Introduction
Services are the applications that run in the operating system’s background waiting to be used. Linux lets you see and manage these services and overall offers more control over them.
In this article, you will learn different ways to start, stop and restart any service in Linux Mint 20.
Prerequisites
You will need a user account with root/sudo privileges, access to the terminal, and the systemctl tool which comes with Linux.
Managing Services Using Systemd
Systemd is itself a daemon which refers to libraries, packages, and utilities around daemons. It is the most advanced system management daemon that is fast and takes much fewer system resources than its counterparts.
View All Services
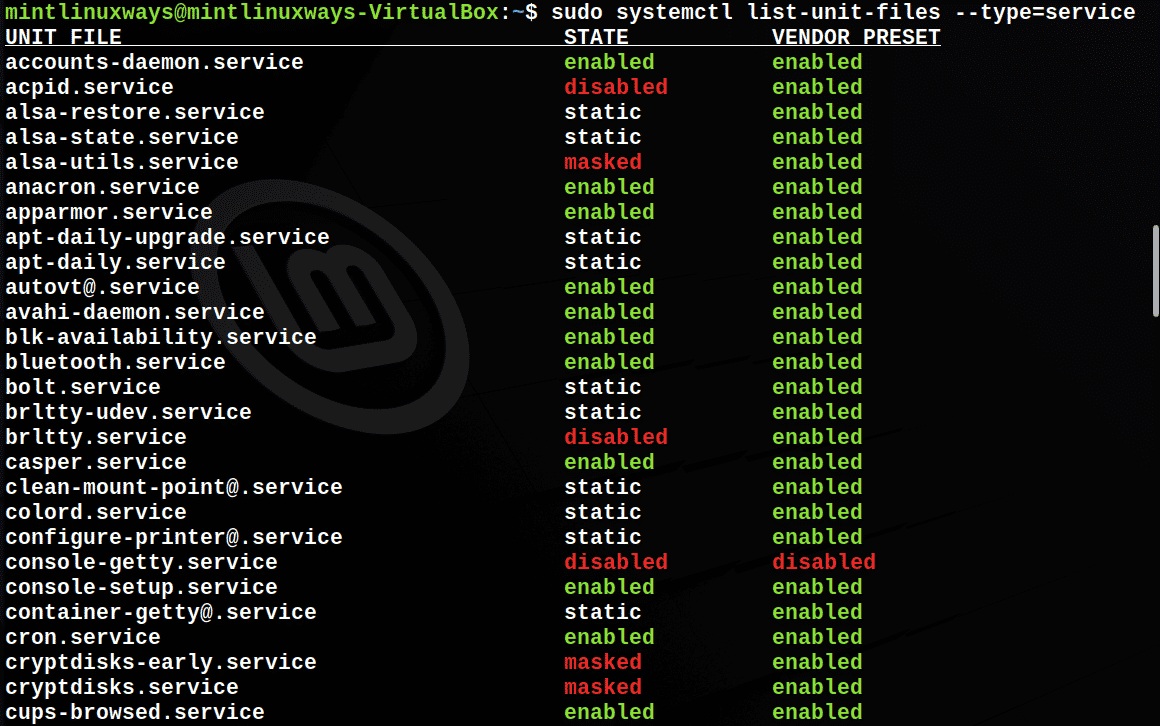
You can see all the available services in your system with the following command.
sudo systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
View Running Services
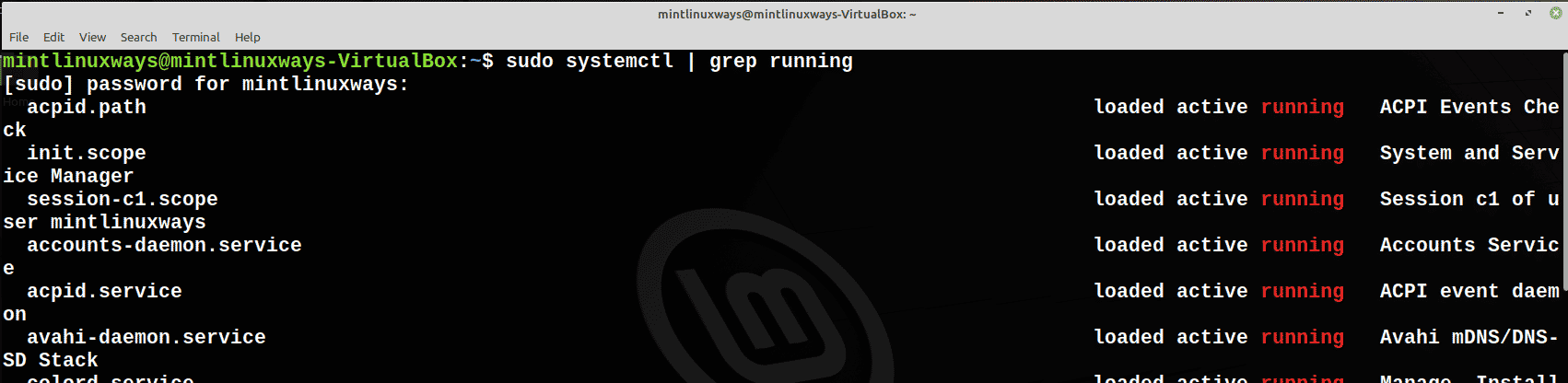
To see all the services that are currently running on your system, run the following command.
sudo systemctl | grep running
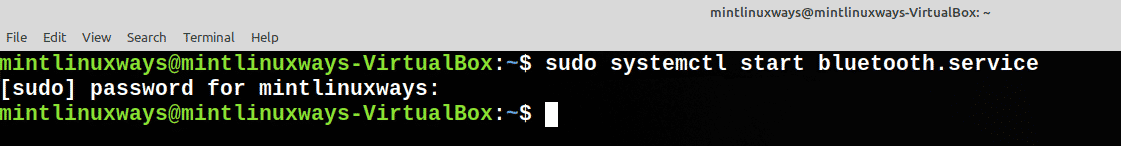
Start a Service
Use the following command to start your service.
sudo systemctl start <service name>
Note: Remember <service name> is a placeholder and you need to replace it with the name of your service.
Stop a Service
Use the following command to stop your service.
sudo systemctl stop <service name>

Restart a Service
Use the following command to restart your service.
sudo systemctl restart <service name>

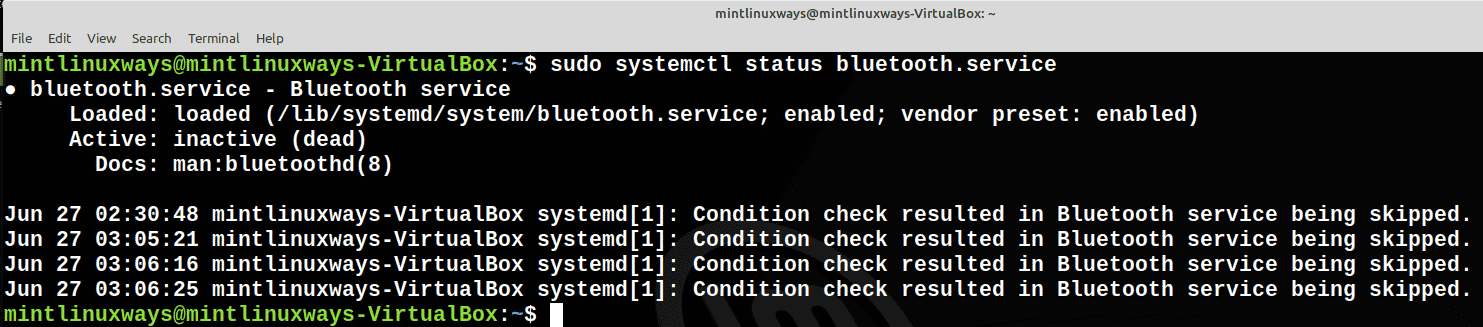
Check Status of the Service
Use the following command to check the status of your service.
sudo systemctl status <service name>
Managing Services Using service Command
Service is an advanced command that is a part of init. But its execution is done now by redirecting commands to systemctl.
View All Services in Your System
To check all the services you have on your system, simply run the command below.
sudo service --status-all
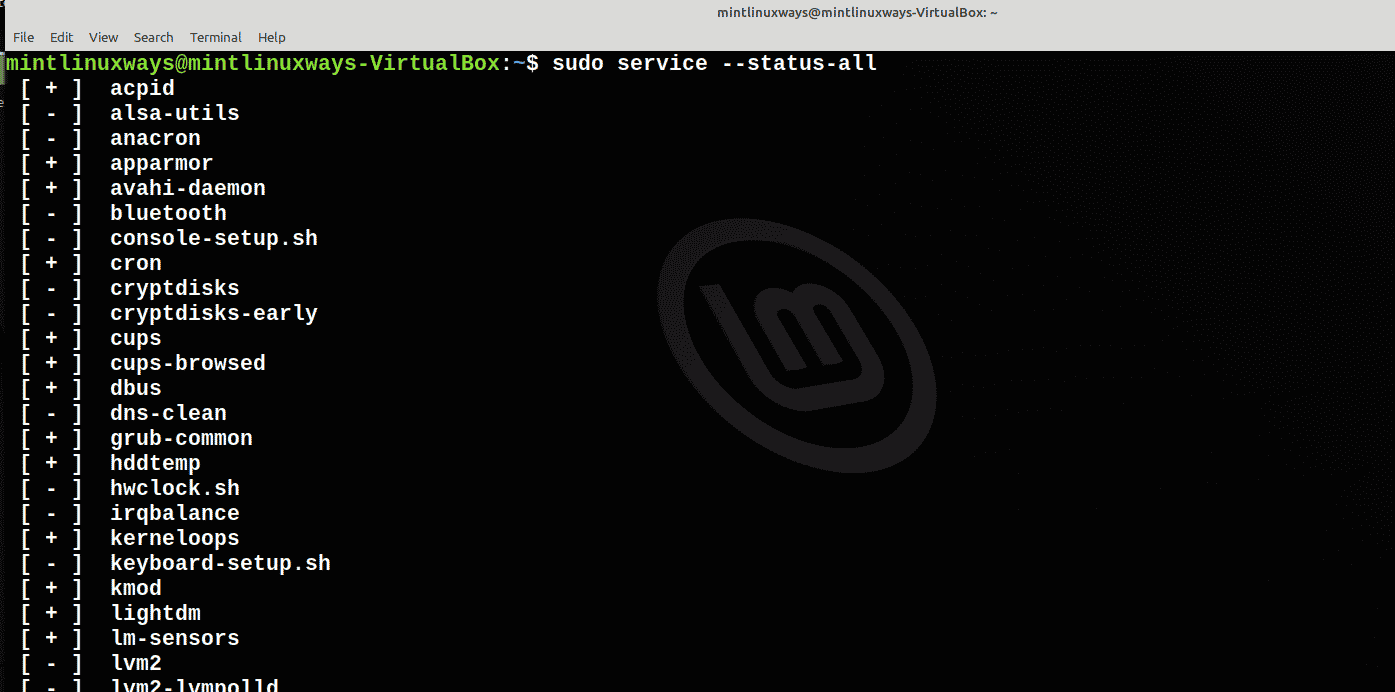
Note that all the enabled services are preceded by the [+] symbol while all the disabled services have the [-] symbol next to them.
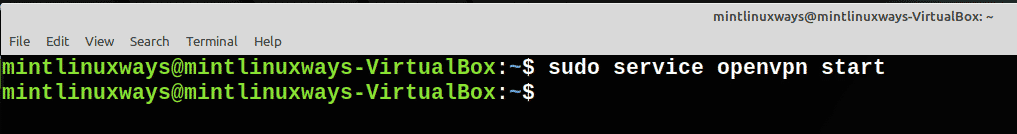
Start a Service
You can start a service using the following command.
sudo service <service name> start
Stop a Service
To stop a service, use the following command.
sudo service <service name> stop
Restart a Service
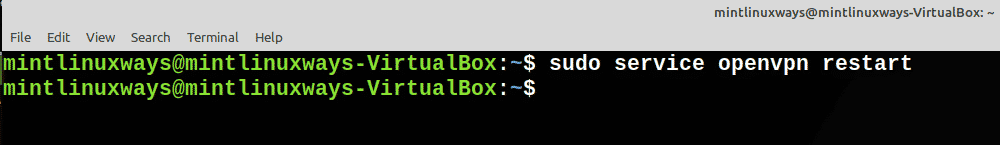
Restart any service with the following command.
sudo service <service name> restart
Check Status of the Service
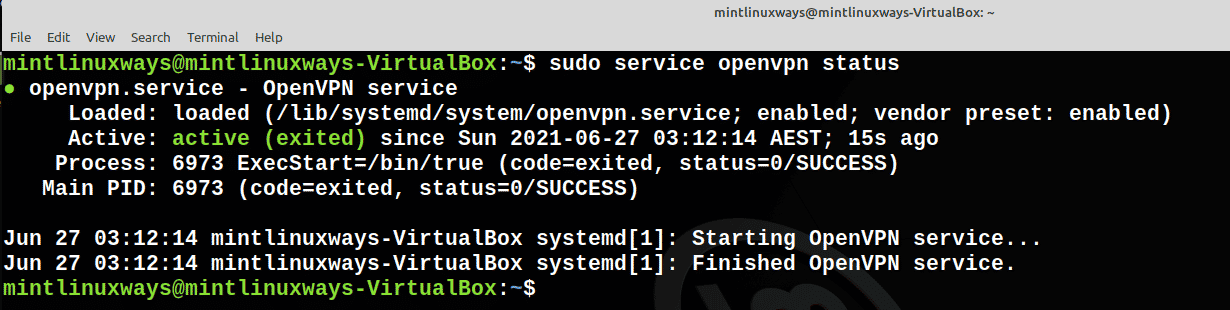
You can check the status of any service with the following command.
sudo service <service name> status
Managing Services Using init Scripts
The init daemon is a daemon management system referred to as System V init. It takes a lot of resources so it was replaced by systemd.
Start a Service
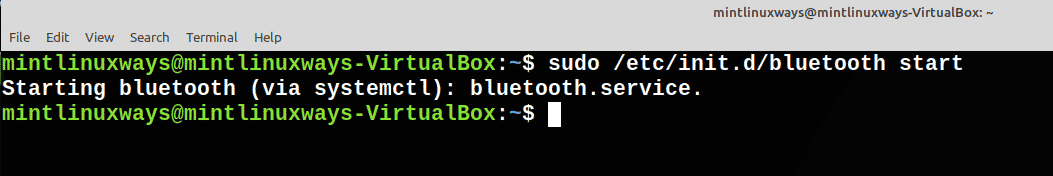
Start service with the following command.
sudo /etc/init.d/<service name>start
Stop a Service
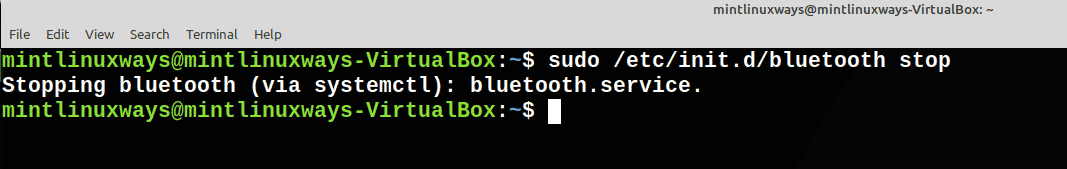
To stop a service, run the following command.
sudo /etc/init.d/<service name> stop
Restart a Service
To restart a service, run the following command.
sudo /etc/init.d/<service name> restart
Check Status of the Service
Check the status of a service using the following command.
sudo /etc/init.d/<service name> status
Conclusion:
This article covers all the basics of service management in Linux Mint 20.