Number comparison is considered as an important arithmetic operation that lets you find out the relative magnitude of one number in comparison to another. Bash also allows you to compare numbers very easily. Therefore, in this article, we will teach you how you can use a Bash script for comparing two numbers.
Number Comparisons in Bash Scripts
Six different comparison operators are used for comparing the numbers in a Bash script in Linux. All of these operators are used in the following examples:
Example 1: Using the Equal and Not Equal Comparison Operators
In this example, we will use the equal and not equal operators in Bash for comparing two numbers. We use the Bash script shown in the following image for this purpose:
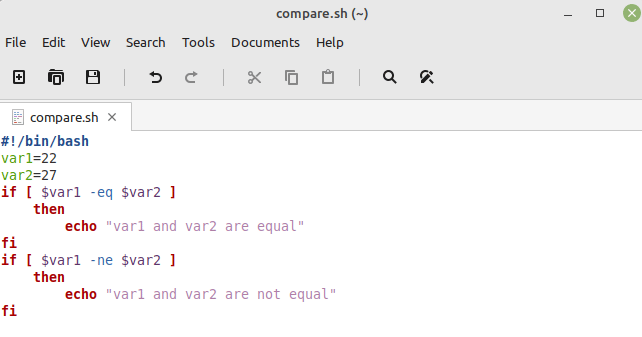
In this Bash script, we first used the shebang for declaring our document as a Bash script. Then, we defined two variables, “var1” and “var2”, and assigned to them to two different integers. Then, we used an “if” statement for checking if these two numbers are equal. If yes, a relevant message is printed on the terminal. After that, we have another “if” statement in which we used the “not equal” operator for checking if these numbers are not equal. If this statement is evaluated to true, a relevant message is printed on the terminal.
Then, after saving our Bash file, we executed it with the following command:
$ bash compare.sh
![]()
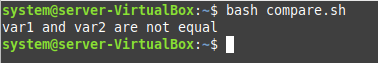
Upon execution, we found out that our second “if” statement turned out to be true since the two specified numbers were not equal as shown in the following image:
Example 2: Using the Greater Than and Greater Than or Equal To Operators
In this example, we will use the greater than and the greater than or equal to operators in Bash for comparing the two numbers. We use the following Bash script for this purpose:
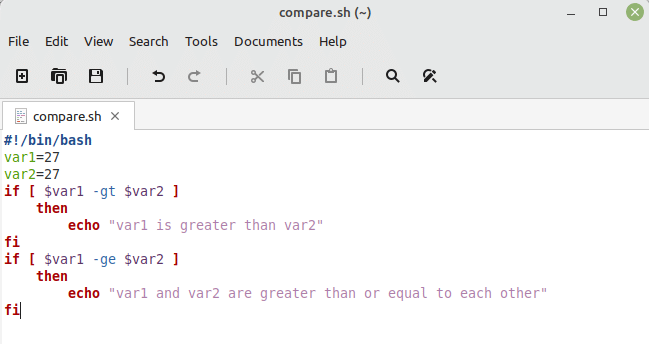
Just like the first example, we defined the two variables in this script and kept their values equal. After that, we used two “if” conditions. In the first condition, we used the “greater than” operator of Bash while in the second condition, we used the “greater than or equal to” operator of Bash for comparing the two numbers. If the first condition is true, it means that the first number is greater than the second number while if the second condition is true, it means that these two numbers are greater than or equal to each other.
When we ran this Bash script, we figured out that these two numbers are greater than or equal to each other as shown in the following image:

Example 3: Using the Less Than and Less Than or Equal To Operators
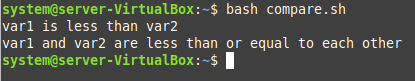
In this example, we want to use the less than and less than or equal to operators in Bash for comparing two numbers. For that, we use of the following Bash script:
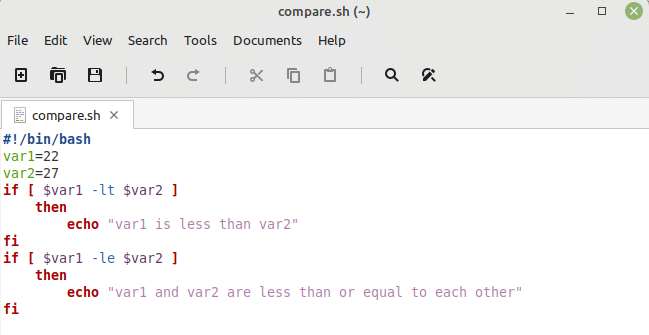
Just like our first two examples, we defined the two variables in this Bash script and assigned to them the two different values. Then, we used two “if” conditions. The first one makes use of the “less than” operator while the second one makes use of the “less than or equal to” operator. If the first condition is true, it means that the first variable is less than the second while if the second condition is true, it means that the given variables are less than or equal to each other. However, in this case, we have chosen both the numbers in a way that both of these conditions are evaluated to true.
You can verify this by looking at the output of this Bash script shown in the following image:
Conclusion
With this article, we want to share with you the methods of comparing two numbers in Bash. For doing that, we shared the working of all the six number comparison operators available in Bash with you in the form of the three examples. After going through these examples, you will easily be able to compare any given numbers within a Bash script.




