Apache Cassandra is an open-source non-relational database that delivers high performance, linear scalability, and continuous availability. All these features make Cassandra an ideal platform for mission-critical data. In today’s post, we will be describing how to install Apache Cassandra on Ubuntu OS.
Note: The procedure shown here has been tested on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa).
Step 1: Install java
Apache Cassandra requires java to be running on the machine. Use these commands to install java on your system:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
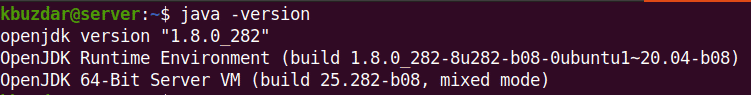
To verify if Java is installed, issue this command in Terminal:
$ java -version
Step 2: Install Apache Cassandra
Before proceeding towards the installation of Apache Cassandra, you will first need to install the apt-transport-https package. You can install it using this command:
$ sudo apt install apt-transport-https
Enter the password for sudo. When prompted for continuation, press y.
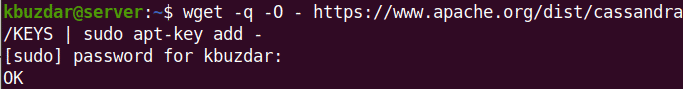
Now import and add the GPG key using this command in the Terminal:
$ wget -q -O - https://www.apache.org/dist/cassandra/KEYS | sudo apt-key add -
If the key is added successfully, you will see OK in the output.
Now add the Apache Cassandra repository to apt list of sources using this command in the Terminal:
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://www.apache.org/dist/cassandra/debian 311x main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cassandra.list'
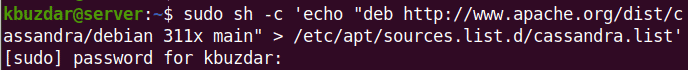
Update the apt list of sources using the command below in the Terminal:
$ sudo apt update
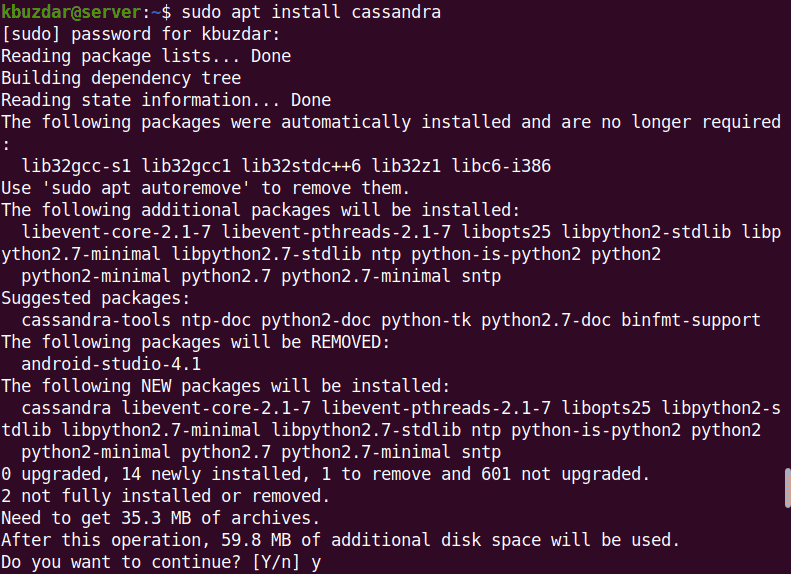
Now that the repository has been added, you can install Apache Cassandra using this command in the Terminal:
$ sudo apt install Cassandra
Enter the password for sudo. When prompted for continuation, press y.
After the installation of Apache Cassandra, its service starts automatically. To verify it, use the command below:
$ sudo systemctl status Cassandra
Also, you can verify the status using the below command:
$ sudo nodetool status
You’ll see something similar to the following:
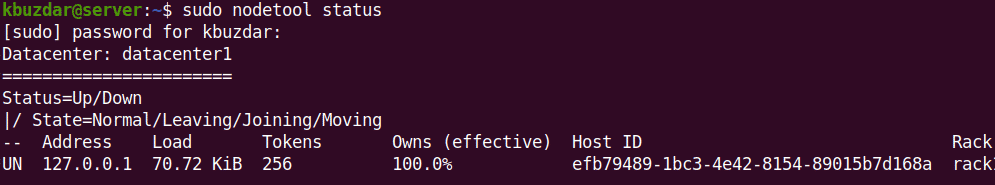
Now the Apache Cassandra has been successfully installed. To login to Apache Cassandra, you can use the cqlsh command-line tool as follows:
$ cqlsh
You will see something similar to the following:
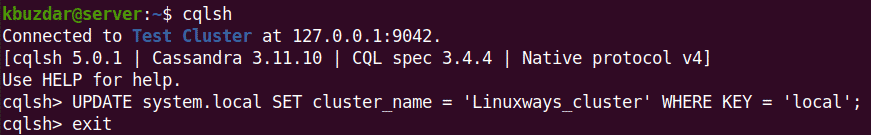
Rename Apache Cassandra Cluster
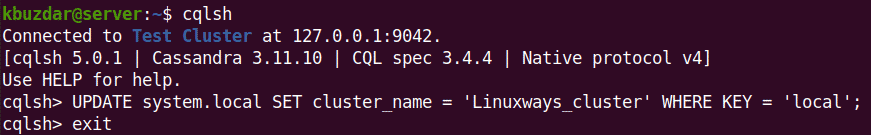
In the previous output, you can see the cluster name is “Test Cluster”. To change the default cluster name, log in to Cassandra using the cqlsh command-line tool as follows:
$ cqlsh
Then issue the command below in the Terminal to rename the Apache Cassandra Cluster to let’s say “Linuxways_cluster”:
$ UPDATE system.local SET cluster_name = ‘Linuxways_cluster' WHERE KEY = 'local';
Make sure to change the Linuxways_cluster with your own desired name.
Now to exit the cqlsh tool, type exit, and press Enter:
$ exit
Then edit the cassandra.yaml configuration file using the command below in the Terminal:
$ sudo nano /etc/cassandra/cassandra.yaml
Now in the cassandra.yaml configuration file, search for the cluster_name.

Once you find it, change its name to your desired value. Then save and exit the file. 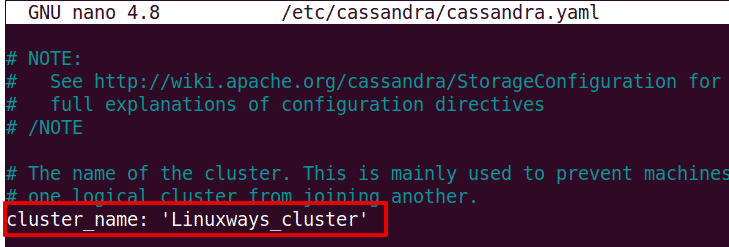
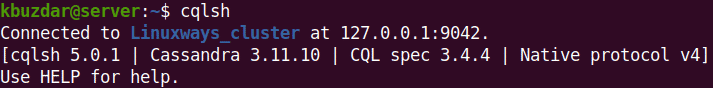
Now to verify if the cluster name has been changed successfully, use the command below:
$ cqlsh
The output below verifies that the cluster name has been changed successfully to Linuxways_cluster.
Uninstall Apache Cassandra
In case you need to remove Apache Cassandra from your machine, you can do this using the following steps:
Stop the service of Cassandra using the command below:
$ sudo service cassandra stop
Then remove the library and log directories using these commands:
$ sudo rm -r /var/lib/cassandra
$ sudo rm -r /var/log/Cassandra
After that, uninstall Apache Cassandra using the command below:
$ sudo apt purge cassandra
This was all about installing Apache Cassandra on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. To learn more about Apache Cassandra, visit its official documentation site.