Most of the IT professionals who work on Docker get stuck at a point when it’s about the size of the docker containers. Sometimes the size of the docker images goes up to in GB’s which consumes large storage of the system and makes it difficult to upgrade and start the container. Fortunately we have a free Open source tool in Linux/Mac system which allows us to secure and minimize the size of the docker containers upto 30 times.
Why use DockerSlim ?
- To minimize the container’s size which reduces the storage usage.
- To create lightweight containers for faster starting
- Reduce bugs
In this article, we will cover how to install DockerSlim and use it to minimize the docker container.
Installation
Dockerslim is currently supported on Linux and UNIX systems including Mac. The dockerslim binary files can be downloaded from DockerSlim GitHub Repository. Go to the GitHub repository link given below, navigate to installation and download the latest binaries for your system.
DockerSlim GitHub Repository: https://github.com/docker-slim/docker-slim
Also, you can use wget command to download the latest DockerSlim binary files as:
$ wget https://downloads.dockerslim.com/releases/1.36.1/dist_linux.tar.gz
To extract the downloaded files, run the following command.
$ tar -zvxf dist_linux.tar.gz
Once the file is extracted, move the binary files to /usr/local/bin directory as:
$ sudo mv dist_linux/* /usr/local/bin
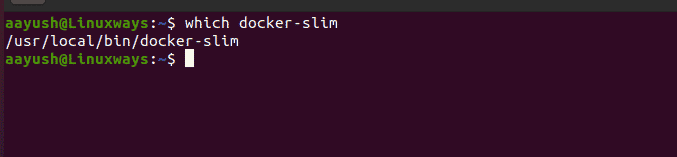
To verify the installation of DockerSlim, run the following command.
$ which docker-slim
Output:
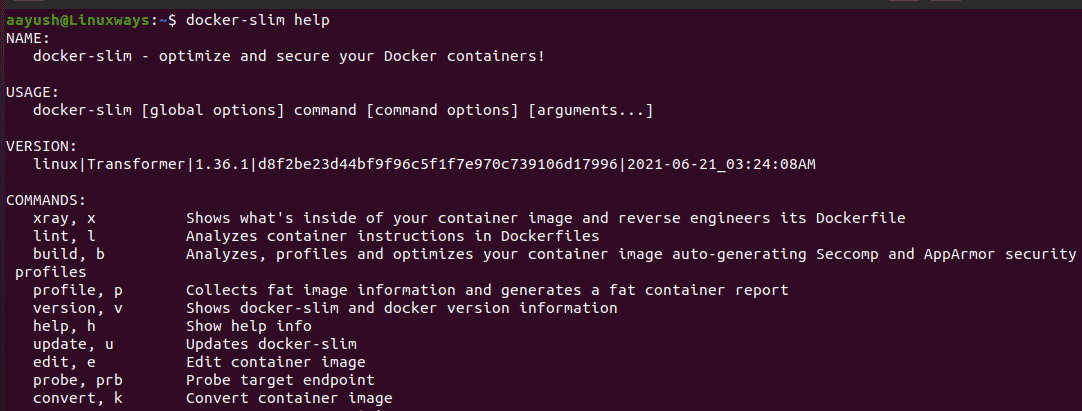
Run the docker docker-slim with option help for useful commands and guides.
$ docker-slim help
Output:
DockerSlim provides a very useful menu-driven command line. To try the available commands, run docker-slim without any arguments . In the DockerSlim shell, type help to get the help menu in the interactive prompt.
Output:
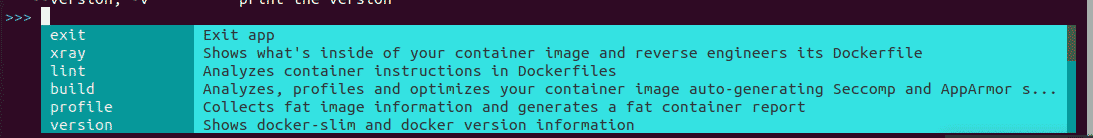
The basic commands includes the followings:
Exit => Exit from DockerSlim shell
Xray => Shows what is inside of the container image and reverse engineers its Dockerfile
Version = > Show DockerSlim and docker version information
Lint => Analyzes container instructions in the Dockerfiles
Preparing a container to slim
To create a slim docker container, we need to have a docker image available in the local system. In this article, I have selected an httpd image. You can select the image as per your requirement. Use the following syntax to pull docker images from the dockerhub. Remember that you should have installed the docker engine and dependencies on your system
Syntax :
$ docker pull <image name>
$ docker pull httpd
Output:

Verifying the Output of the Container
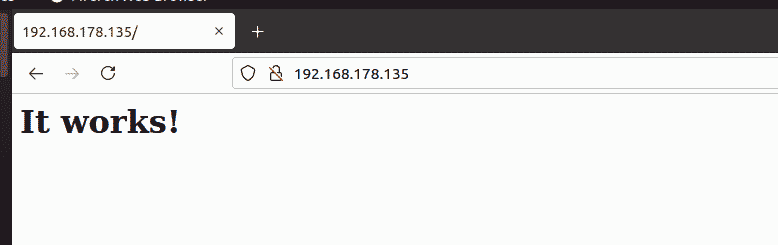
Once the image is pulled, run it as the container and verify the output. In this example, I have exposed port 80 of the httpd docker container and access the default apache page using the browser.
$ docker run -d --name apache -p 80:80 httpd
Output:
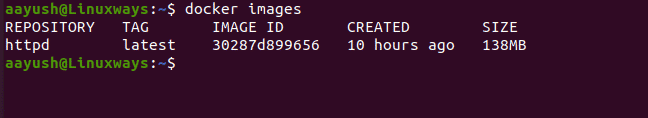
Also, to check the size of the docker images run the following command
$ docker images
Output:
Using DockerSlim to build the image
Docker image has been pulled and we have verified the container is working fine. Now we will use DockerSlim to build optimized images. Use the following syntax to create minimized Docker images.
$ docker-slim build --target <image name>
Example:
$ docker-slim build --target httpd
Output:
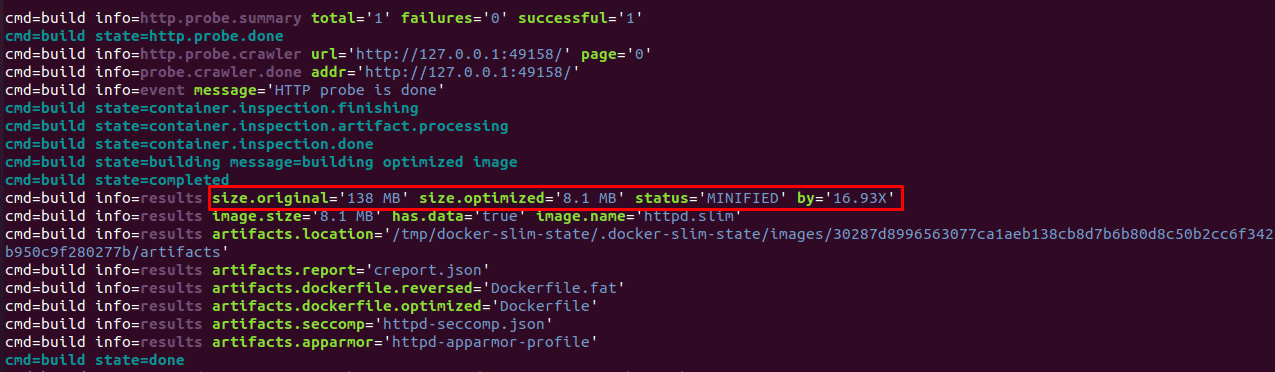
The output shows that the size of the docker image has been reduced from 138MB to 8.1 MB which is minimized by 16.3 times from the original image.
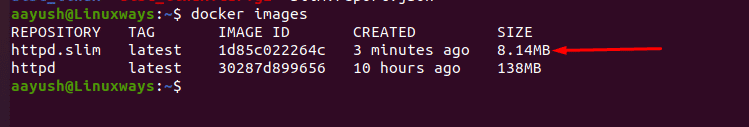
Verifying the final image
To check the size of the final image, run the following command.
$ docker images
Output:
Running the container from the DockerSlim build image
Finally, we will create a container from the optimized image and monitor the output. As I have used httpd docker images to minimize, I am going to run an httpd container from the latest image. You can select your images accordingly.
Syntax:
$ docker run -d --name <name of the container > -p <host port : container port> <image name>
Example
$ docker run -d --name apache -p 80:80 httpd.slim
Where,
httpd.slim is the optimized httpd docker image
Output:
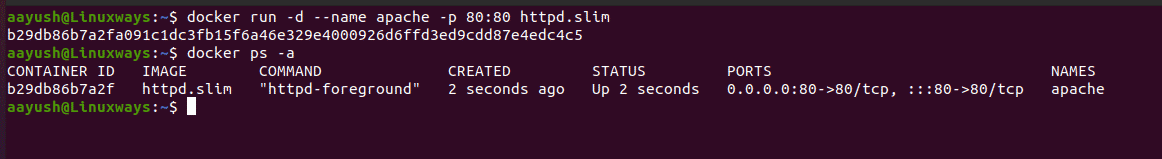
You can find that the container is up with an optimized image. Lets browse the container in the browser and find the output.
You can find that the httpd docker container is working fine with the minimized Docker image.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about how to install DockerSlim in the Linux system and how it can be used to optimize and secure Docker containers.




![How_to_Install_ElasticSearch_on_AlmaLinux_8[1]](https://linuxways.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/How_to_Install_ElasticSearch_on_AlmaLinux_81.png)