Introduction
When working with a Linux system, sometimes you encounter networking issues or you have to configure the firewall. In these situations, maybe you need to check whether specific ports are opened or not?
This article will explain the details of several ways to figure out what ports are opened on your Linux system.
All of the examples in this tutorial were executed on Ubuntu 20.04.
What is an Open Port?
An open port is a TCP or UDP network port that accepts incoming packets from outside.
For example, if an SSH server is installed on your Linux system, it will listen on port 22. In case this port is open on the firewall, the users from remote systems will be able to establish an SSH connection to your system. We say that port 22 is an open port.
Bearing in mind that we should expose only the necessary ports for the applications can run properly. Other unnecessary ports should be closed for avoiding security risks.
Using nmap to check open ports
Nmap stands for Network Mapper. It is a useful and powerful utility that used to scan hosts and services on a network.
Other than the host ports scanning feature, nmap can also discover the MAC addresses, operating systems, kernel versions, and so on.
By default, nmap is not pre-installed on Ubuntu 20.04. You can install it by running the following commands:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install nmap
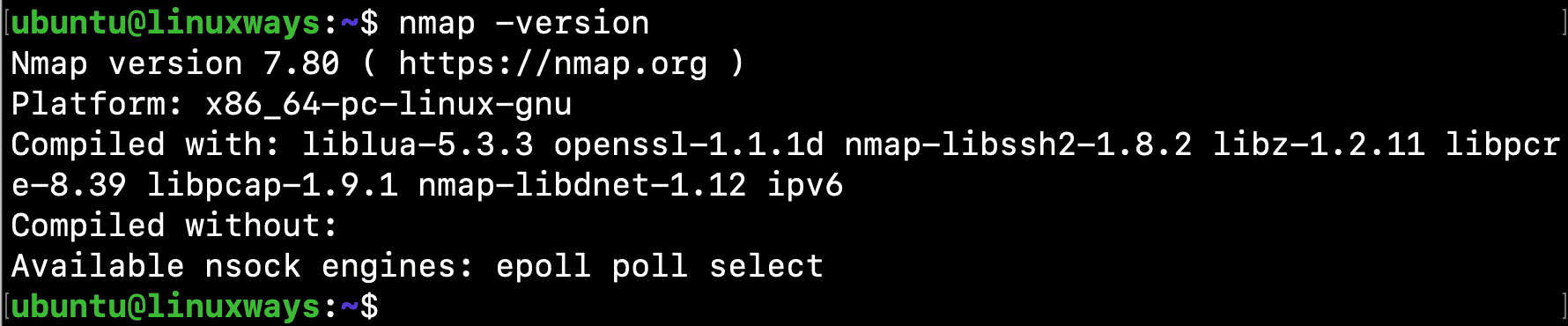
Verify that nmap is successfully installed:
$ nmap -version
Output:
Now, it’s time to use nmap to check the opening ports on your system. Let’s run the command:
$ sudo nmap -sT -p- 10.128.0.2
Output:
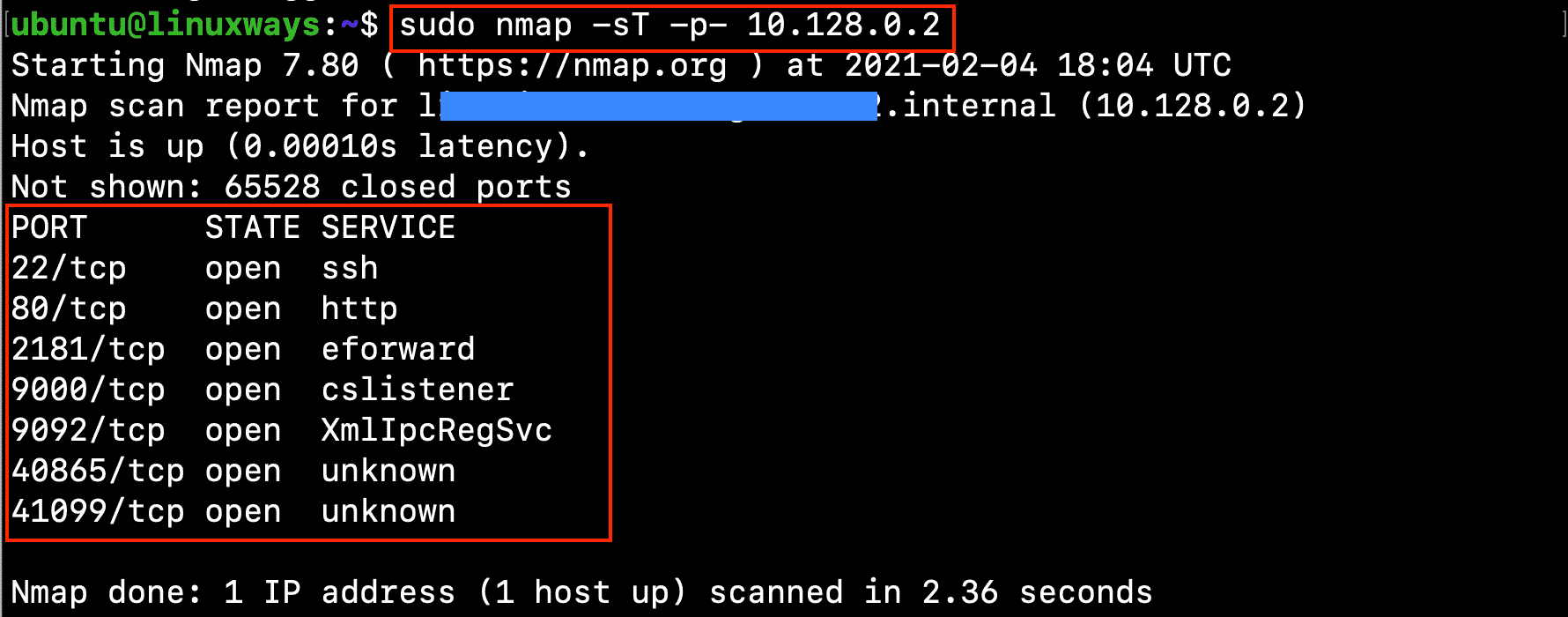
In which:
-sT -p- indicates that nmap will scan for all TCP ports.
10.128.0.2 is your internal IP address of your host.
If you want to scan for UDP ports, running nmap with -sU option:
$ sudo nmap -sU -p- 10.128.0.2
Output:
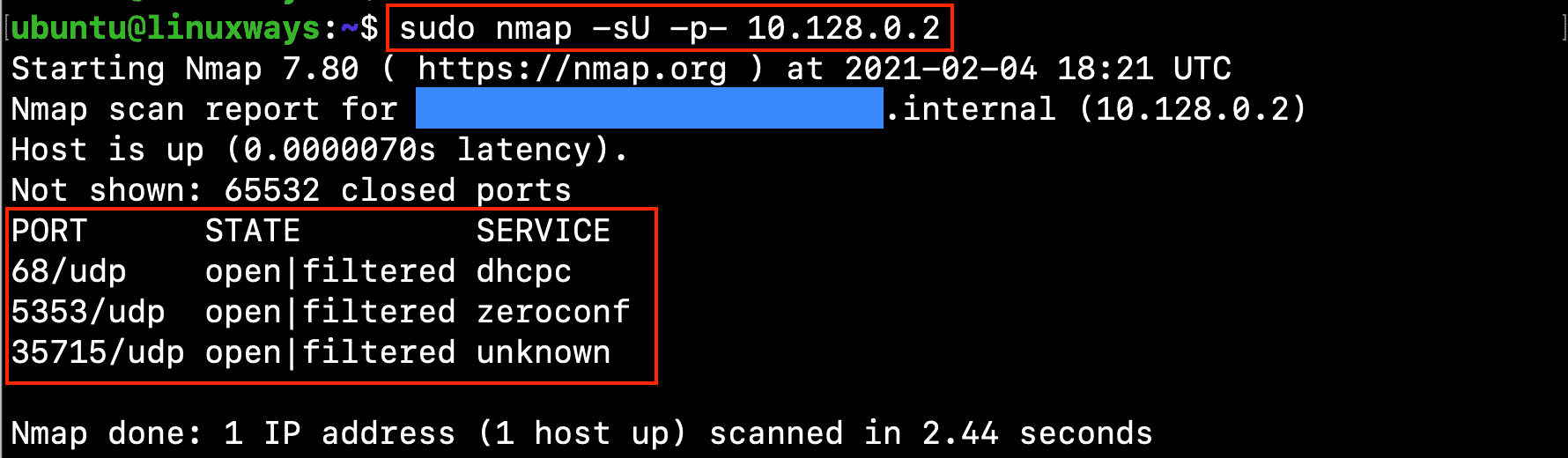
Using netcat to check open ports
Netcat is a powerful command line tool that performs the networking operation. It uses TCP and UDP protocols for reading and writing data across networks.
Necat can be used for scanning and redirecting network ports as well.
If you want to check open ports in the range 20-25 on a Ubuntu 20.04 machine that has IP 10.128.0.2, run the following command:
$ netcat -z -v 10.128.0.2 20-50
Output:
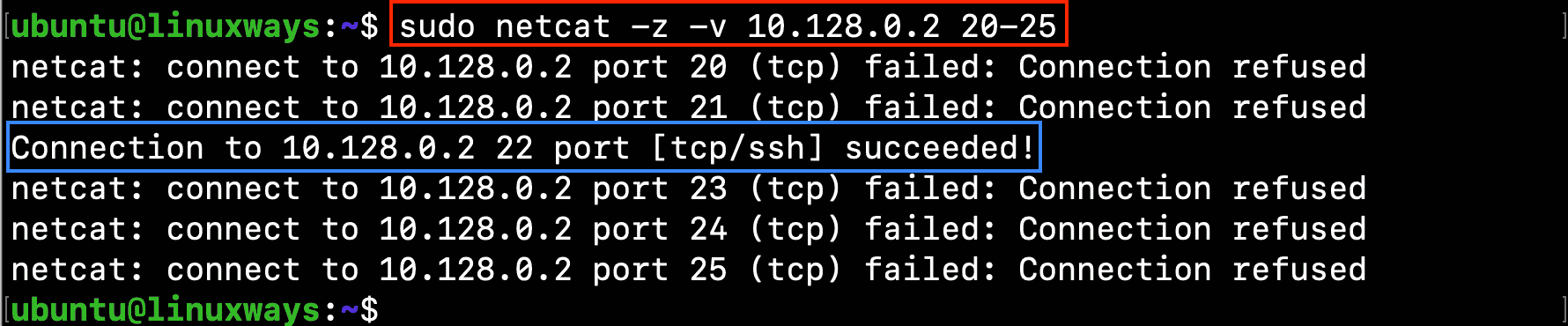
In which:
-z indicates that netcat scan only for open ports
-v sends verbose information to the terminal
In case you want to show only the open ports, you can run:
$ netcat -z -v 10.128.0.2 20-80 2>&1 | grep succeeded
Output:

To scan for ports in UDP, let’s use -u option as follows:
$ netcat -z -v -u 10.128.0.2 20-80 2>&1 | grep succeeded
Output:

Conclusion
This tutorial has shown you some common tools that can be used to check the open ports on a Linux system.
If you have any concerns, please let me know in the comment section.
System Engineer with 6 years of experience in software development, specializes in Embedded Linux, C/C++, Python, Go, and Shell Scripts. He has a solid background in Computer Networking, OpenStack, Kubernetes, Docker/Container, CI/CD, and Google Cloud as well. Now, he is Head of GDG Cloud Hanoi – a non-profit community of cloud developers who meet/share ideas on everything Google Cloud Platform related.




