen form, the output of ntpdate command that time difference is very less, so we can now configure ntp.conf on the client machine to automatically sync it with the NTP server.
First, you will need to install NTP on the client machine. Enter the following command in the Terminal:
$ sudo apt install ntp
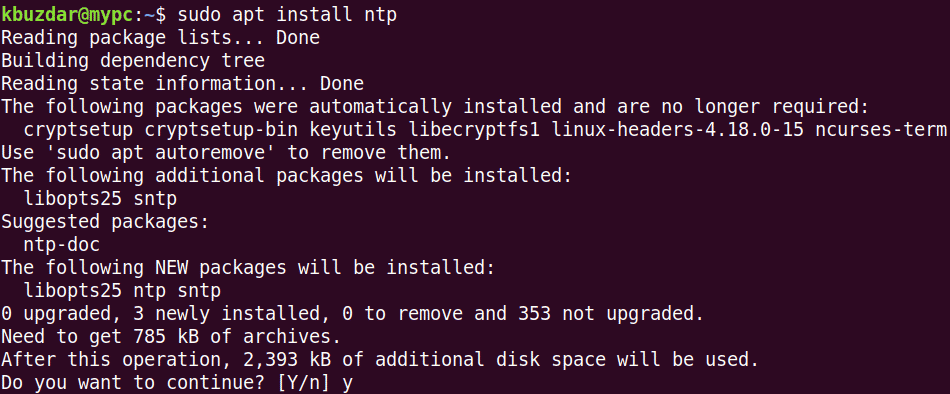
When asked for confirmation, enter y, after which the system will start the installation of NTP. Once completed, you can configure NTP as described in the next step.
Step 5: Configure ntp.conf in client machine to automatically sync it with NTP server
In this step, we will configure the npt.conf to automatically synchronize the client machine with the NTP server.
In the client machine, edit the ntp.conf file as follows:
$ sudo nano /etc/ntp.conf
Add the below line in the config file replacing the <server-hostname> with your NTP server host name.
server <NTP-server-hostname> prefer iburst
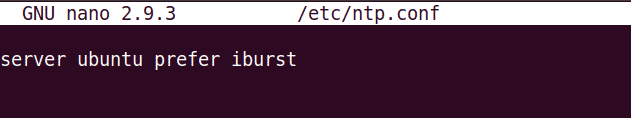
Once you are done, press Ctrl+x. Now, you will be prompted if you want to save the changes, press y.
After making change to the /etc/ntp.conf file, restart the NTP service using the following command:
$ sudo service ntp restart
Now the client machine has been connected to the host system for the time synchronization.
View NTP Synchronization Status
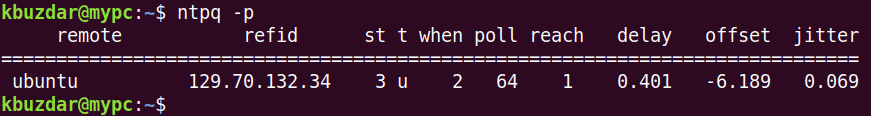
In order to view NTP current synchronization status, issue the following command in Terminal:
$ ntpq -p
In the output, you can see “ubuntu” as the connected time server along with some other information.
That is all there is to it! In this article, you have learned how to configure the NTP server on the Ubuntu machine and then sync a clock of NTP client machine. Now you can easily set up NTP server and connect multiple client machines with it for time synchronization.