Introduction
In this guide, we are going to work with advanced configurations of Grsync. Grsync is a graphical tool developed on top of the world-famous rsync utility. Grsync helps Linux users to keep their system backed up without messing with the command line. I am using Linux Mint 20.1 while writing this guide. All instructions are valid for other apt-based distributions.
Installing Grsync
If HexChat is not installed on your system then execute the following command on your terminal to begin
$ sudo apt install grsync
Let’s begin setting up Grsync
When you install Grsync it will look something like the following:
We will begin how to take backups with advanced and extra options.
Advanced Options
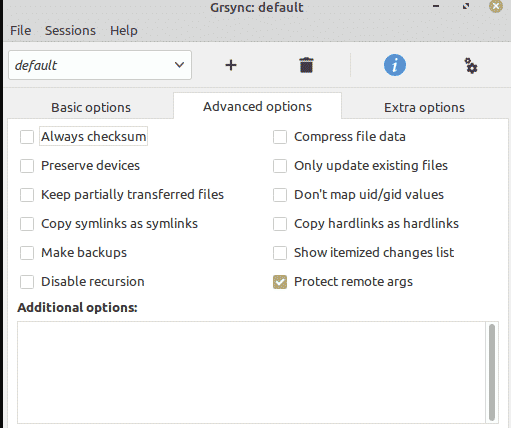
Grsync provides more than a dozen advanced options to take serious backups of directories on a Linux system. In our case, we will only use the following three.
- Always checksum
- Compress file data
- Show itemized changes list
All three do a great job to secure, minimize the size, and list the changes of a backup. They are absolute in any back-up in our honest opinion.
You are always free to choose anything else and any additional options to further protect your backups.
Extra Options
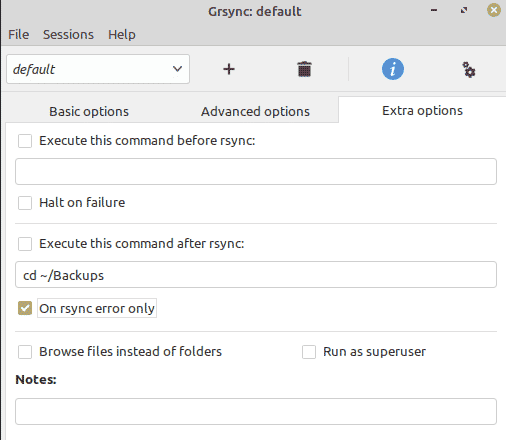
In extra options, we love the second option of executing a command after rsync. Sometimes rsync fails to take a quality backup. At that time I needed to visit my backup folder immediately to check what’s going wrong.
Instead of typing, I save the directory change command in Grsync to execute it directly whenever rsync leaves any error. You can also choose many other options according to your needs.
Conclusion
In this guide, we worked with Grsync advanced and extra options to create better backups. Grsync is a handy tool whenever it comes to taking backup of a local or a remote directory. It does not let the user down.