Kali Linux is an open-source powerful Linux distribution that you can used for web testing, penetration testing, network security assessment and ethical hacking. You can install Kali Linux on Windows, Mac, Linux, Mobile and Chromebook. Apart from installing this operating system on a computer from scratch, you can also use it live through a USB device. This requires creating a live Kali Linux bootable USB, which you can insert into a system and start using the operating system. The advantage of having a live Kali Linux bootable USB is that you can have it in your pocket and tackle any security challenges that may come in your way.
Follow this blog to learn:
How to Make a Live Kali Linux Bootable USB
There are several methods you can follow to make a live Kali Linux bootable USB. However, these methods vary based on the system you are using. Some methods include GUI tools, while others are done through the terminal. The following are most popular methods to make a live Kali Linux bootable USB on different systems:
How to Make a Live Kali Linux Bootable USB Using BalenaEtcher
BalenaEtcher is a cross-platform application that you can download on Windows, Mac and Linux systems. With BalenaEtcher, you can quickly create a live Kali Linux bootable USB from an iso file. To make a live Kali Linux bootable USB using BalenaEtcher, simply follow the below-given steps:
Step 1: Download Kali Linux Live Bootable Image
First, you have to move towards official Kali Linux website and download the Live bootable image (64-bit or 32-bit) by clicking on the Download option:

Step 2: Load Kali Linux Image File
After, you have downloaded the image, open the BalenaEtcher application and load the Kali Linux image, you can do this by selecting the Flash from file option:

Then choose the downloaded Kali Linux image from your computer, double-click on the file or use the Open button to load it in BalenaEtcher:

Step 3: Select the Kali Linux Target Location
You should insert a USB (minimum 32 GB) into your computer and then choose Select target option from the BalenaEtcher’s menu:

Then choose your USB storage as the target location for saving the Kali Linux live image, once done use the Select 1 button:

Step 4: Begin the Flash Process
To start creating the Kali Linux live image, simply click on the Flash! option:

Wait till BalenaEtcher finishes the flash process on your system, which can take time depending on your USB writing speed:

Step 5: Boot Kali Linux
Now, to boot Kali Linux on your system, simply reboot your computer, and open the Boot menu. The Boot menu on most system can be opened by pressing the F12 key. At the Boot menu, choose USB Storage Device option as LEGACY BOOT:

Note: If the above option is not working you can try using the UEFI BOOT option.
This will open the Kali Linux live menu, where you have to select Live system (amd64) option:

Wait until your system boots Kali Linux on your computer:

How to Make a Live Kali Linux Bootable USB Using Rufus
If you are using a Windows system, you can also use Rufus utility to make a live Kali Linux bootable USB. Rufus is a lightweight GUI utility that can only be installed on Windows systems and it allows you to make a bootable USB. If you are interested in making a live Kali Linux bootable USB on Windows using Rufus, you can follow the below-given steps:
Step 1: Download and Install Rufus on Windows System
First, navigate to the Rufus download page, download the exe file and run it to install Rufus on your Windows system.
Step 2: Load Kali Linux iso File in Rufus
Next, open Rufus from the Windows’ Start Menu and click on the SELECT button:
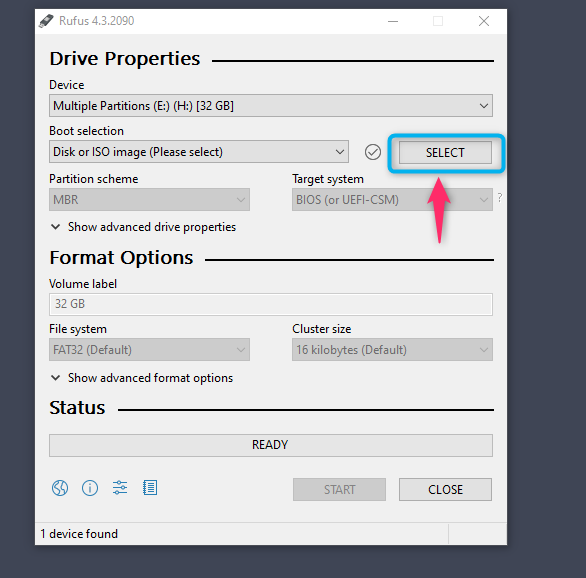
Then load the Kali Linux file:

Step 3: Select the Partition Scheme and Target System
Now, you will need to select your Partition Scheme, MBR or GPT. Most modern operating systems provides compatibility with both MBR and GPT, but if you are using an older operating system, go with MBR. If you select MBR, the target system will automatically be selected to BIOS or UEFI. While for GPT, UEFI (non CSM) will be selected automatically. Once selected, go with the default option and click on the START button:

Step 4: Select Mode for Writing Image
You will see a prompt that asks your permission to select the mode that you want to choose to write the Kali Linux image onto the USB drive. You can go with the default one and select the OK button to continue:

Step 5: Remove Data from USB Drive
Do the final step by removing the data from the USB drive by clicking on the OK button, once this is done, the Rufus will begin writing the image of Kali Linux on your USB drive.

Note: After the completion of the above steps, you can then insert the USB into any system by following Step 5 of the first method to boot Kali Linux.
How to Make a Live Kali Linux Bootable USB Using Terminal
If you are using a Mac or Linux system, you can also use the dd command to make a live Kali Linux bootable USB, this can be done using the following steps:
Step 1: Check the USB Device is Connected to System
First, insert a USB device into your Linux system and use the following command to check for the device label:

If you are using Mac, use the following command:

Step 2: Make a Live Kali Linux Bootable USB
Now, use the following command by replacing sdX with the device label on your Linux system while keeping the other parameters the same. Make sure you must provide the correct path for the Kali Linux iso file.

Note: On Mac, replace sdX with the diskX, also, you have to unmount the disk on your Mac from the following command:

Step 3: Check Progress of Live USB Process
If you want to check the progress of the dd command, you can use the above command in the following way:

The process will take around 5–10 minutes, depending on how fast your USB is in terms of writing. Once done, remove the USB device and follow Step 5 of the first method. However, select UEFI BOOT if the USB Storage Device option is not working.
Conclusion
Making a live Kali Linux bootable USB is a simple task and can be done using BalenaEtcher and Rufus applications. Besides that, you can also use the terminal to create a live Kali Linux bootable USB with the dd command. The advantage of using the BalenaEtcher application is that you can use it on any system either Windows, Mac or Linux. However, Rufus will only work on Windows, while the terminal method will work on Mac and Linux systems. You must choose the method based on the system you are using and once you create a live USB, you can seamlessly run Kali Linux on your system.
By day, I am an engineer and researcher, building bridges and figuring out how the universe works. But when the clock strikes five, I turn into a wordsmith!
I write about my adventures on my blog, sharing tips and tricks to help others join the tech fun. I have worked on Raspberry Pi, Ubuntu, Debian, and Laptops. Right now, I have accepted the challenge of working on the Kali Linux system, and with my vast expertise in Linux systems, I will help users overcome the challenges through my blogs.



