RPM is a packaging format used by most popular Linux distributions such as CentOS, Red hat, and Fedora. In the official CentOS repository, a large number of packages are available that can be installed directly using the yum package manager tool. The RPM packages that are not available in the CentOS Standard repository can be installed easily by activating or enabling the relevant repository. Often, you need to download and manually the rpm packages from the official software pages.
We will elaborate in this tutorial on how to install rpm packages on CentOS 8 system through the command line.
Prerequisites
You need root privileges to execute the administrative commands.
The rpm packages can install on CentOS 8 system by using the following two different ways:
- Install rpm package using the yum package manager
- Install rpm package using the rpm command
Method 1: Install rpm package using the Yum package manager
Yum is used as a default package manager for CentOS distribution. Using this package manager tool, the user can install, download, update, search and remove packages from the CentOS official repository and can do the same task with the third-party repository. Just launch the terminal window on your CentOS desktop from left sidebar menu and then do the following steps:
Download the rpm file from the official website
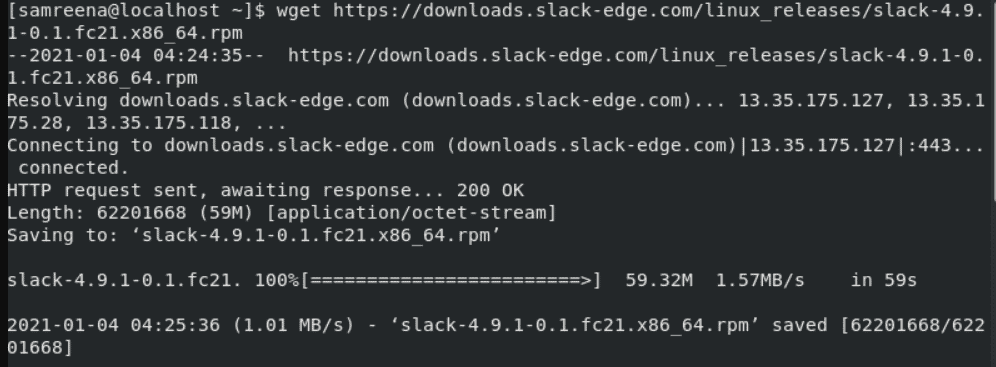
If you are using this method then, download the rpm package from a website. In the following example, the slack rpm file is downloaded from the official download package using the following ‘wget’ command:
$ wget https://downloads.slack-edge.com/linux_releases/slack-4.9.1-0.1.fc21.x86_64.rpm
Install the rpm file
The downloaded rpm package can be installed on your system by running the following ‘yum localinstall’ command along with the package name:
$ sudo yum localinstall filename.rpm
To install all rpm files from a directory use the following command:
$ sudo yum localinstall ./slack-*.rpm
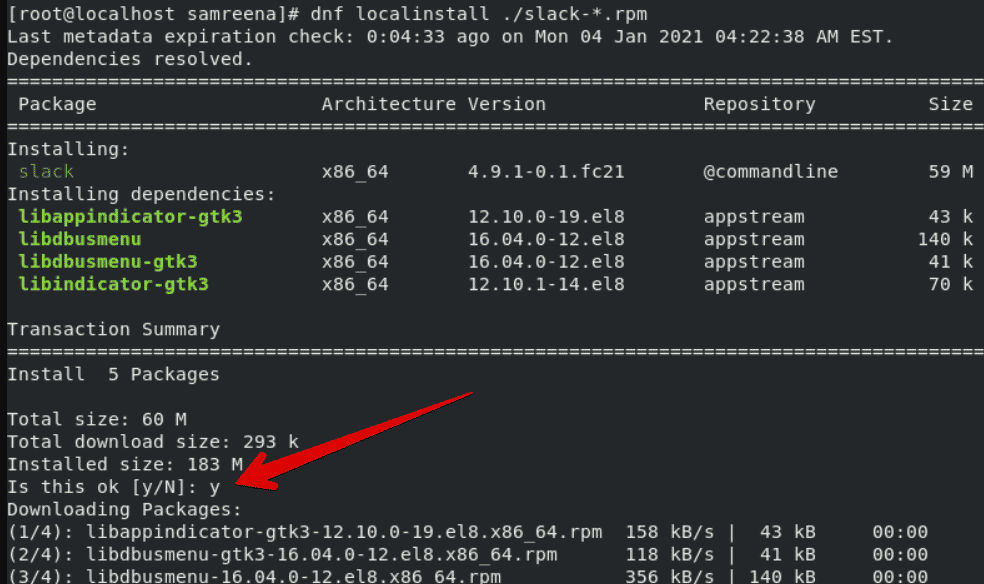
Here, we are assuming the above rpm file is compatible with your system. So, press ‘y’ and ‘Enter’ as a prompt appears on the terminal that will automatically install all dependencies required for this package.
In some cases, RPM packages depend on other packages that are not installed currently on your system. So, if these packages are present in the repository, enabled on your CentOS system. Yum automatically installs all dependencies. But, if dependencies are not available in the repository then, first you need to install these dependencies on your system independently using yum package manager tool.
You can also adopt another option that instead of separately downloading the rpm file, just pass the RPM package URL with following command:
$ sudo yum localinstall https://domain.com/file.rpm
The installed rpm package can also remove from your system using the yum package manager by using the following command:
$ sudo yum remove file.rpm
Method 2: Install RPM package using the rpm tool
Using the rpm tool, you can install, update and remove a package from your CentOS system.
Use the following command to install any rpm package:
$ sudo rpm -ivh file.rpm
In the above command -v shows the verbose and h shows the hash marked progress bar. However, if this package depends on other packages then, during the installation it will list the names of missing dependencies on the terminal. Then, you need to download and install manually all those dependencies.
You can also use the URL of rpm package with the following command instead of downloading the rpm package.
$ sudo rpm -ivh https://domain.com/file.rpm
Use option ‘-U’, to update any rpm package using the rpm tool as follows:
$ sudo rpm -Uvh file.rpm
To install a RPM package without its dependencies, use the following terminal command:
$ sudo rpm -Uvh --nodeps file.rpm
To erase or remove the RPM package from your system, use the option ‘-e’ followed by the rpm file name as follows:
$ sudo rpm -e file.rpm
Conclusion
We have mentioned all information about how to install the RPM package on the CentOS 8 system. We have explained two methods through which you can easily download, install, update and erase Rpm packages on your CentOS system. For more understanding, test all those commands with your own RPM packages URL on CentOS and in case of any problem give us your feedback via comments.