Redis is a database caching service and an In-memory data structure storage. Meaning, the frequent request to the database is cached by Redis and served from the fastest memory RAM. It helps to reduce time delays and increase the performance of your application by accessing in microseconds. Data structures such as hashes, lists, sorted sets, strings, sets, are supported by Redis.
Normally, some GB of RAM is allocated to Redis. When running the applications, the memory is occupied. To refresh the storage at Redis maxmemory policy is used. The following are supported maxmemory policy algorithms:-
volatile-lru : remove the (LRU) less recently used keys first which has an expire set
allkeys_lru : remove the less recently used keys first regardless of expire set
volatiel_random : Remove random key with an expire set
allkeys_random : Keys are removed randomly without expire set
volatile_ttl : Remove nearest expire time keys ie. having minor TTL value
noeviction : None of the keys are expired, just return write operation.
In this article, I’m going to install the latest version of Redis service on Ubuntu 20.04 and configure it.
Installation
To install Redis on Ubuntu first make your system up to date.
$ sudo apt update
When an update is completed, install Redis using the apt package manager,
$ sudo apt install redis -y
After the installation is completed, check the version,
$ redis-cli -v
Now, start the Redis server by entering the following command.
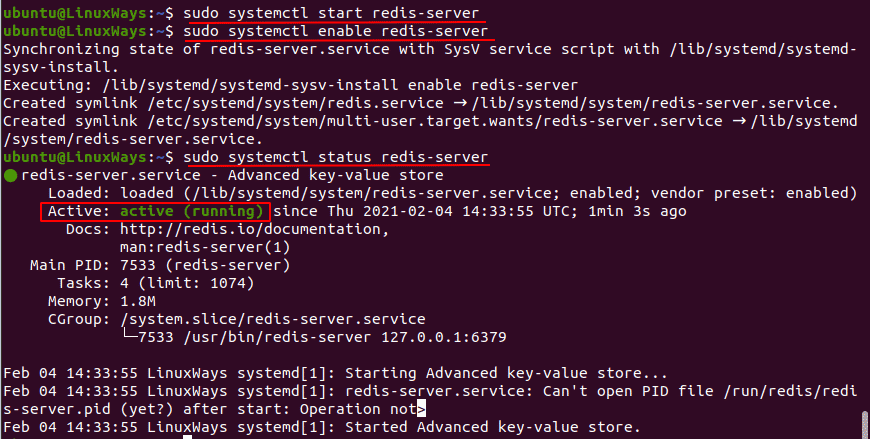
$ sudo systemctl start redis-server
Enable the service so that it automatically starts when the server reboots,
$ sudo systemctl enable redis-server
Also, check the status of Redis server,
$ sudo systemctl status redis-server
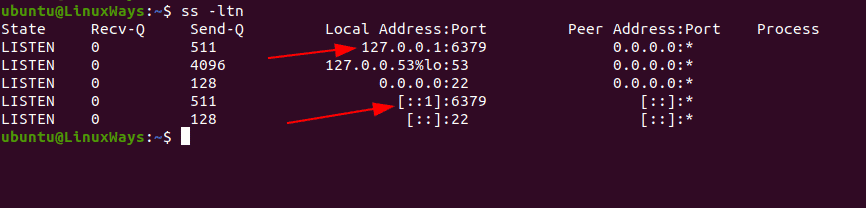
The default port for Redis is 6379 and listens on IPv4 localhost 127.0.0.1 as well as IPV6 loopback address. You can verify by executing the following command.
$ ss -ltn
Configuring Redis
In the default installation of Redis, the configuration file is at /etc/redis/redis.conf .
To apply max memory limit and policy, first open the configuration file.
$ vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
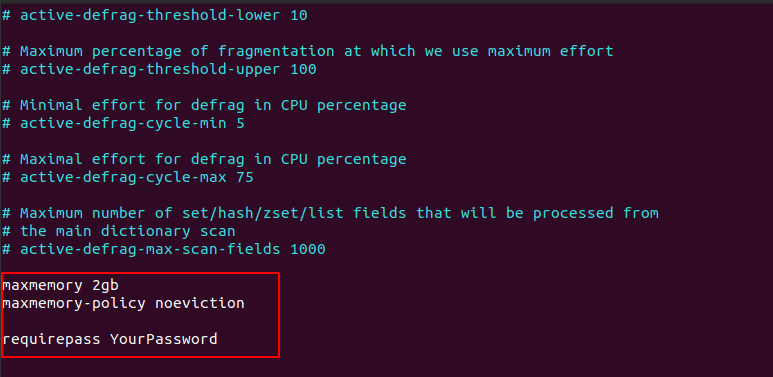
You can add the following parameter in the file. For example, set memory limit to 2 GB. and noeviction maxmemory policy.
maxmemory 2gb
maxmemory-policy noeviction
Similarly, to add password add following in the same configuration file,
requirepass YourPassword
Your file should look like,
Save the file and restart the Redis service.
$ sudo systemctl restart redis-server
Note: You can also change default port and bind address from the configuration file.
Redis CLI
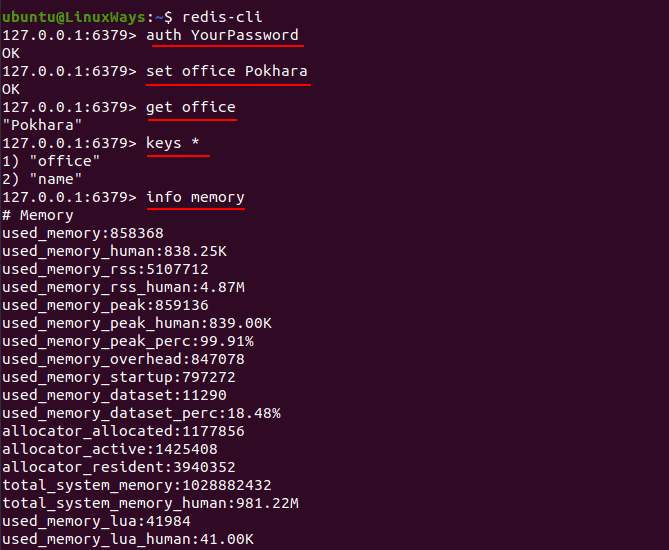
Now, let’s access Redis from its CLI. To login to Redis server just type,
$ redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379>
Now use password to login. ( if you have setup )
12.0.0.1:6379> auth YourPassword
Set name ‘office’ and value ‘Pokhara’
127.0.0.1:6379> set office Pokhara
Get the key from name
127.0.0.1:6379> get office
See all the keys in Redis
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
See memory details
127.0.0.1:6379> info memory
Flush all the key
127.0.0.1:6379> flushall
login to different Redis server hosts and non-default port. For Example 10.10.18.6 with default port 6380
$ redis-cli -h 10.10.18.6 -p 6380
Conclusion
The article gives you the idea of installing and configuring the Redis server on Ubuntu 20.04. Hope you like the article.
Pratik Gautam is a system engineer on Cloud Computing, Linux system, and Amazon Web Services. He is a certified Linux administrator and a tech enthusiast having more than three years of experience at fintech and media house of Nepal. He has Bachelor’s degree in computer science and information technology from Tribhuvan University. He always believes in sharing IT knowledge and adopting new technology.