Apache Spark is an open-source computational framework for high scale analytical data and machine learning processing. It supports various preferred languages such as scala, R, Python, and Java. It provides high-level tools for spark streaming, GraphX for graph processing, SQL, MLLib.
In this article, you will get to know the way to install and configure Apache Spark on ubuntu. To demonstrate flow in this article I have used the Ubuntu 20.04 LTS version system. Before installing Apache Spark you have to install Scala as well as scala on your system.
Installing Scala
If you haven’t installed Java and Scala you can follow up the following process to install it.
For Java, we will be installing open JDK 8 or you can install your preferable version.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
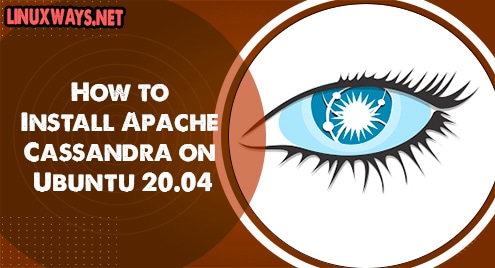
If you need to verify the java installation you can execute the following command.
$ java -version
As for Scala, scala is a object oriented and functional programming language that combines it into single concise. Scala is compatible with both javascript runtime as well as JVM granting you easy access to the large libraries ecosystem which helps in building high performance system. Execute the following apt command to install scala.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install scala
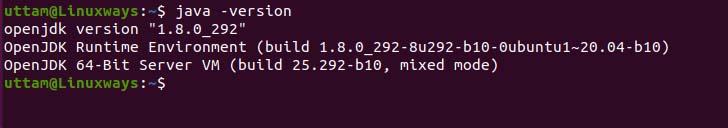
Now, check the version to verify the installation.
$ scala -version
Installing Apache Spark
There is no official apt repository to install apache-spark but you can pre-compiled binary from the official site. Use the following wget command and link to download the binary file.
$ wget https://downloads.apache.org/spark/spark-3.1.2/spark-3.1.2-bin-hadoop3.2.tgz
Now, extract the downloaded binary file using the following tar command.
$ tar -xzvf spark-3.1.2-bin-hadoop3.2.tgz
Lastly, move the extracted spark files to /opt directory.
$ sudo mv spark-3.1.2-bin-hadoop3.2 /opt/spark
Setting Up Environment Variables
Your path variable for spark in your .profile in the file needed to set up in order for the command to work without a complete path, you can do so either using the echo command or do it manually using a preferable text editor. For an easier way execute the following echo command.
$ echo "export SPARK_HOME=/opt/spark" >> ~/.profile
$ echo "export PATH=$PATH:/opt/spark/bin:/opt/spark/sbin" >> ~/.profile
$ echo "export PYSPARK_PYTHON=/usr/bin/python3" >> ~/.profile
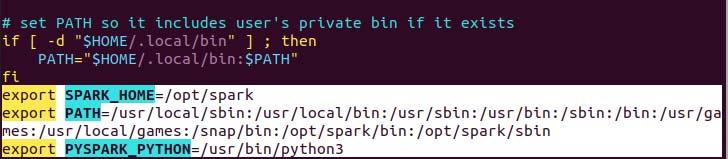
As you can see the path variable is appended to at the bottom of .profile file using echo with >> operation.
Now, run the following command to apply the new environment variable changes.
$ source ~/.profile
Deploying Apache Spark
Now, we have set up everything we can execute the master service as well as worker service using the following command.
$ start-master.sh
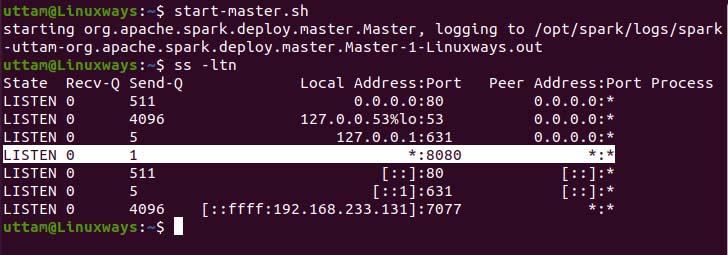
As you can see our spark master service is running on port 8080. If you browse the localhost on port 8080 which the default port of spark. You may encounter the following type of user interface when you browse the URL. You may not find any worker processor running by starting only master service. When you start the worker service you will find new node listed just like in the following example.
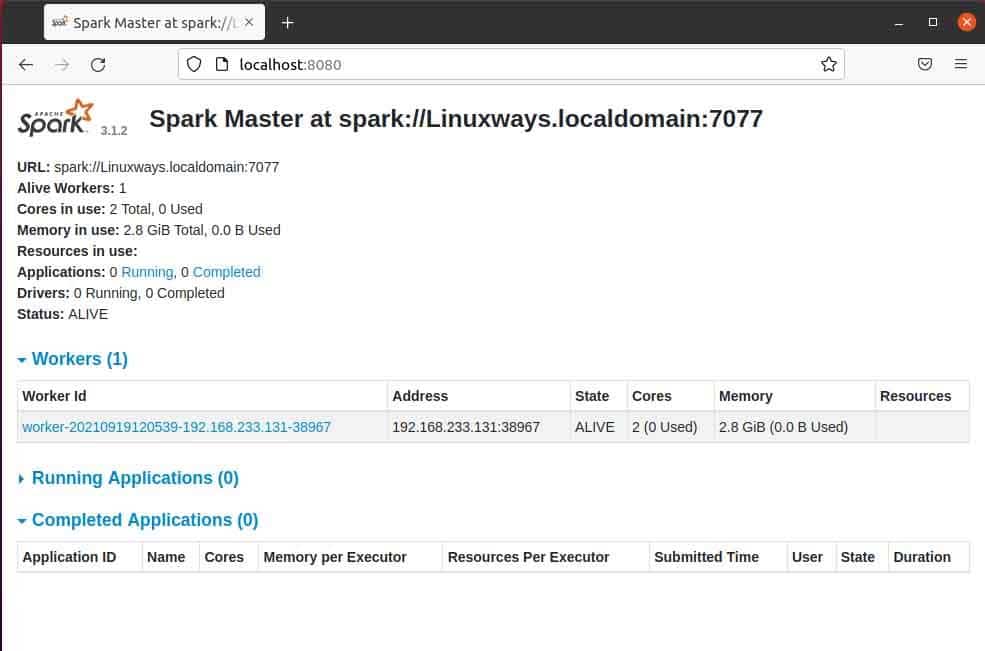
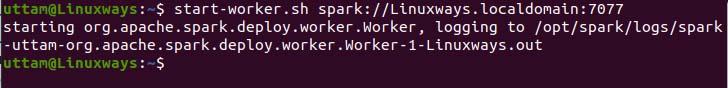
When you open master page in browser then you can see spark master spark://HOST:PORT URL which is used to connect the worker services through this host. For my current host my spark master url is spark://Linuxways.localdomain:7077 so you need to execute the command in the following way to start the worker process.
$ start-workers.sh <spark-master-url>
To execute the following command to run the worker services.
$ start-workers.sh spark://Linuxways.localdomain:7077
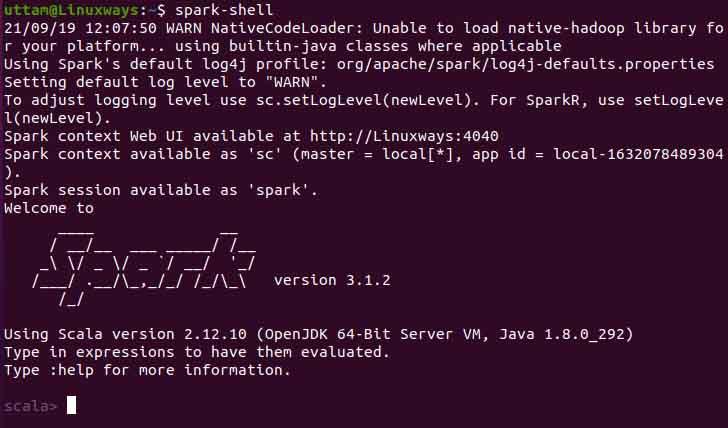
Also, you can use spark-shell by executing the following command.
$ spark-shell
Conclusion
I hope from this article you learn the way to install and configure apache spark on ubuntu. In this article, I attempted to make the process as understandable as I can.